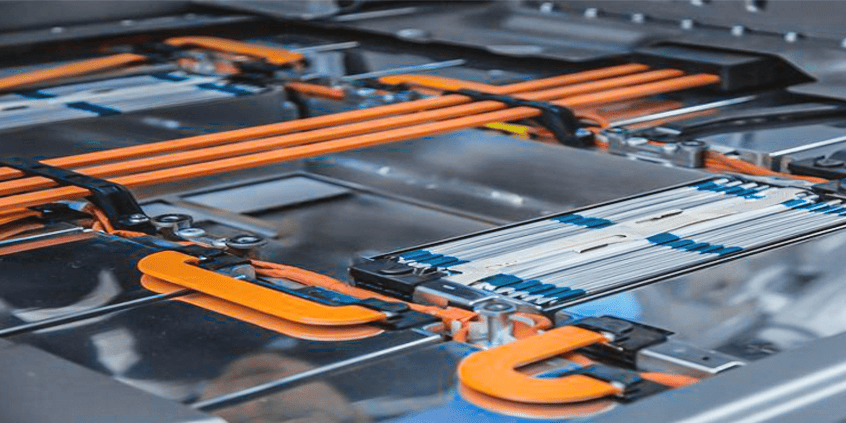
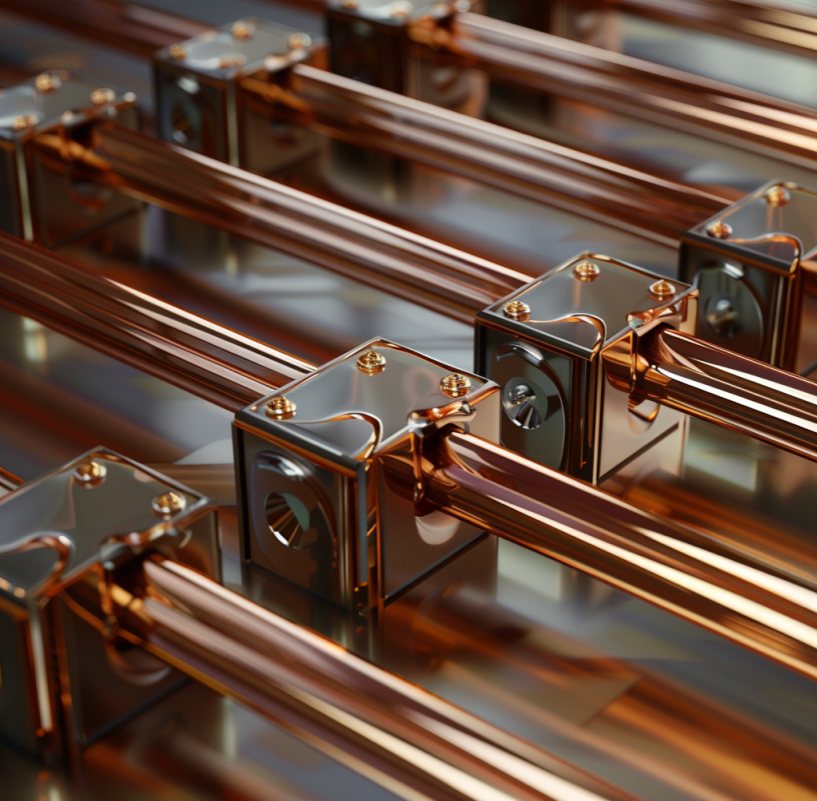
What is Electrical Bus Bar? Everything You Need To Know
Provide a comprehensive guide to what an electrical bus bar is, its purpose, types, materials, and applications in various electrical systems.
What is Electrical Bus Bar?
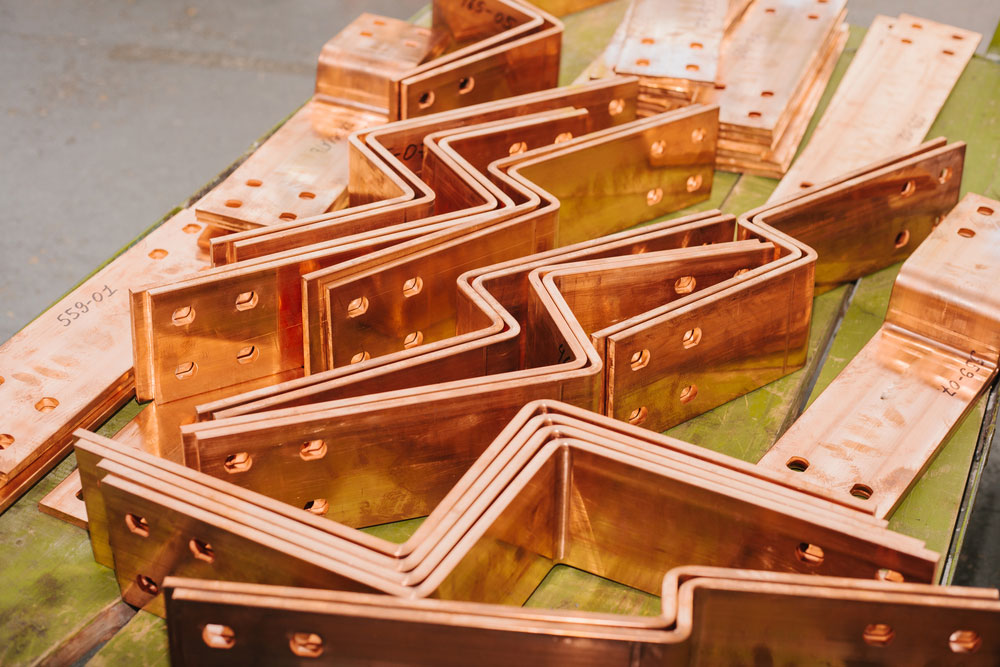
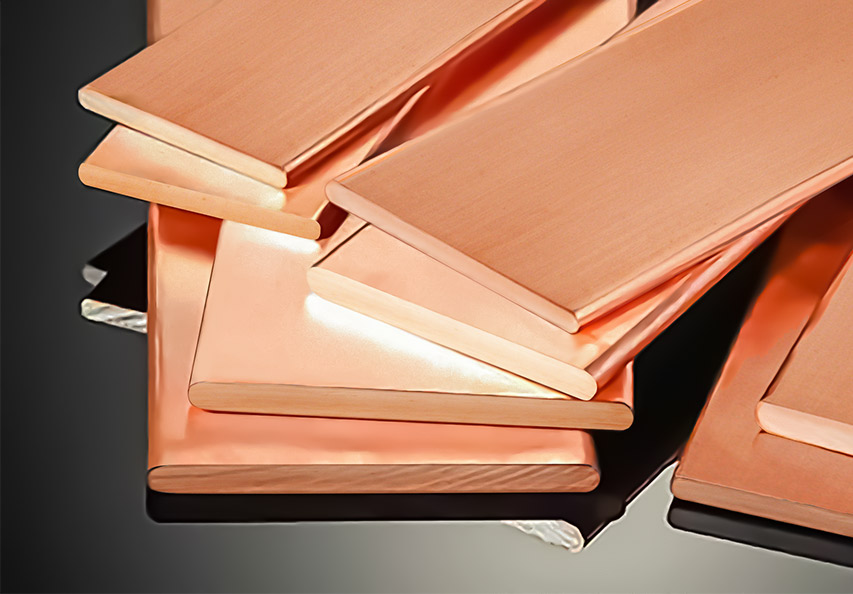
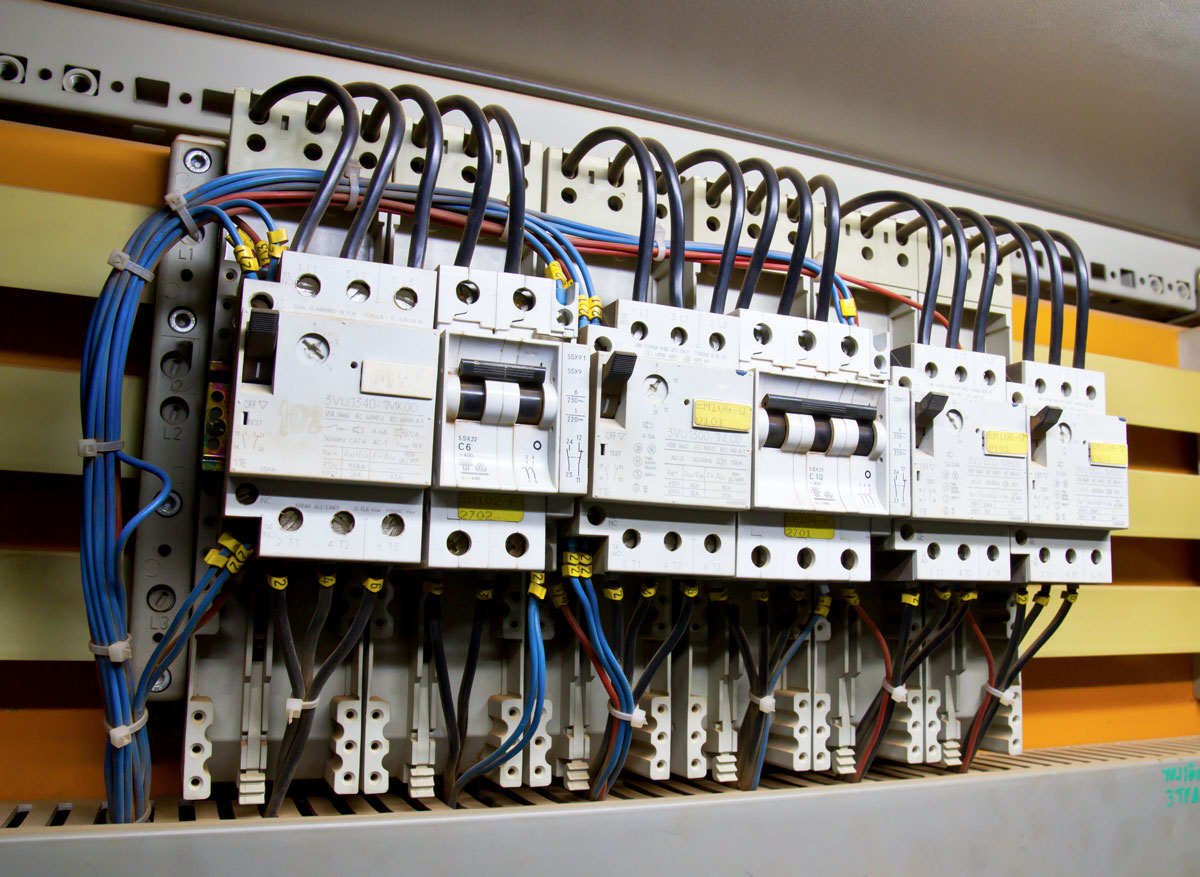
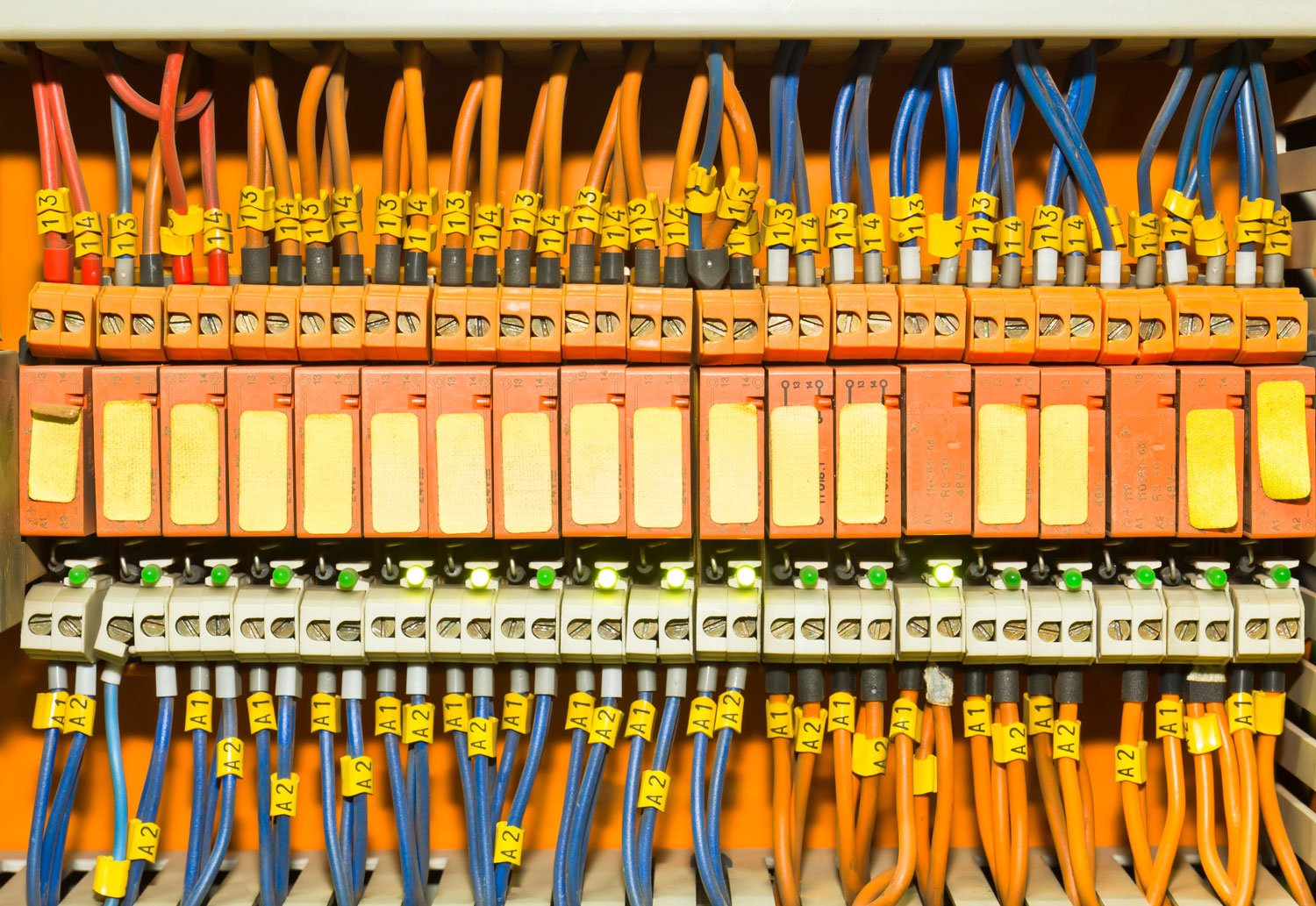
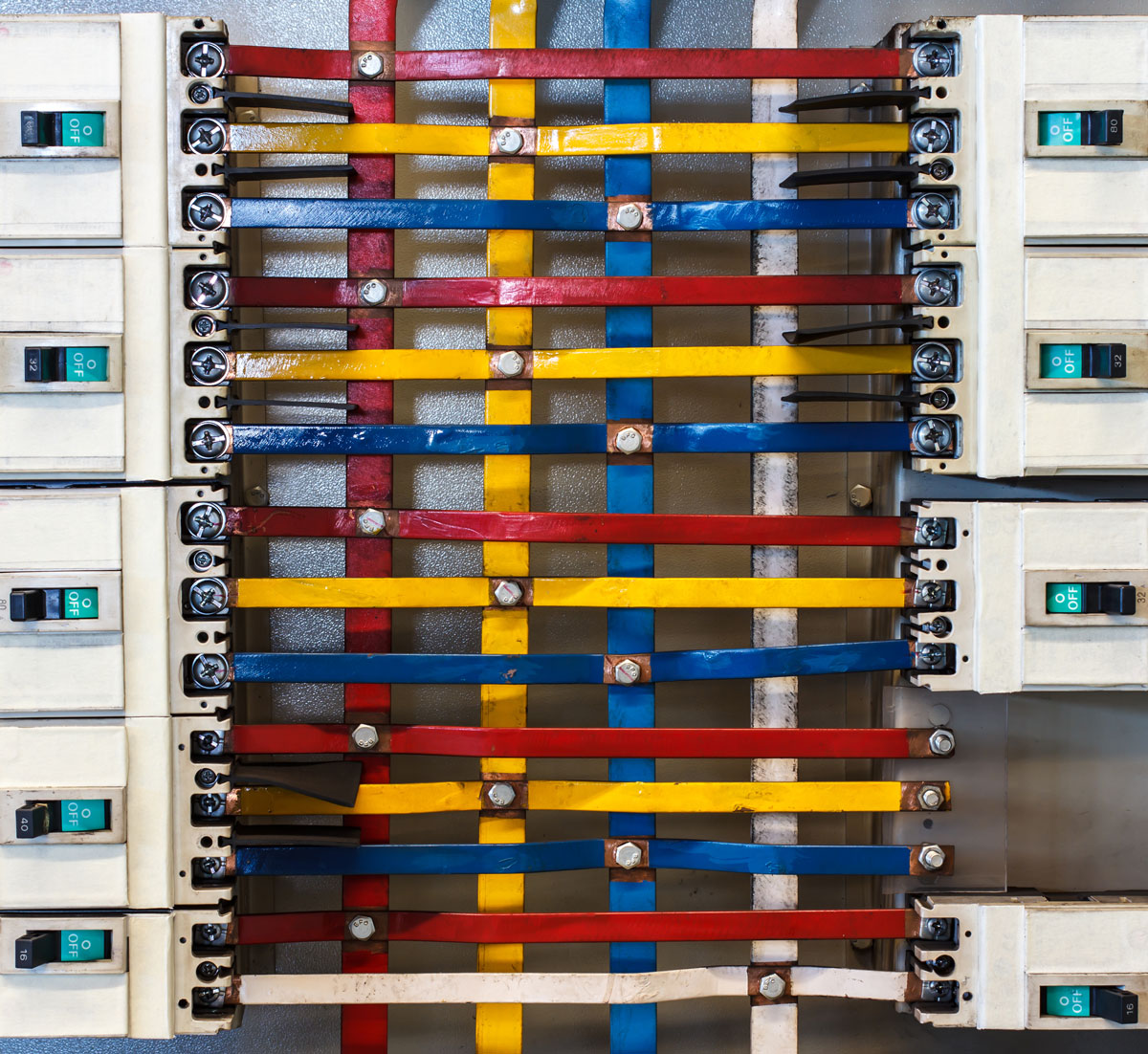
An electrical bus bar is a conductive material, usually in the form of a metal bar or a series of interconnected strips, that serves as a central connection point for distributing electrical power. In essence, it acts as a high-capacity electrical conductor that allows the efficient transmission of electricity from one point to another, often connecting various circuit breakers, fuses, or other electrical devices.
The primary function of a bus bar is to provide a safe and organized way to manage the flow of electrical current within a system. It can carry large amounts of current and allow multiple connections to be made, making it an indispensable component in complex electrical setups like power distribution boards, switchboards, and electrical panels.
How Does an Electrical Bus Bar Work?
An electrical bus bar operates by distributing electrical power from a source (like a transformer or a generator) to various circuits that need it. The bus bar is usually placed inside an enclosure, where it connects with other electrical components, such as circuit breakers, switches, or fuses.
When electricity flows through a bus bar, it is evenly distributed across its surface, which helps prevent overheating and ensures consistent voltage delivery. In large-scale industrial setups, bus bars may be used to supply power to different parts of a facility, making them a critical part of electrical infrastructure. Bus bars come in various sizes and configurations, depending on the system’s requirements for current capacity and the number of circuits to be connected.
Types of Electrical Bus Bars
There are several types of electrical bus bars, each designed for specific applications and load capacities. Let’s explore the most common types:
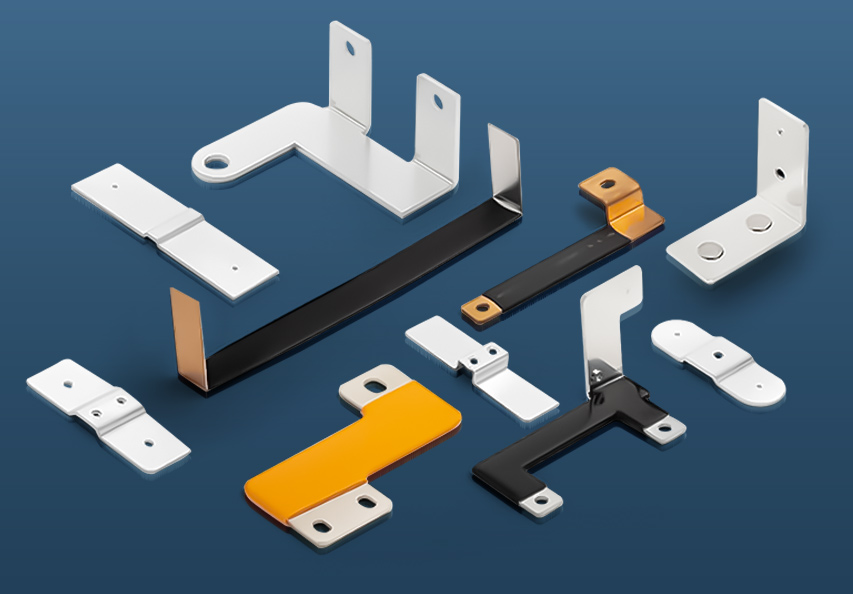
1. Solid Bus Bar
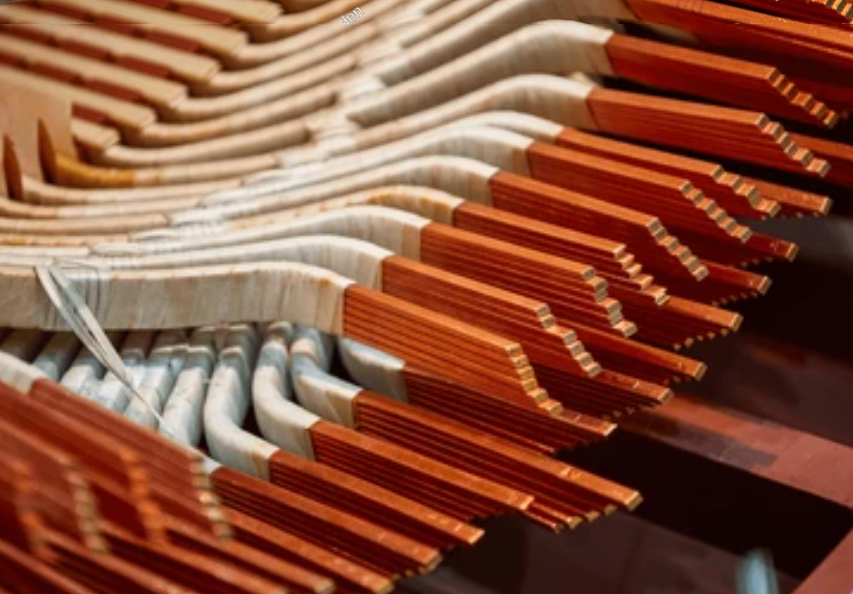
A solid bus bar consists of a single, solid conductor made from metal, typically copper or aluminum. These bus bars are commonly used in systems that require a high level of durability and performance, such as electrical distribution boards and switchgear panels. Solid bus bars are rigid, making them ideal for situations where the connection points are fixed and do not require flexibility.
2. Stranded Bus Bar
A stranded bus bar is made up of multiple smaller wires or strands of copper or aluminum twisted together. This design provides greater flexibility compared to solid bus bars, allowing them to bend and adjust to different configurations. Stranded bus bars are used in applications where flexibility is required, such as in mobile equipment or systems that need to accommodate frequent movements.
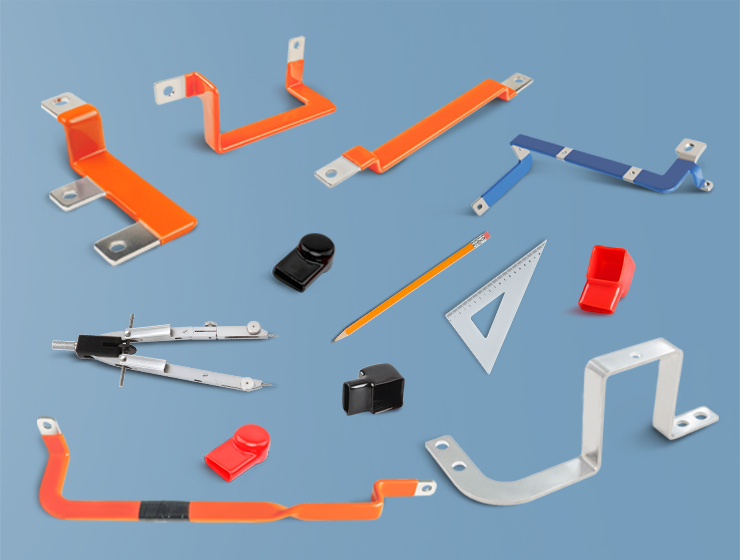
3. Flexible Bus Bar
A flexible bus bar is similar to a stranded bus bar but is designed to be even more adaptable, with a higher degree of flexibility. These bus bars are often insulated and can be easily shaped to fit within tight spaces or around complex electrical components. Flexible bus bars are commonly used in high-power applications, where space limitations or the need for continuous motion or adjustment is a concern.
Materials Used in Electrical Bus Bars
Electrical bus bars are typically made from highly conductive metals to minimize energy loss and ensure efficient power transmission. The most common materials used in the construction of bus bars include:
- Copper: Copper is the most commonly used material for bus bars due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. It is ideal for systems that require high current capacity and reliability.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is a lightweight, cost-effective alternative to copper. While it has slightly lower conductivity than copper, it is still an excellent choice for applications that do not demand extremely high performance.
- Brass: Brass is used in some specialized applications where corrosion resistance and durability are required. It is typically used in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
The choice of material depends on factors like current load, environmental conditions, and the specific requirements of the electrical system.
Applications of Electrical Bus Bars
Electrical bus bars are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the most common areas where bus bars are utilized:
1. Power Distribution Systems
One of the most significant applications of electrical bus bars is in power distribution systems. In these systems, bus bars are used to distribute electricity from a main power source to various circuits within a facility or network. Bus bars help manage high current loads and ensure that power is delivered safely and efficiently.
2. Switchboards and Electrical Panels
Electrical switchboards and panels use bus bars to connect circuit breakers, fuses, and other protective devices. This allows for the centralized control and protection of the electrical circuits within a building or industrial complex. Bus bars in switchboards facilitate quick and easy connection and disconnection of circuits, helping prevent overloads and short circuits.
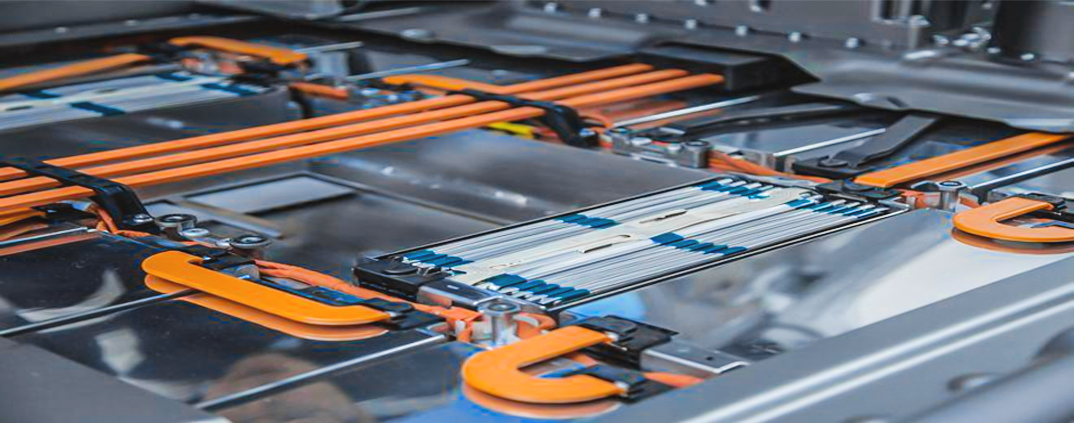
3. Motor Control Centers (MCCs)
Motor Control Centers (MCCs) often use bus bars to distribute power to various electric motors. Bus bars in MCCs enable quick and easy connections between the power supply and the motors, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operation of equipment in industries such as manufacturing and automation.
4. Renewable Energy Systems
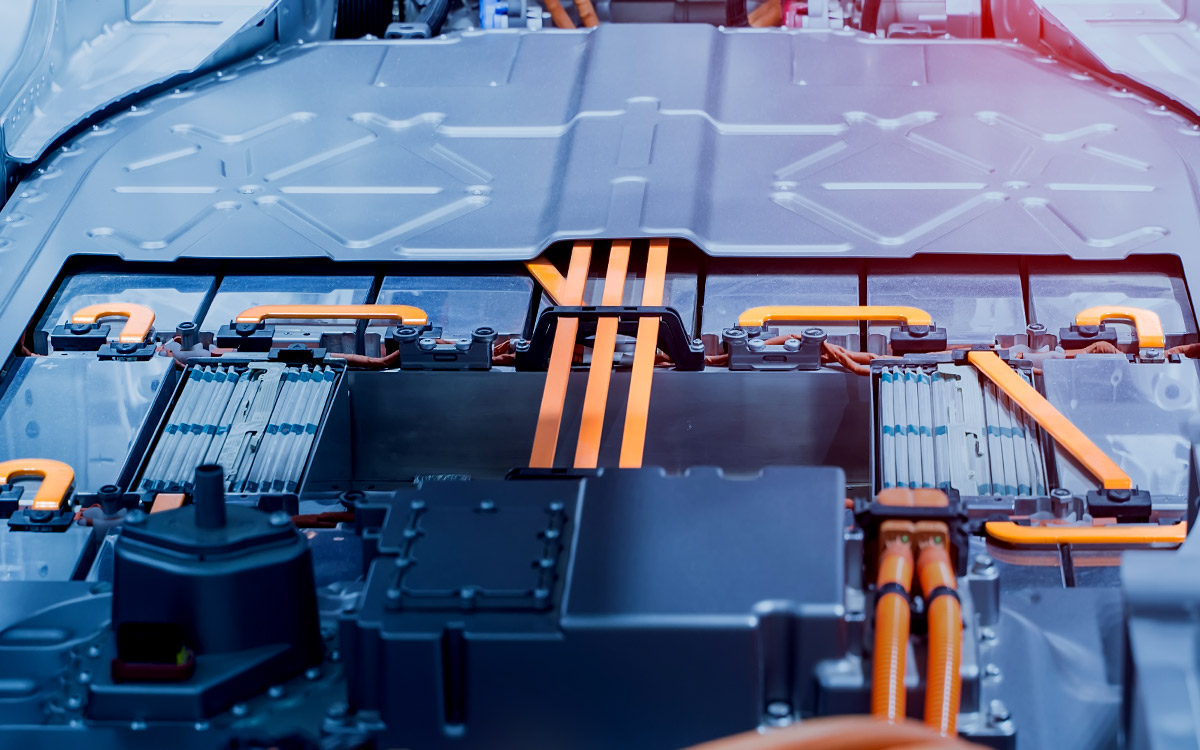
In renewable energy systems, such as solar or wind power installations, bus bars are used to connect multiple solar panels or wind turbines to a central inverter or battery storage unit. These bus bars help streamline the power distribution process and make it easier to scale the system as needed.
Benefits of Using Electrical Bus Bars
Electrical bus bars offer numerous advantages over traditional wiring systems, making them a preferred choice in many applications. Some of the key benefits include:
- Efficient Power Distribution: Bus bars allow for the smooth distribution of electrical power across a system, minimizing energy loss and improving efficiency.
- Space-Saving Design: Bus bars can be compact and offer a space-saving alternative to traditional wiring, making them ideal for use in cramped electrical enclosures and panels.
- Simplified Installation: Bus bars simplify the process of connecting electrical components, making installation quicker and less complicated.
- Improved Safety: By providing centralized power distribution, bus bars help prevent the risk of overloads, short circuits, and other electrical hazards.
- Cost-Effective: The use of bus bars can reduce the overall cost of electrical wiring, especially in large-scale installations.
How to Select the Right Bus Bar for Your System
Choosing the right electrical bus bar for your system requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Current Load: Determine the amount of current that the bus bar will need to carry, as this will dictate the size and material of the bus bar.
- Voltage Rating: Ensure that the bus bar is rated for the voltage level of your system to avoid potential overloads or damage.
- Space Constraints: Consider the available space for the bus bar, as this will influence the type and size of bus bar you choose.
- Environmental Conditions: Take into account factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals, as these will affect the material and design of the bus bar.
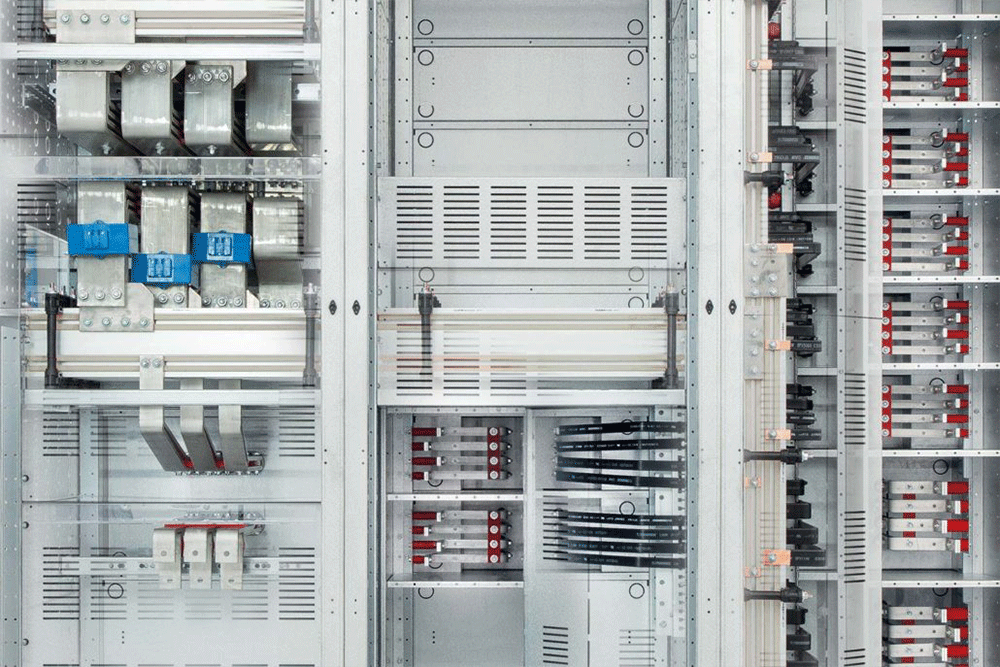
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Electrical Bus Bars
To ensure that your electrical bus bars function properly and safely, regular maintenance and safety precautions are essential. Here are some tips:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the bus bars for signs of wear, corrosion, or overheating. Any damage or wear should be addressed immediately to avoid potential safety hazards.
- Cleanliness: Keep the bus bars free of dust, dirt, and other debris that could interfere with the flow of electricity and increase the risk of short circuits.
- Proper Tightening of Connections: Ensure that all connections to the bus bar are securely tightened to prevent overheating and electrical arcing.
- Safety Precautions: Always follow proper safety protocols when working with bus bars, including de-energizing the system and using personal protective equipment (PPE).
Conclusion
In summary, an electrical bus bar is a critical component in the safe and efficient distribution of electrical power across various systems. Whether in residential, industrial, or commercial applications, bus bars ensure that electricity is distributed in a controlled and organized manner. By understanding what is an electrical bus bar, its types, materials, applications, and benefits, you are better equipped to make informed decisions when designing or maintaining electrical systems.
If you are planning an electrical installation or upgrade, selecting the right bus bar is crucial to ensuring reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness. By following best practices for maintenance and safety, you can prolong the life of your bus bar and improve the overall performance of your electrical system.