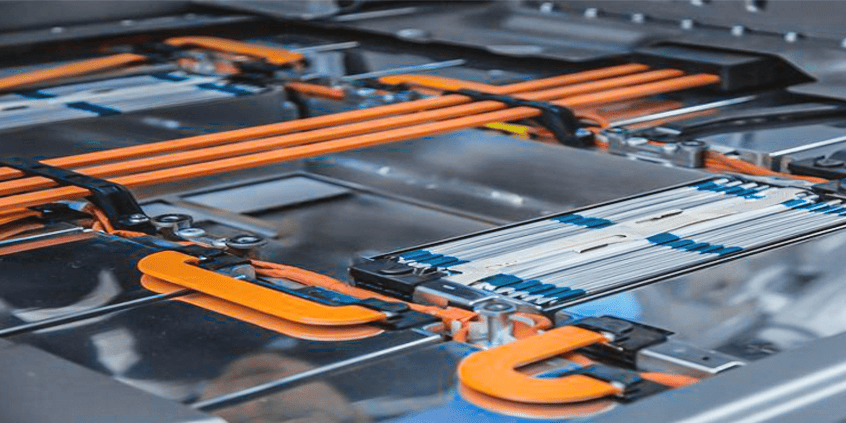
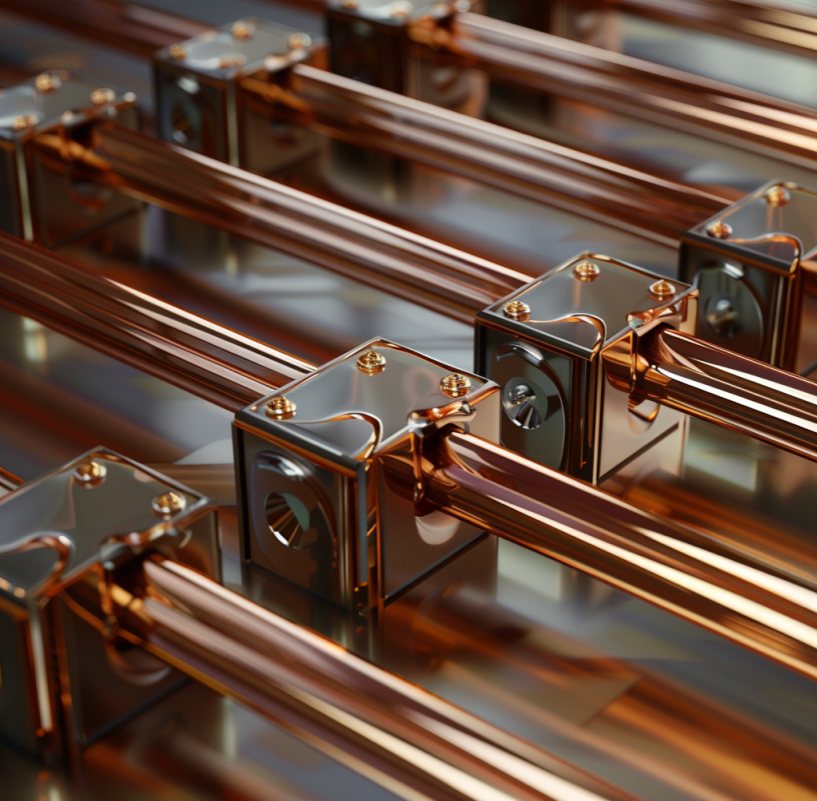
What does a bus bar do for the electrical systems?
Explore the function, types, advantages, and applications of bus bars in different electrical systems.
Introduction
In modern electrical systems, efficient power distribution is critical to ensuring stability, reliability, and safety. One essential component that plays a key role in this process is the bus bar. A bus bar electric system acts as a central hub for electrical power, facilitating the distribution of electricity between various circuits and components.
From industrial power distribution to vehicle electrical systems, bus bars are indispensable for organizing electrical connections, reducing wiring complexity, and improving system performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the function, types, advantages, and applications of bus bars in different electrical systems.
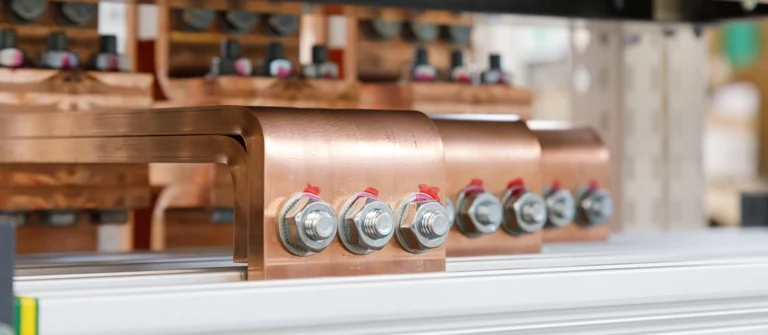
What Is a Bus Bar?
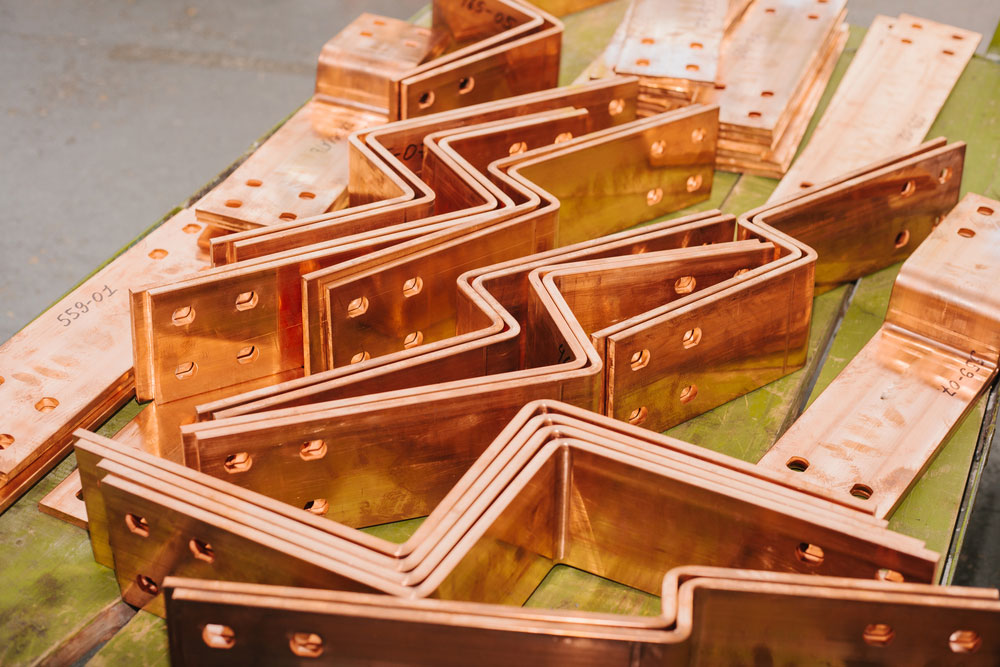
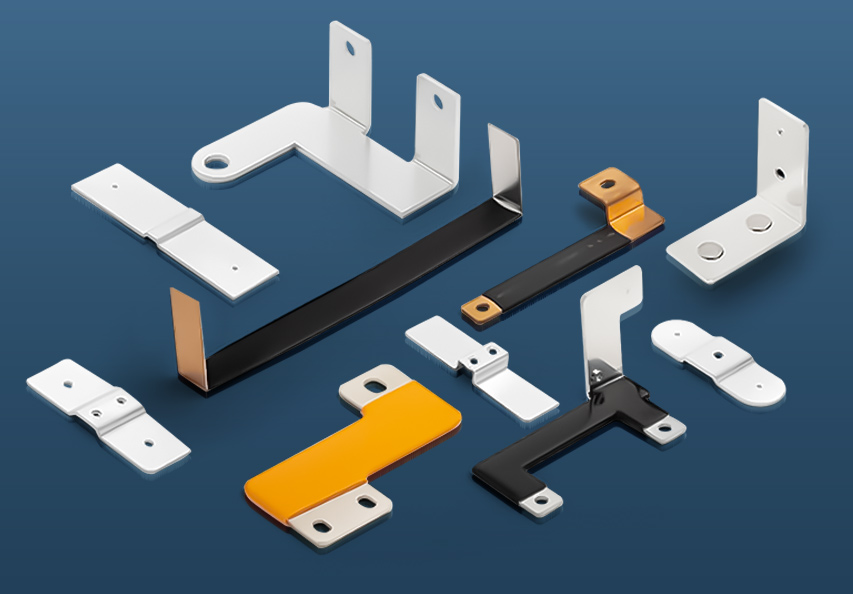
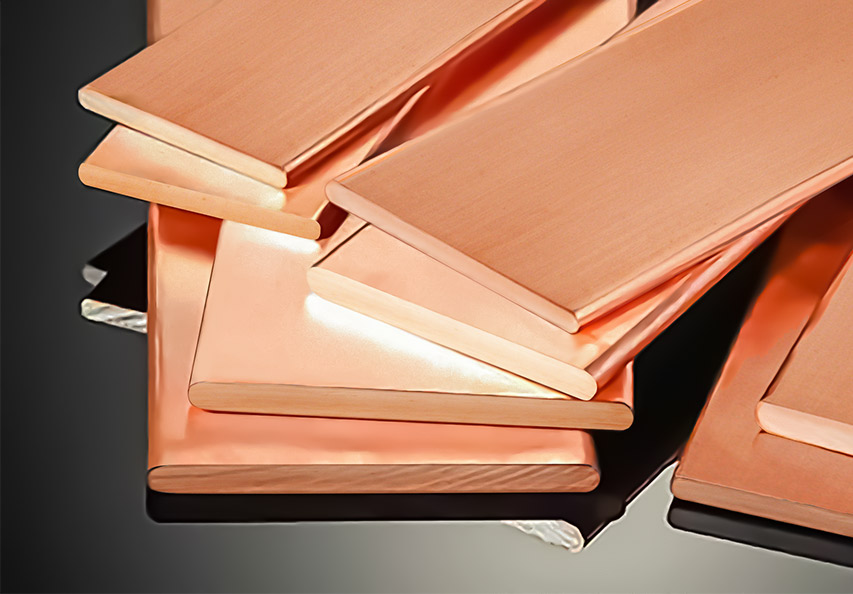
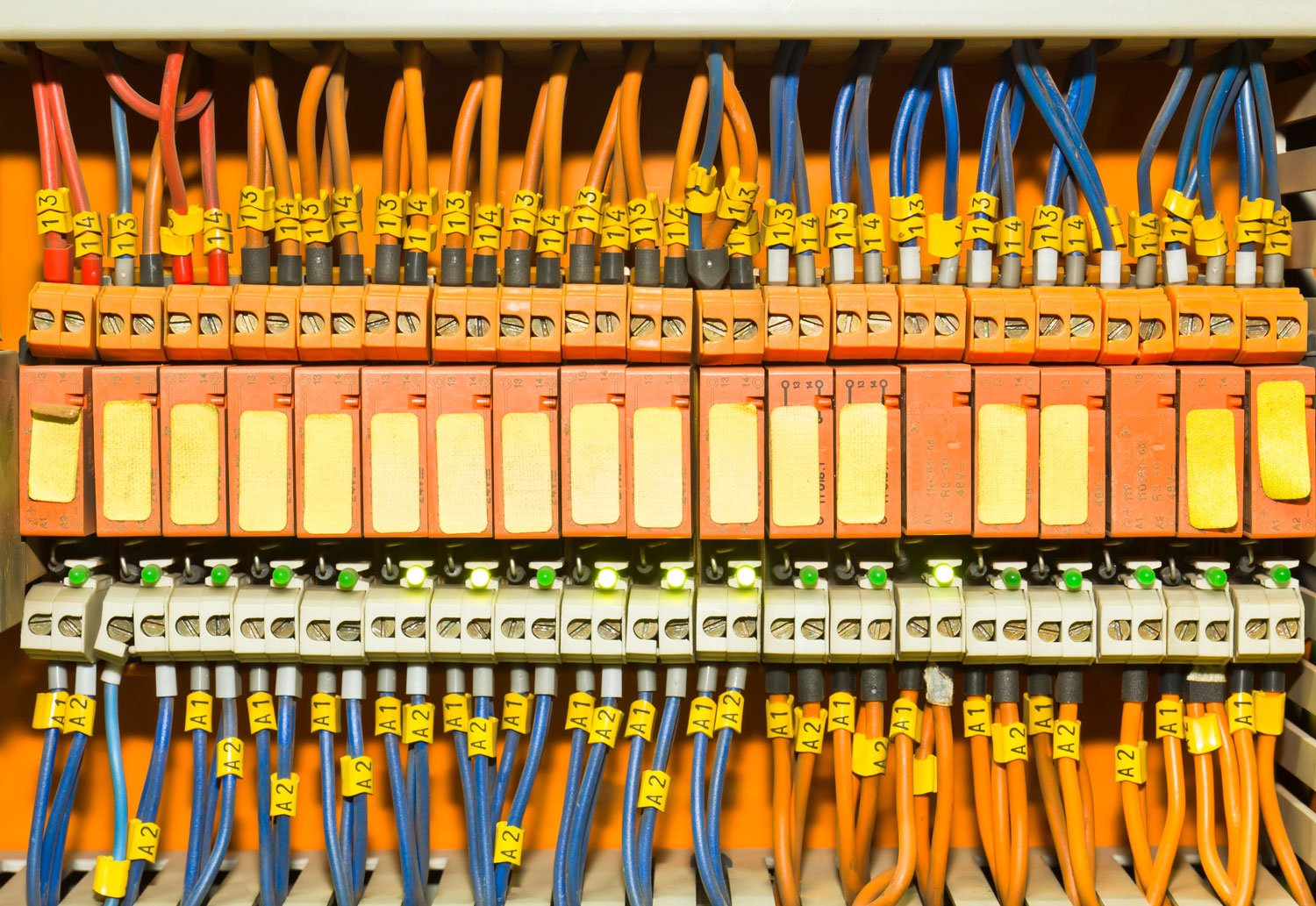
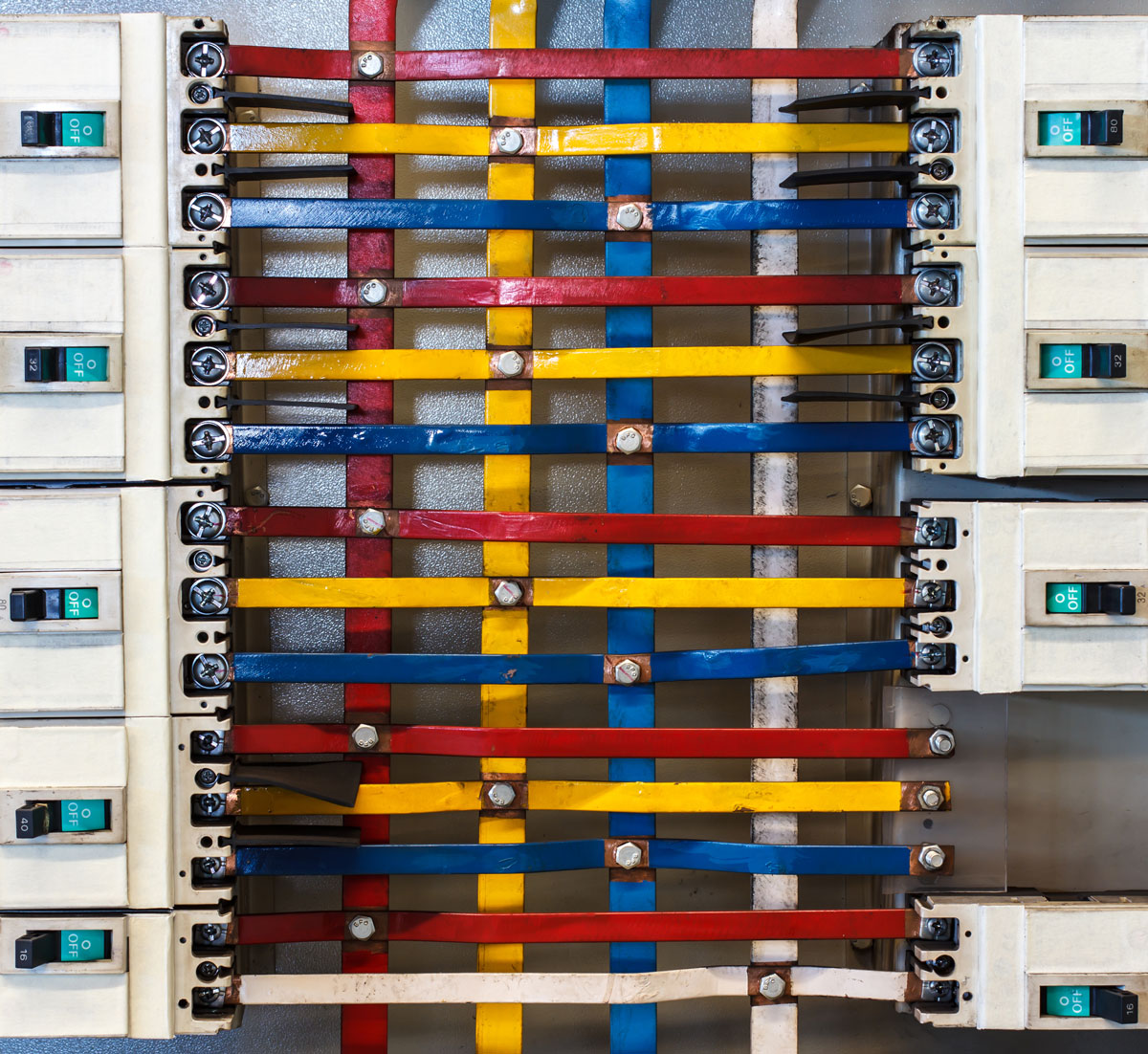
A bus bar is a conductive metal strip or bar used to distribute electrical power within a system. Typically made of copper or aluminum, bus bars serve as connection points for multiple electrical circuits, eliminating the need for extensive wiring.
How Does a Bus Bar Work?
A bus bar acts as a junction for electrical power distribution. Instead of running multiple individual wires from a power source to different components, a bus bar consolidates these connections. It receives electrical energy from an input source (such as a generator, transformer, or battery) and distributes it to various circuits or loads.
For example, in an electrical panel, a bus bar distributes power from the main circuit breaker to individual branch circuits, ensuring a streamlined and organized connection system.
Types of Bus Bars
Different types of bus bars are used depending on the application and power requirements. The most common types include:
1. Copper Bus Bar
- Material: High-conductivity copper
- Advantages: High electrical conductivity, excellent thermal performance, and corrosion resistance
- Applications: Industrial switchgear, power plants, electrical substations
2. Aluminum Bus Bar
- Material: Lightweight aluminum
- Advantages: Cost-effective, lighter than copper, corrosion-resistant when anodized
- Applications: Large-scale power distribution, automotive and aerospace industries
3. Insulated Bus Bar
- Feature: Encased in insulation material to prevent short circuits
- Advantages: Enhances safety by reducing the risk of electrical faults
- Applications: Power distribution panels, high-voltage systems
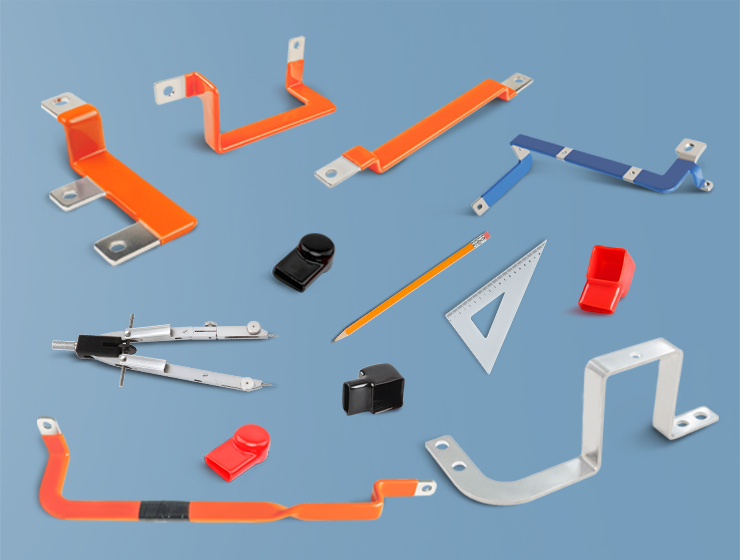
4. Flexible Bus Bar
- Material: Thin layers of conductive metal laminated together
- Advantages: Can bend and adjust to different installations, reducing mechanical stress
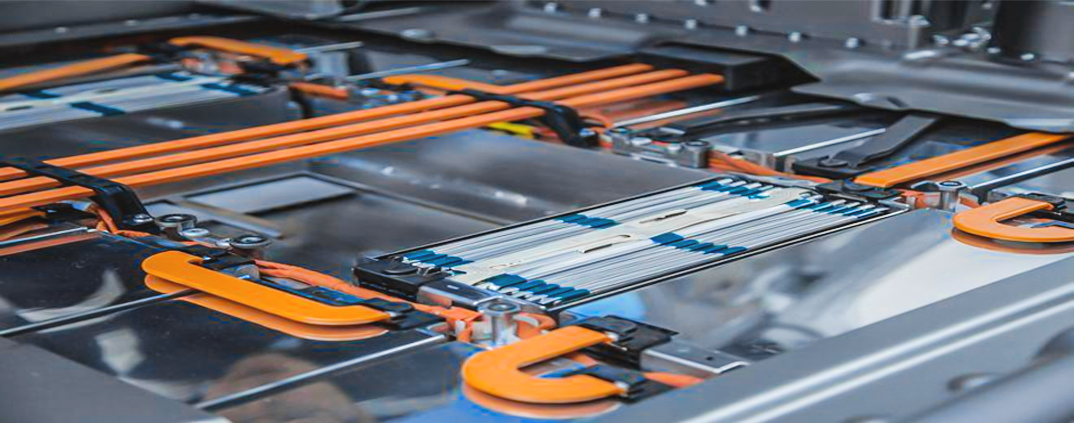
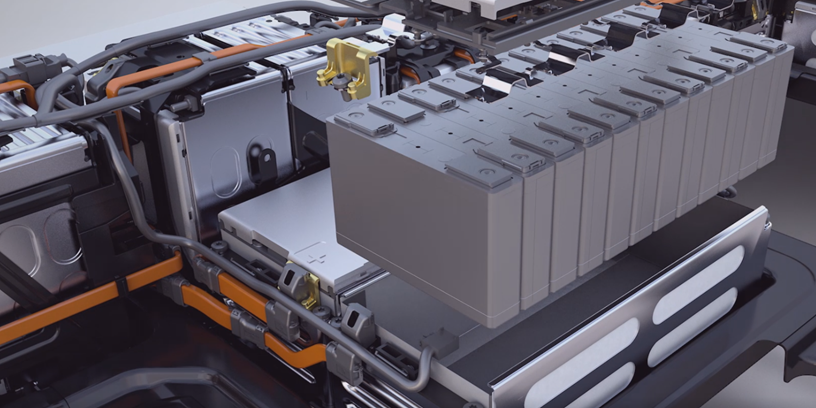
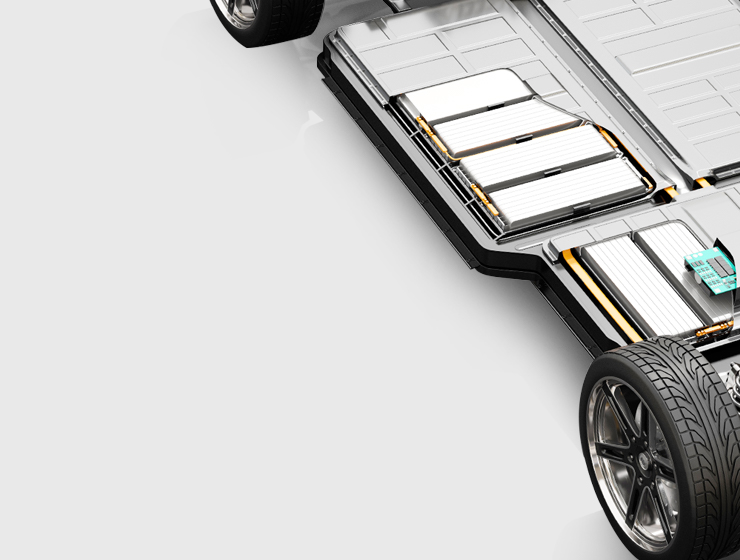
- Applications: Electrical vehicles (EVs), aerospace, battery packs
5. Rigid Bus Bar
- Feature: A solid, fixed structure designed for stable power distribution
- Advantages: Durable, reliable, and efficient for high-current applications
- Applications: Electrical substations, industrial plants
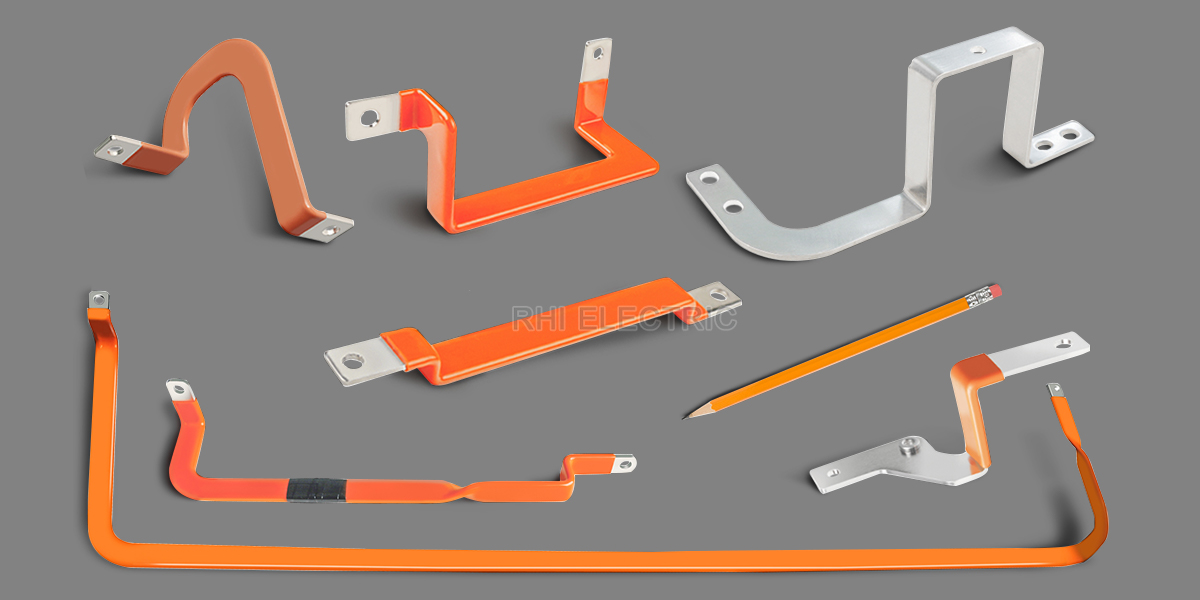
Advantages of Using a Bus Bar
1. Improved Electrical Efficiency
Bus bars offer lower electrical resistance than traditional wiring, reducing energy loss and improving efficiency. This is particularly important in high-power applications where even minor losses can result in significant inefficiencies.
2. Space-Saving and Organized Wiring
A bus bar electric system simplifies wiring by replacing multiple wires with a single, consolidated structure. This reduces clutter, saves space, and makes maintenance easier.
3. Enhanced Safety
By minimizing the number of loose wires and electrical joints, bus bars reduce the risk of electrical faults such as short circuits, overheating, and fires. Insulated and enclosed bus bars further enhance safety by preventing accidental contact.
4. Better Heat Dissipation
Compared to traditional wiring, bus bars provide superior thermal management, as their flat design allows for more effective heat dissipation. This helps prevent overheating and ensures long-term reliability.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Bus bars allow for easy expansion of an electrical system. Additional connections can be made without complex rewiring, making them ideal for applications requiring future scalability.
6. Durability and Longevity
Made from robust materials like copper and aluminum, bus bars are highly durable and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including high temperatures, vibrations, and corrosive elements.
Applications of Bus Bars
Bus bars are used in various industries and applications, including:
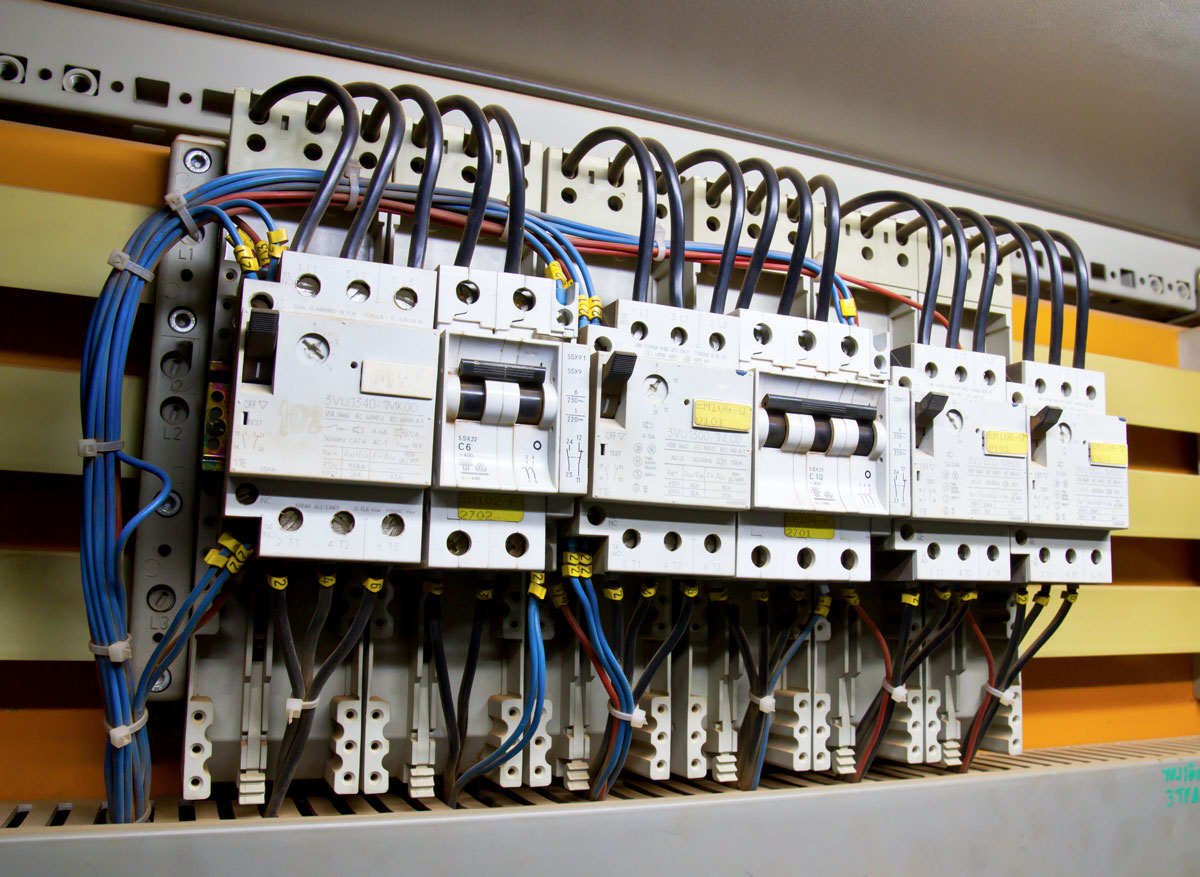
1. Power Distribution Panels
Bus bars are commonly found in electrical switchboards and panels, where they distribute power from the main breaker to multiple branch circuits.
2. Industrial Electrical Systems
Factories and industrial plants use bus bar electric systems to handle high-current loads efficiently. Bus bars allow for the safe distribution of power to heavy machinery.
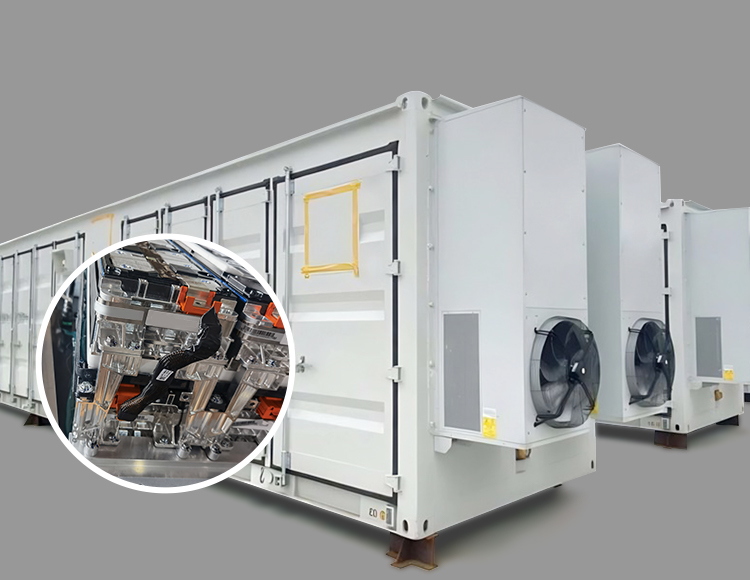
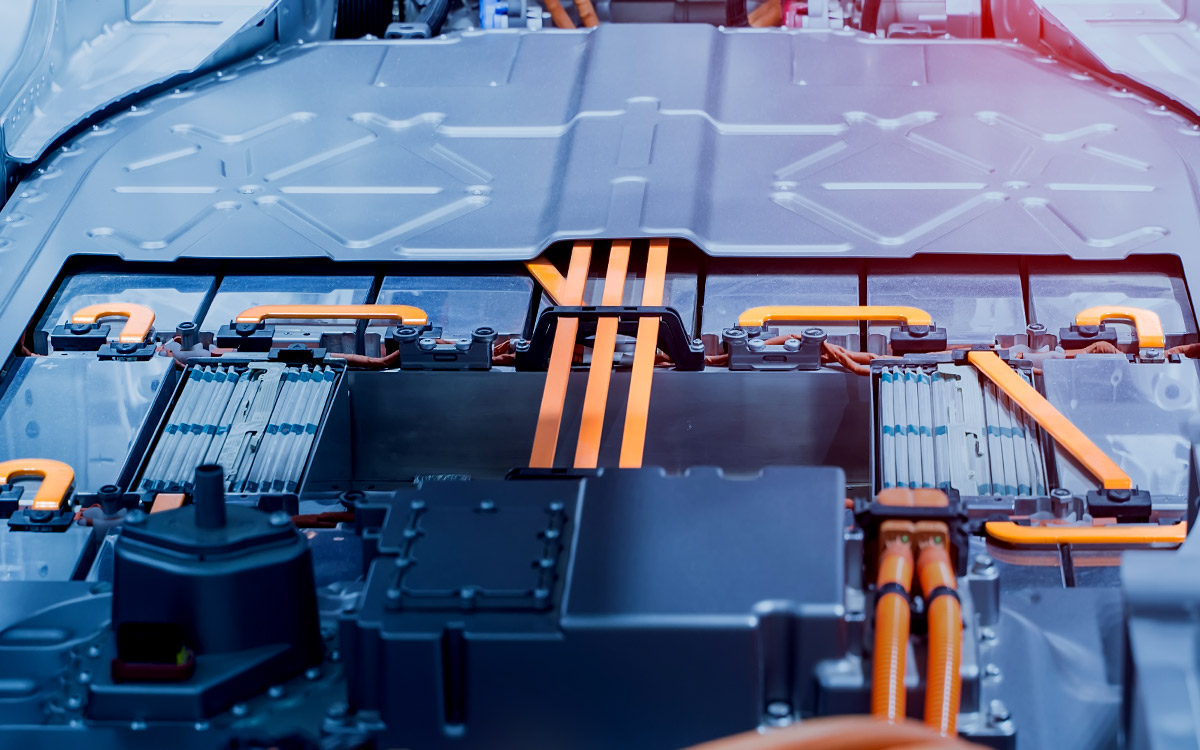
3. Automotive and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Bus bars are widely used in EV battery packs to distribute power between cells efficiently. Their lightweight and compact design make them ideal for modern vehicle applications.
4. Renewable Energy Systems
Solar power and wind energy systems use bus bars to connect and distribute energy from solar panels or wind turbines to inverters and batteries.
5. Data Centers
In data centers, bus bars provide reliable power distribution to servers and networking equipment, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
6. Aerospace and Military Applications
High-performance electrical systems in aircraft, spacecraft, and military vehicles rely on bus bars for efficient power management.
7. Residential and Commercial Buildings
Electrical distribution in buildings often includes bus bars within electrical panels, ensuring efficient power delivery to different floors and sections.
Choosing the Right Bus Bar for Your System
When selecting a bus bar, consider the following factors:
1. Current Rating
Ensure the bus bar can handle the expected electrical load without excessive heating or voltage drop.
2. Material Selection
Copper bus bars offer the best conductivity but are more expensive.
Aluminum bus bars are more affordable and lightweight but have slightly higher resistance.
3. Size and Shape
The width, thickness, and length of the bus bar should be appropriate for the power demands and available space.
4. Insulation Requirements
For applications requiring additional safety, consider insulated bus bars to prevent accidental short circuits.
5. Environmental Conditions
If the bus bar will be exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, or corrosive environments, choose materials with appropriate protective coatings or enclosures.
Conclusion
A bus bar electric system is a vital component in electrical power distribution, providing efficient, safe, and organized connectivity. Whether in industrial plants, residential buildings, vehicles, or renewable energy systems, bus bars improve electrical efficiency, reduce wiring complexity, and enhance safety.
By understanding the different types, advantages, and applications of bus bars, you can make informed decisions when designing or upgrading an electrical system. Whether you're optimizing a data center, installing a solar power system, or upgrading an EV battery pack, bus bars offer a reliable and scalable solution for modern electrical needs.