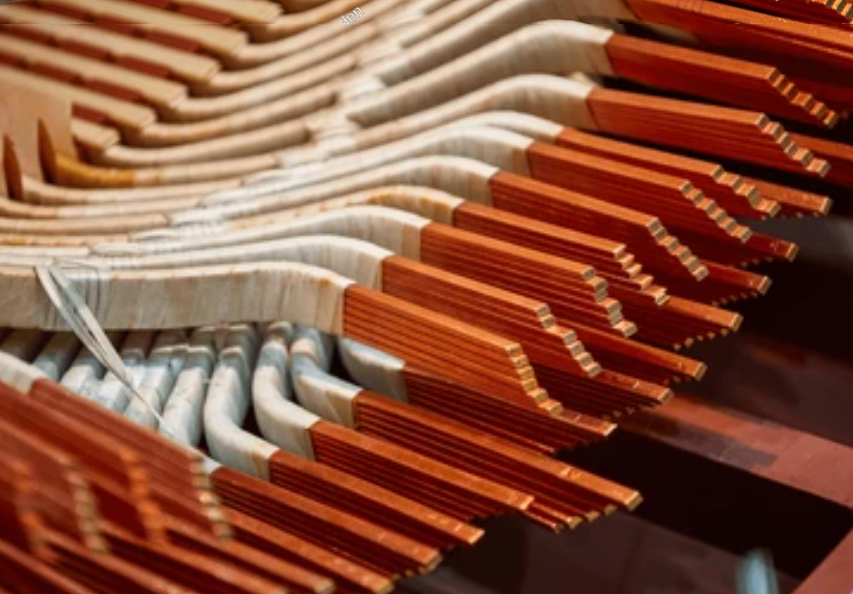
Electrical Copper Bus Bar vs. Electrical Grade Aluminum Bus Bar: What’s the Difference
Bus bars are a critical component in electrical systems, ensuring efficient power distribution in industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Among the various materials used for bus bars, electrical copper bus bars and electrical grade aluminum bus bars dominate the market. While both materials serve the same purpose, their properties, applications, and advantages differ significantly.
This comprehensive guide explores these differences, providing insights into their characteristics, performance, and suitability for different applications. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clear understanding of which material aligns best with your needs.
What is a Bus Bar?
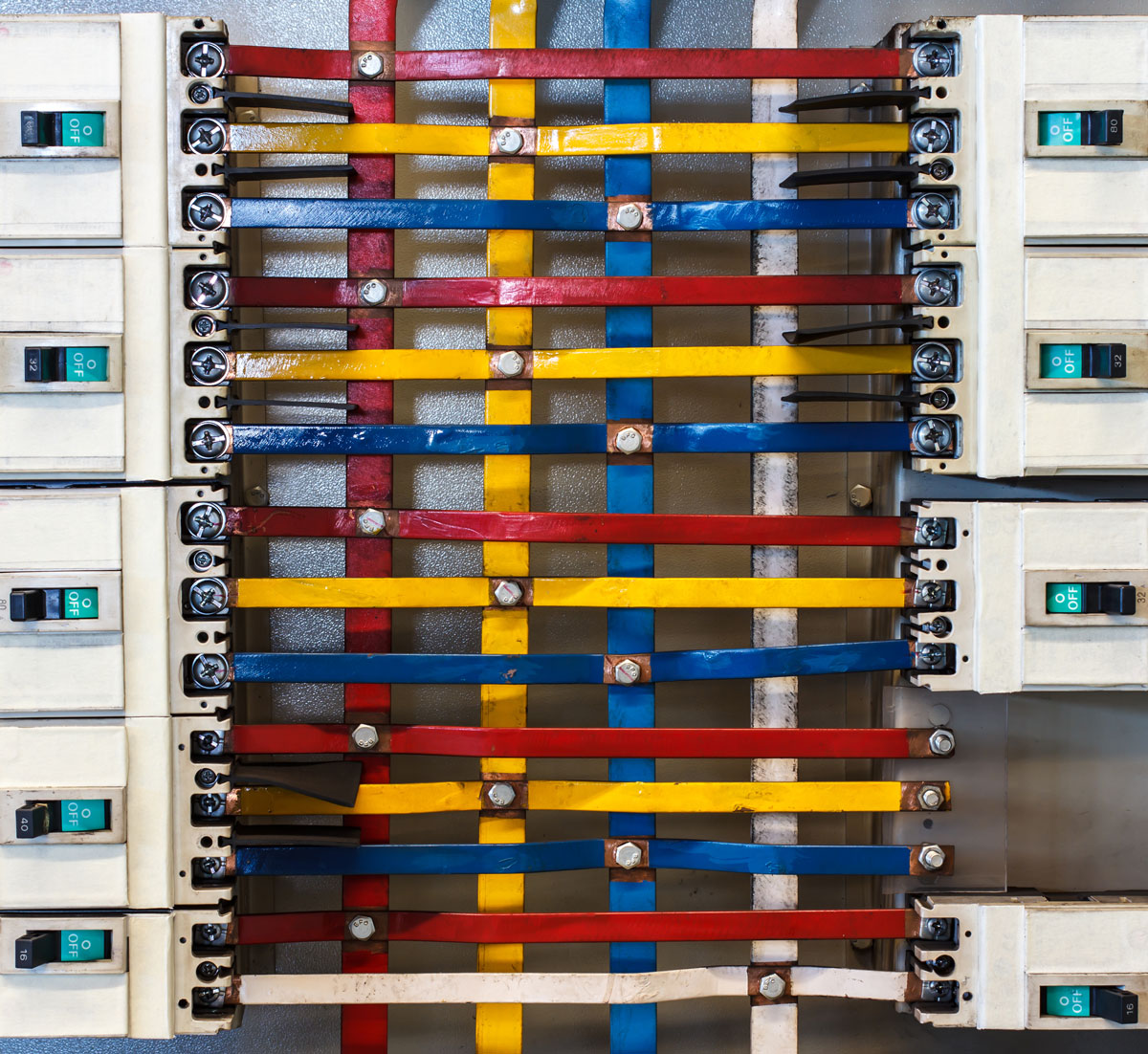
A bus bar is a metallic strip or bar that serves as a centralized point for distributing electrical power. Its primary purpose is to carry and distribute electricity with minimal energy loss. Bus bars are a vital component in switchboards, substations, and distribution panels, streamlining electrical connections and improving system efficiency.
Key Functions of Bus Bars:
- Conducting Electricity: They transfer power from one point to another with minimal resistance.
- Power Distribution: Bus bars allow for the organized and efficient distribution of electricity across multiple circuits.
- Simplifying Connections: They reduce the complexity of wiring by serving as a central hub for connections.
Bus bars come in various shapes and sizes, including flat strips, rods, and hollow tubes, to meet specific system requirements. Their material composition plays a crucial role in determining their performance and suitability for different applications.
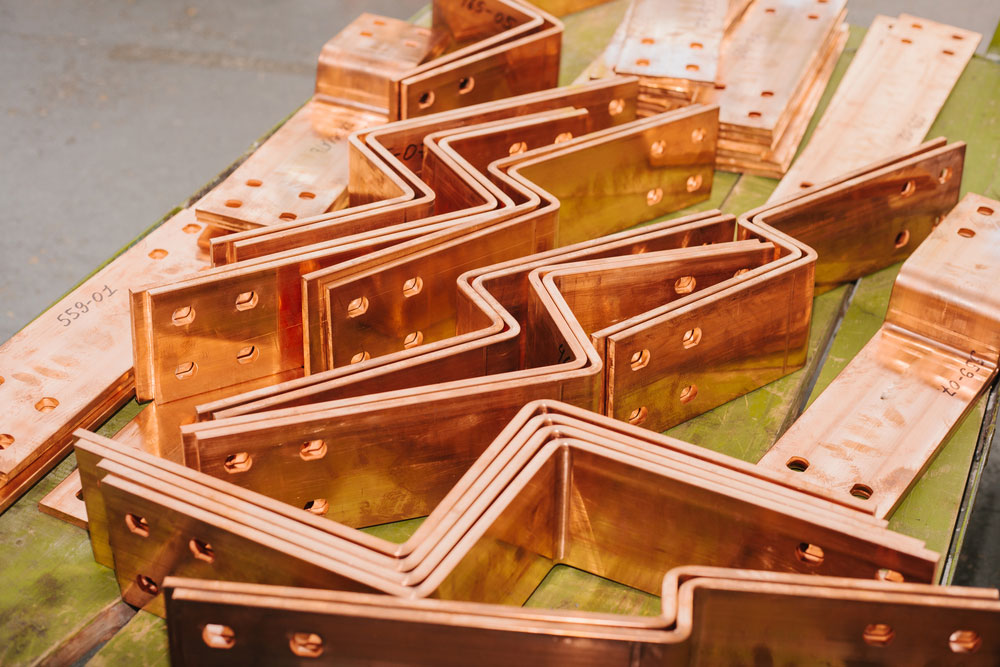
Overview of Electrical Copper Bus Bars
Copper has been the material of choice for electrical applications for decades, thanks to its exceptional conductivity and durability. Electrical copper bus bars are crafted from high-purity copper, ensuring optimal electrical and thermal performance.
Characteristics of Copper Bus Bars:
- Superior Electrical Conductivity: Copper boasts the highest conductivity among commonly used metals, ensuring efficient power transmission.
- Excellent Thermal Performance: It effectively dissipates heat, reducing the risk of overheating.
- High Mechanical Strength: Copper can withstand mechanical stress and deformation, making it ideal for demanding applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper forms a protective oxide layer, offering natural resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
Advantages of Electrical Copper Bus Bars:
- High Efficiency: Copper’s superior conductivity minimizes energy losses, enhancing system performance.
- Durability: Its resistance to wear and tear ensures a long operational lifespan.
- Thermal Stability: Copper remains stable under high temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Low Maintenance: Its corrosion resistance reduces the need for frequent inspections or repairs.
Disadvantages of Electrical Copper Bus Bars:
- Cost: Copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum, which can impact budget-sensitive projects.
- Weight: Copper is denser and heavier, making it less suitable for weight-sensitive applications.

Overview of Electrical Grade Aluminum Bus Bars
Aluminum is a popular alternative to copper, offering a balance between cost and performance. Electrical grade aluminum bus bars are made from high-purity aluminum alloys to enhance their conductivity and mechanical properties.
Characteristics of Aluminum Bus Bars:
- Good Electrical Conductivity: Although lower than copper, aluminum’s conductivity is sufficient for many applications.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is approximately one-third the weight of copper, making it easier to handle and install.
- Corrosion Resistance: When treated or coated, aluminum can resist corrosion effectively, even in harsh environments.
- Cost-Effective: Aluminum is significantly cheaper than copper, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale projects.
Advantages of Electrical Grade Aluminum Bus Bars:
- Affordability: Aluminum’s lower cost makes it ideal for projects with tight budgets.
- Ease of Installation: Its lightweight nature simplifies transportation and installation.
- Eco-Friendliness: Aluminum is highly recyclable, contributing to sustainable practices.
- Availability: Aluminum is widely available, ensuring consistent supply for large projects.
Disadvantages of Electrical Grade Aluminum Bus Bars:
- Lower Conductivity: Aluminum requires a larger cross-sectional area to match the performance of copper.
- Thermal Expansion: Aluminum expands more than copper when heated, which can lead to joint loosening over time.
- Corrosion Risk: Without proper treatment, aluminum is more susceptible to galvanic corrosion, especially in mixed-metal systems.
Comparing Electrical Copper and Aluminum Bus Bars
Understanding the differences between copper and aluminum bus bars is crucial for selecting the right material for your application. Below is a detailed comparison:
|
Aspect |
Electrical Copper Bus Bar |
Electrical Grade Aluminum Bus Bar |
|
Electrical Conductivity |
100% IACS |
61% IACS |
|
Weight |
Heavy |
Lightweight |
|
Cost |
Expensive |
Affordable |
|
Thermal Stability |
Superior |
Good |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent |
Requires coating or treatment |
|
Mechanical Strength |
High |
Moderate |
This comparison highlights the strengths and limitations of each material, emphasizing their suitability for different scenarios.
Applications of Copper and Aluminum Bus Bars
Electrical Copper Bus Bar Applications
Copper bus bars are ideal for:
- High-Current Systems: Power stations and substations where minimal energy loss is critical.
- Mission-Critical Environments: Hospitals, data centers, and aerospace applications requiring maximum reliability.
- Compact Installations: Systems where space-saving is a priority, such as in urban infrastructure.
Electrical Grade Aluminum Bus Bar Applications
Aluminum bus bars are widely used in:
- Renewable Energy Systems: Solar and wind power installations where cost efficiency is vital.
- Weight-Sensitive Applications: Electric vehicles, aircraft, and portable power systems.
- Large-Scale Projects: Power grids and industrial setups requiring bulk materials at lower costs.

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Bus Bar
1. Electrical Performance Requirements
- For high-current, high-efficiency systems, copper is the better choice.
- Aluminum is suitable for standard or low-current applications.
2. Budget Constraints
- Copper’s superior performance comes at a premium.
- Aluminum offers a cost-effective solution without significant compromises.
3. Weight Sensitivity
- Copper’s weight can be a disadvantage in mobile or lightweight systems.
- Aluminum’s lighter density makes it more practical in these scenarios.
4. Environmental Conditions
- Copper is naturally resistant to harsh conditions.
- Aluminum requires additional coatings to perform well in similar environments.
5. Installation Space
- Copper bus bars are more compact, making them suitable for confined spaces.
- Aluminum bus bars need more space due to their larger cross-sectional area.
Maintenance and Longevity
Copper Bus Bars
- Require minimal maintenance thanks to their durability and resistance to corrosion.
- They can last for decades, providing a high return on investment.
Aluminum Bus Bars
- May need periodic inspections to ensure joint integrity and corrosion protection.
- Proper care can significantly extend their operational life.
Environmental Impact
Copper
- Mining and refining copper have a significant environmental footprint.
- Copper recycling is efficient but less common due to market demand.
Aluminum
- Aluminum production is energy-intensive but offset by its recyclability.
- Recycling aluminum requires only 5% of the energy used for primary production.
Recent Innovations in Bus Bar Materials
Copper Bus Bars
- Development of ultra-thin copper strips for compact systems.
- Advanced coatings to further enhance corrosion resistance.
Aluminum Bus Bars
- High-conductivity aluminum alloys are bridging the gap with copper.
- Improved surface treatments for better durability and corrosion resistance.
Making the Right Choice
The decision between electrical copper bus bars and electrical grade aluminum bus bars depends on several factors, including your budget, performance needs, and environmental considerations.
Choose Copper if:
- Maximum conductivity and reliability are essential.
- The application demands compact and robust components.
Choose Aluminum if:
- Cost and weight are critical factors.
- You’re working on a large-scale or environmentally focused project.
Conclusion
Both electrical copper bus bars and electrical grade aluminum bus bars are essential components in modern electrical systems, each with unique strengths and limitations. By understanding their differences and evaluating your project requirements, you can select the material that best aligns with your needs. Whether prioritizing performance, cost, or sustainability, the right choice will ensure efficient and reliable power distribution for years to come.