A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Bus Bar Types
Introduction
In modern electrical systems, efficiency, safety, and reliability are paramount. A crucial component that ensures these qualities is the electrical bus bar. Bus bars serve as central points for distributing electrical power, enabling streamlined connections across various electrical devices and systems. Whether in industrial machinery, residential electrical panels, or renewable energy setups, electrical bus bars play a vital role in maintaining smooth operations.
This guide delves into the different electrical bus bar types, their functions, materials, and applications. By understanding the nuances of bus bars, engineers, electricians, and even DIY enthusiasts can make informed decisions on which bus bar best suits their needs.
The Role of Bus Bars in Electrical Systems
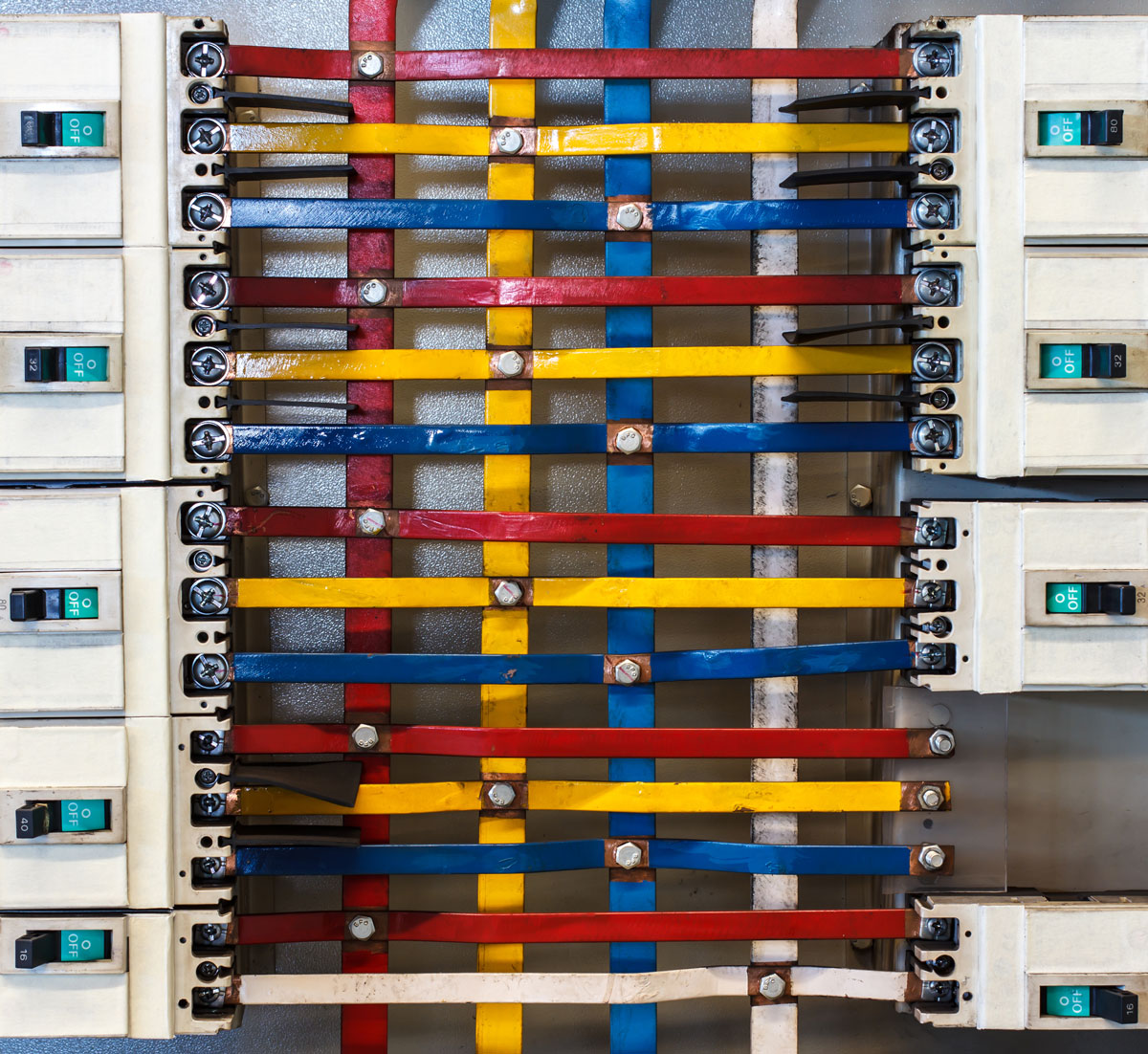
A bus bar is a conductive material used in electrical circuits to collect and distribute electrical power. Instead of using a series of individual wires, bus bars provide a centralized location where electrical connections can be made. They are designed to handle large currents efficiently, making them indispensable in electrical panels, switchboards, and power distribution systems.
Bus bars reduce the complexity of wiring by acting as a junction point for various electrical connections. They ensure that power flows seamlessly across multiple components, reducing the risk of overloading or overheating in individual wires.
Construction and Materials
The construction of a bus bar typically involves a flat, rectangular or cylindrical conductor that is mounted in electrical panels or switchgear. The most common materials used for bus bars include:
- Copper: Known for its excellent electrical conductivity, copper is one of the most widely used materials for bus bars.
- Aluminum: Aluminum offers a lighter and more cost-effective alternative to copper, though it has lower conductivity.
- Brass: Brass is resistant to corrosion and is often used in environments where durability is critical.
- Silver-Plated Materials: Silver plating is used for applications requiring high conductivity, especially in high-performance systems.
Why Bus Bars Are Essential
Electrical bus bars offer several advantages:
- Space-Saving: Bus bars take up less space than traditional wiring, allowing for compact installations.
- Safety: Bus bars are less prone to faults, overheating, or damage compared to individual wires, especially in high-power systems.
- Efficiency: By minimizing resistance and reducing the number of connections, bus bars enhance the overall efficiency of electrical systems.

Electrical Bus Bar Types
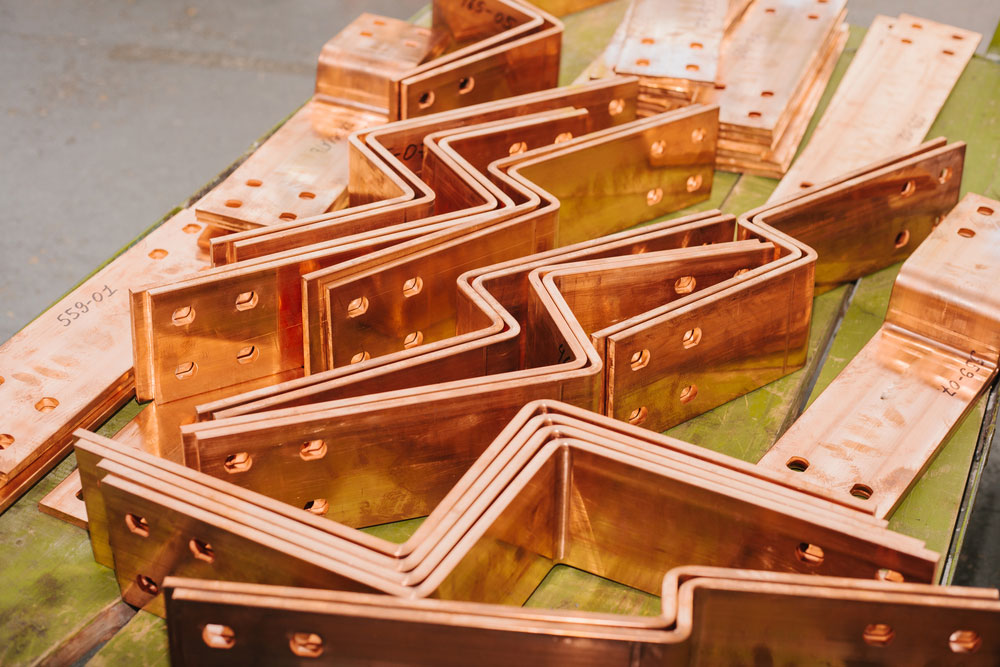
Copper is the most common material used for electrical bus bars due to its superior conductivity. Copper bus bars provide the highest level of performance, making them ideal for high-power applications.
Advantages:
- Excellent conductivity, which reduces energy loss.
- Durability and long lifespan, even under high current loads.
- Easier to solder and connect.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to other materials.
- Heavier weight, which may require additional support in some installations.
Applications: Copper bus bars are often used in industrial settings, power plants, substations, and electrical panels for commercial buildings. They are particularly suitable for high-voltage systems and critical infrastructure where performance and reliability are paramount.
Aluminum is an attractive alternative to copper because it is lighter and more affordable. However, aluminum bus bars have lower conductivity than copper, which can be a drawback in high-power applications.
Advantages:
- Lightweight and cost-effective.
- Resistant to corrosion, especially in outdoor or harsh environments.
- Suitable for low to medium power systems.
Disadvantages:
- Lower conductivity compared to copper.
- More prone to oxidation, which can affect performance over time.
Applications: Aluminum bus bars are commonly used in residential and commercial electrical systems, particularly in applications where weight and cost are important considerations. They are also favored in outdoor installations, such as solar energy systems, due to their corrosion resistance.
Brass Bus Bars
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, known for its corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Brass bus bars are used in environments where resistance to corrosion is critical, such as marine or industrial settings.
Advantages:
- Excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for marine and industrial environments.
- Good strength and durability under heavy loads.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to aluminum.
- Lower conductivity than copper.
Applications: Brass bus bars are used in specialized applications such as marine power systems, corrosive industrial environments, and high-humidity areas where resistance to corrosion is crucial.
Silver-Plated Bus Bars
Silver-plated bus bars are typically made from copper or brass and coated with a layer of silver to enhance conductivity. These bus bars are ideal for high-performance applications where minimal electrical resistance is critical.
Advantages:
- Superior conductivity compared to copper or aluminum.
- Resistant to oxidation, which ensures long-lasting performance.
- High efficiency in systems requiring high-frequency or high-power transmission.
Disadvantages:
- Expensive due to the cost of silver.
- Requires specialized handling and maintenance.
Applications: Silver-plated bus bars are commonly used in high-frequency circuits, telecommunications, and high-power electrical systems where optimal performance is required.
Flexible Bus Bars
Flexible bus bars are designed to allow movement and adaptability within electrical systems. They are often used in applications where vibration or movement is expected, such as in renewable energy systems or transformers.
Advantages:
- Flexibility allows for easier installation in tight spaces.
- Can withstand mechanical stress and vibration.
- Suitable for dynamic applications where movement is inevitable.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than traditional rigid bus bars.
- May have lower current-carrying capacity than solid bus bars.
Applications: Flexible bus bars are often used in renewable energy systems (such as solar and wind power installations), electric vehicles, and other applications where flexibility and adaptability are required.
Insulated Bus Bars
Insulated bus bars are covered with a protective coating to prevent electrical faults, enhance safety, and reduce the risk of accidental contact. These bus bars are often used in high-voltage or high-risk applications.
Advantages:
- Increased safety by preventing electrical shock.
- Suitable for use in high-voltage or hazardous environments.
- Reduces the risk of short circuits and electrical faults.
Disadvantages:
- Insulation can wear over time, requiring periodic checks and maintenance.
- More expensive than non-insulated bus bars.
Applications: Insulated bus bars are used in high-voltage switchgear, control panels, and systems where safety is a critical concern. They are also common in industrial machinery, electrical substations, and sensitive electronic equipment.

Key Features to Consider When Choosing Electrical Bus Bar Types
When selecting the right electrical bus bar for a project, several factors must be taken into account:
Current Rating
The current rating of a bus bar is one of the most critical specifications. It defines the maximum current the bus bar can safely carry without overheating or failing. To determine the appropriate current rating, it is essential to consider the total electrical load and the number of devices connected to the bus bar.
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the bus bar can handle. This is particularly important in high-voltage applications such as substations or industrial power distribution. Choosing a bus bar with an appropriate voltage rating ensures safe operation and reduces the risk of electrical hazards.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive elements, can significantly impact the performance and longevity of a bus bar. In harsh environments, materials like brass, aluminum, or silver-plated bus bars may be more suitable than copper.
Space and Design Constraints
In compact or space-constrained installations, such as residential electrical panels or small electrical devices, the size and design of the bus bar become crucial. Flexible bus bars or custom-designed bus bars can help meet space-saving requirements while maintaining functionality.
Cost Considerations
While copper is the most conductive material, it can also be expensive. Aluminum bus bars offer a more affordable alternative, though they come with certain trade-offs in conductivity. When choosing a bus bar, it's essential to balance cost with performance requirements to find the most cost-effective solution.
Applications of Electrical Bus Bars
Industrial and Commercial Applications
In industrial settings, bus bars are used to distribute power across large facilities. They are integral to power substations, manufacturing plants, and electrical switchgear. Bus bars simplify the connection between electrical devices, reducing the complexity of wiring systems and ensuring a steady flow of power.
Renewable Energy Systems
Bus bars are commonly used in solar energy systems, wind turbines, and energy storage units. Flexible and insulated bus bars are particularly useful in these applications due to their ability to withstand environmental factors and mechanical stress.
Automotive and Transportation Systems
Electric vehicles (EVs) and other transportation systems, such as buses and trains, rely on bus bars for efficient power distribution. Bus bars allow for compact, lightweight, and high-performance power connections, ensuring smooth operation in mobile environments.
Residential Use
In residential buildings, bus bars are used in electrical panels to distribute power to various circuits. They offer a cleaner and more efficient solution than traditional wiring, reducing clutter and improving the overall safety of the electrical system.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Electrical Bus Bars
Overloading Bus Bars
One of the most common mistakes when using bus bars is overloading them. Ensure that the current rating of the bus bar matches the total load it will carry. Overloading can lead to overheating, fires, or electrical failures.
Poor Installation Practices
Incorrect installation can lead to serious safety issues. Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines and ensure that connections are secure. Improperly installed bus bars can cause shorts or electrical faults.
Neglecting Environmental Factors
Choosing the wrong material for the environment can lead to premature wear and failure. For example, using copper bus bars in highly corrosive environments can result in corrosion and reduced conductivity. Select materials based on the environmental conditions they will face.

FAQs
What is the difference between copper and aluminum bus bars?
Copper bus bars offer superior conductivity but are heavier and more expensive. Aluminum bus bars are lighter and more affordable but have lower conductivity.
Can I use a flexible bus bar for high-power applications?
Flexible bus bars are suitable for applications where movement is required, but for high-power systems, rigid copper or aluminum bus bars are typically recommended.
How do I calculate the correct current rating for a bus bar?
The current rating depends on the load and the bus bar's material. You can calculate it by considering the total current expected to flow through the system and matching it with the bus bar's specifications.
What are the benefits of silver-plated bus bars?
Silver-plated bus bars provide excellent conductivity and are ideal for high-performance applications, especially in high-frequency systems.
Why do bus bars need to be insulated in certain systems?
Insulation prevents accidental contact with live parts and protects against short circuits, particularly in high-voltage systems.
Conclusion
Electrical bus bars are an essential component in power distribution systems, providing a reliable, efficient, and safe way to manage electrical currents. By understanding the different electrical bus bar types, their materials, and applications, engineers and electricians can make informed decisions that improve the performance and safety of electrical systems.
Whether you are designing a new installation, upgrading an existing system, or maintaining an electrical network, selecting the right bus bar is crucial. Always consider the specific requirements of your application, the environmental factors at play, and the material characteristics of each bus bar type.