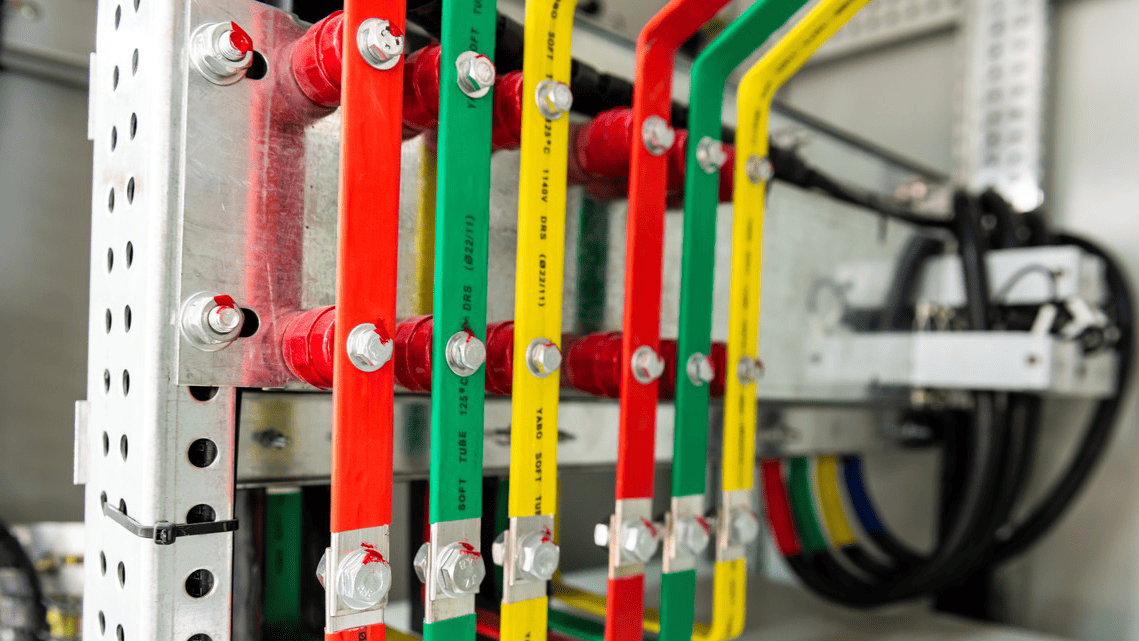
Understanding Electrical Ground Bus Bar: An Ultimate Guide
In any electrical system, safety and reliability are paramount. One of the most crucial components in maintaining both of these factors is the electrical ground bus bar. While it’s a component often overlooked by the average person, it plays a vital role in grounding an electrical system, ensuring that dangerous electrical faults are safely managed and that the overall system operates efficiently. This ultimate guide will provide you with everything you need to understand about electrical ground bus bars, from their function and types to installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
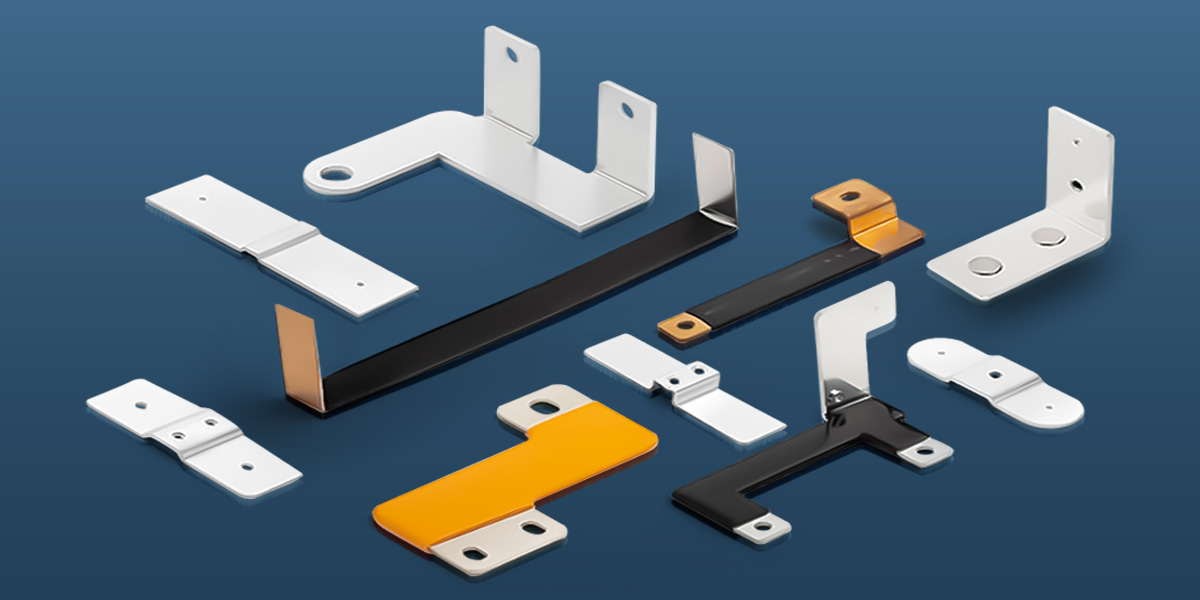

What is an Electrical Ground Bus Bar?
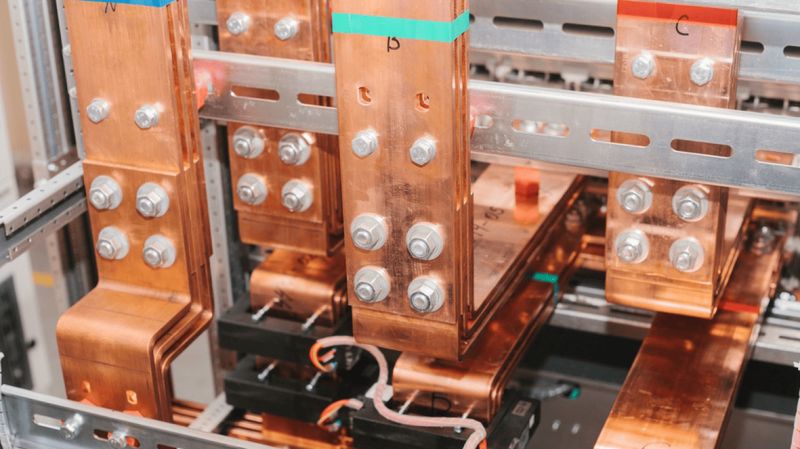
An electrical ground bus bar is a conductive bar made from materials like copper or aluminum, and it serves as the central point for connecting multiple grounding conductors in an electrical system. Grounding is one of the most crucial safety measures in electrical installations, and the bus bar ensures that all parts of an electrical system are properly grounded.
Key Features of an Electrical Ground Bus Bar
1. Material: Ground bus bars are typically made from copper or aluminum due to their high electrical conductivity. Copper is more commonly used due to its superior conductivity, while aluminum is a more cost-effective alternative.
2. Size and Shape: The size of the bus bar depends on the number of connections it needs to support. It is generally a long, rectangular piece with terminals or screws for securing the grounding wires.3. Installation Location: An electrical ground bus bar is usually located within an electrical panel, control panel, or distribution board. It connects all the ground wires that run from various circuits, appliances, or equipment to a central ground point.
How It Functions
The electrical ground bus bar provides a central, reliable point where all ground wires in a system are connected. It helps ensure that any fault current or electrical surge is safely channeled to the earth, preventing damage to equipment and reducing the risk of electric shock.
Role in Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding is the process of connecting the non-current-carrying parts of an electrical system to the earth. The electrical ground bus bar plays a pivotal role in this process by providing a dedicated and organized way to attach all grounding wires, ensuring a uniform and efficient grounding system.
How Does an Electrical Ground Bus Bar Work?
Understanding how an electrical ground bus bar works is essential to grasping the importance of grounding in electrical systems. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of its function:
1. Connecting Ground Conductors: The primary function of an electrical ground bus bar is to connect the ground conductors that come from various electrical components. These components can include circuit breakers, outlets, switches, appliances, and electrical panels. By connecting all these ground conductors to a central point, the bus bar helps ensure that all equipment is grounded to the same reference point: the earth.
2. Pathway for Fault Currents: In the event of an electrical fault, such as a short circuit or leakage of electricity, the electrical ground bus bar provides a low-resistance path for the current to flow safely to the ground. This is crucial because it prevents the fault current from traveling through the rest of the electrical system, thereby reducing the risk of electrical fires, equipment damage, or electrocution.
3. Preventing Voltage Imbalance: Grounding through the electrical ground bus bar also helps maintain voltage stability in the electrical system. If electrical systems aren't grounded correctly, voltage imbalances can occur, which may lead to equipment malfunction or even damage. A properly installed bus bar ensures that the electrical system remains balanced and safe for operation.
Why is an Electrical Ground Bus Bar Important?
The electrical ground bus bar serves several critical purposes in any electrical system. Below are some of the key reasons why it is so important:
1. Safety of People and Equipment: The primary reason for grounding electrical systems is to prevent electrical shock hazards. The electrical ground bus bar acts as the central point for all ground conductors, ensuring that any fault currents are safely conducted to the earth, thus protecting both people and equipment.
In the case of a short circuit, the grounding system ensures that the excess electrical energy is safely discharged into the ground, preventing dangerous voltage buildup. Without an electrical ground bus bar, there is a significant risk of electrical shock, fire, and other safety hazards.
2. System Efficiency and Stability: In addition to safety, grounding helps ensure the efficiency and stability of an electrical system. Proper grounding through a dedicated bus bar minimizes the risk of ground loops and electrical noise, which can interfere with the operation of sensitive equipment. This is especially important in industrial, commercial, and residential systems where high-value machinery and appliances are used.
3. Compliance with Electrical Codes: Electrical codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S., mandate the use of proper grounding in all electrical installations. These codes often specify the use of an electrical ground bus bar in electrical panels and distribution boards to ensure that grounding is done safely and effectively.
Failing to adhere to these codes can lead to electrical system failures and safety hazards, and could even result in legal and financial consequences. For this reason, the electrical ground bus bar is essential in meeting electrical code requirements.
Types of Electrical Ground Bus Bars
There are several types of electrical ground bus bars, each designed to suit different applications. Below are the most common types:
1. Single-Pole Ground Bus Bar: The single-pole electrical ground bus bar is typically used in residential electrical panels, where the number of ground connections is relatively low. It has a single row of terminals for connecting ground wires from various circuit breakers and outlets.
2. Multi-Pole Ground Bus Bar: In commercial or industrial electrical systems, a multi-pole ground bus bar is often used. It has multiple rows of terminals, allowing it to handle a higher number of ground wires. This type of bus bar is used in larger electrical panels or systems with more circuits and equipment.
3. Isolated Ground Bus Bar: An isolated ground bus bar is used when it is necessary to ground sensitive equipment separately from other parts of the electrical system. This is typically used in industrial and data center environments where electrical noise could interfere with the operation of sensitive equipment.
4. Copper vs. Aluminum Ground Bus Bars: Copper Ground Bus Bars: Copper is the most common material used for electrical ground bus bars due to its excellent conductivity and durability. Copper bus bars are typically used in high-performance and high-reliability applications where optimal conductivity is needed.
5. Aluminum Ground Bus Bars: Aluminum is a more affordable alternative to copper. While it doesn’t offer the same level of conductivity as copper, it is still an effective material for most residential and commercial grounding applications.
Applications of Electrical Ground Bus Bars
The electrical ground bus bar is used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Below are some of the most common areas where they are used:
1. Residential Electrical Panels: In residential electrical panels, the electrical ground bus bar serves as the central grounding point for all household circuits. It connects the ground wires from various appliances, outlets, and circuit breakers, ensuring that the entire electrical system is properly grounded.
2. Commercial and Industrial Electrical Panels: Commercial and industrial electrical systems require larger and more robust grounding solutions. The electrical ground bus bar plays a crucial role in these environments by safely directing fault currents away from sensitive equipment and ensuring the overall stability of the system.
3. Control Panels: In control panels, especially in industrial automation systems, the electrical ground bus bar ensures that the grounding system is properly organized, preventing issues such as electrical interference or malfunction caused by improper grounding.
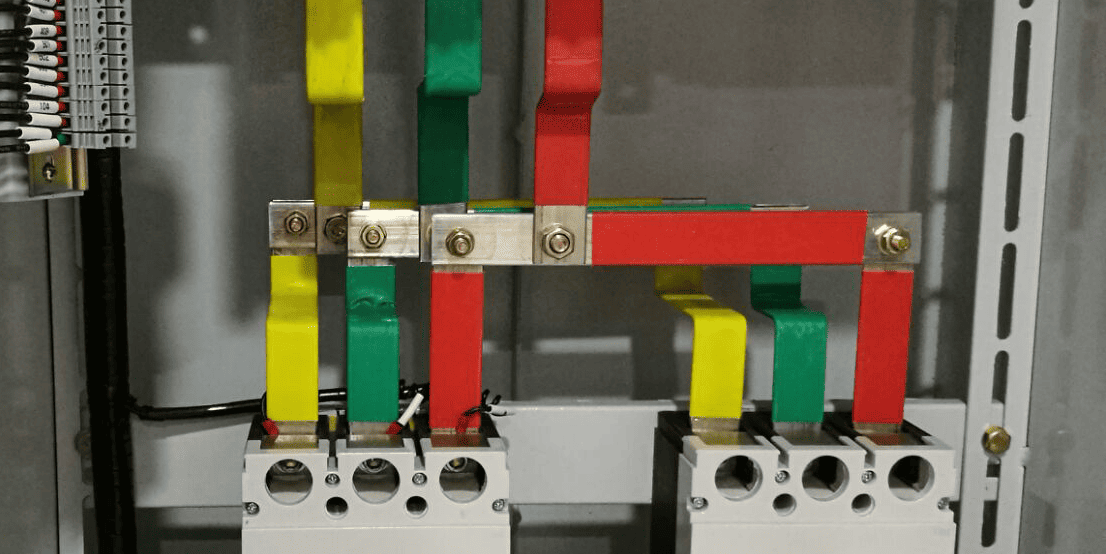
4. Electrical Substations: In electrical substations, where high voltages are managed, the electrical ground bus bar helps ensure the safety of both equipment and personnel by providing a direct path to the earth for fault currents, protecting the substation from electrical surges.
5. Telecommunication Systems: Telecommunications equipment, particularly in remote or outdoor locations, often uses electrical ground bus bars for grounding. This ensures that any electrical surges, such as those caused by lightning strikes, are safely discharged into the earth.
Installing an Electrical Ground Bus Bar
Proper installation of an electrical ground bus bar is essential for ensuring safety and functionality. Below is a step-by-step guide to installing a bus bar:
Step 1: Determine the Proper Size
The size of the electrical ground bus bar depends on the number of ground connections required. Ensure that the bus bar you choose is large enough to accommodate all of the ground wires from various components.
Step 2: Choose the Right Material
Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical ground bus bars. Choose copper for higher conductivity and durability, or aluminum if cost is a concern.
Step 3: Mount the Bus Bar
The electrical ground bus bar should be securely mounted within the electrical panel or distribution board. Ensure it is insulated and kept away from live conductors to avoid accidental contact.
Step 4: Connect the Ground Wires
Connect the ground wires from all circuits, appliances, and outlets to the bus bar. Ensure each connection is tight and secure to prevent loose connections, which could lead to arcing or system failure.
Step 5: Test for Proper Grounding
Once the bus bar is installed and all ground wires are connected, test the system to ensure it is properly grounded. This can be done using a grounding tester, which measures the resistance of the connection to the earth.
Troubleshooting Common Ground Bus Bar Issues
If you experience problems with grounding, it’s important to troubleshoot the electrical ground bus bar to identify the cause. Common issues include:
1. Loose Connections: Loose connections can lead to high resistance in the grounding system, resulting in potential electrical hazards. Tighten all connections and ensure they are securely fastened.
2. Corrosion: Corrosion can reduce the conductivity of the electrical ground bus bar. Check for signs of rust or degradation, especially in outdoor or high-humidity environments. Clean and replace any corroded components as necessary.
3. Overloaded Bus Bar: An overloaded electrical ground bus bar can cause overheating or failure. Ensure that the bus bar is not overloaded and that it can handle the number of ground connections it is supporting.
Maintenance of Electrical Ground Bus Bars
Maintaining an electrical ground bus bar is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability. Regular inspection, cleaning, and testing will help prevent issues and extend the lifespan of your grounding system. Here are some key maintenance tips:
1. Inspect Connections Regularly: Check that all ground connections are secure and free of corrosion.
Clean the Bus Bar: Regularly clean the bus bar to remove any dust, dirt, or oxidation.
2. Test Grounding Resistance: Use a grounding tester to check the resistance of the ground connection and ensure it meets safety standards.
3. Replace Damaged Components: If any part of the bus bar or grounding system is damaged or worn out, replace it immediately to prevent safety risks.