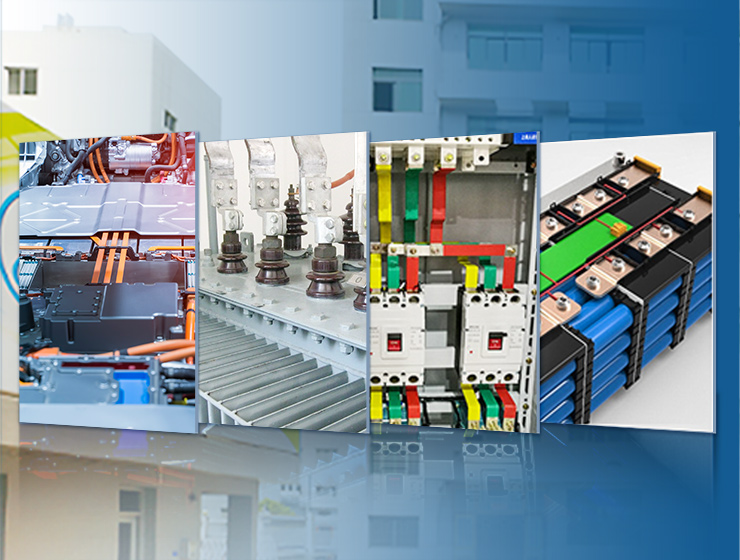
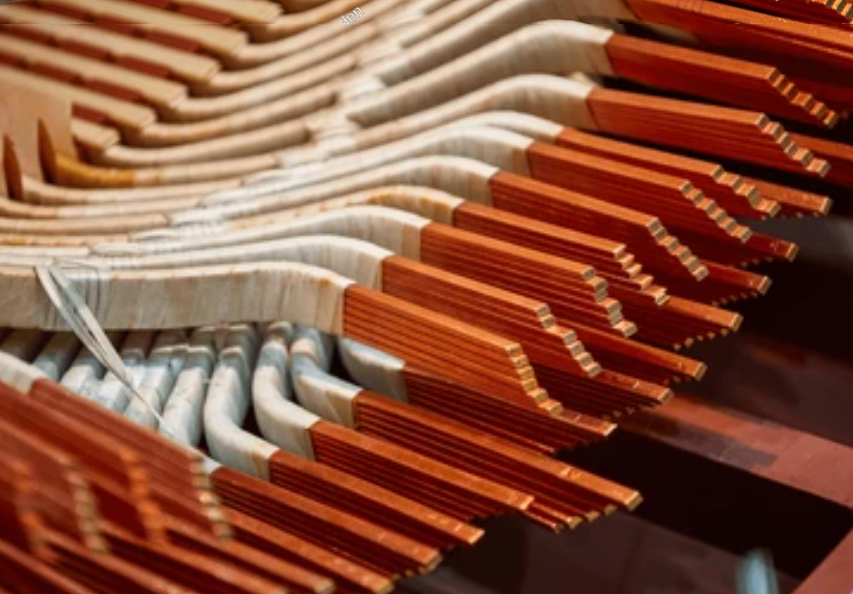
Understanding Electric Bus Bars: Functions, Types, and Applications
Explore the functions, types, and applications of electric bus bars while discussing their advantages, materials, and safety considerations.
Introduction
In modern electrical systems, efficient power distribution is crucial to maintaining stability and reliability. One of the most essential components in power distribution is the electric bus bar. These conductive bars act as a central hub, enabling seamless electricity transfer between power sources and connected circuits. Whether in industrial setups, commercial buildings, or renewable energy projects, electric bus bars play a fundamental role in ensuring optimal energy transmission.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the functions, types, and applications of electric bus bars while discussing their advantages, materials, and safety considerations.
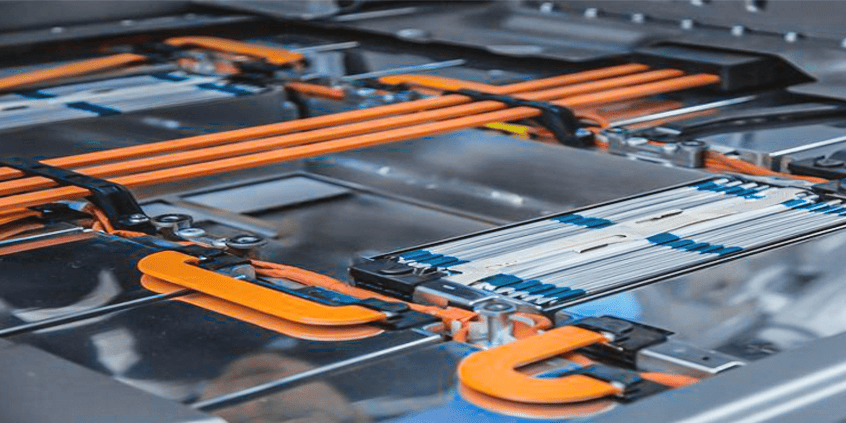
What Is an Electric Bus Bar?
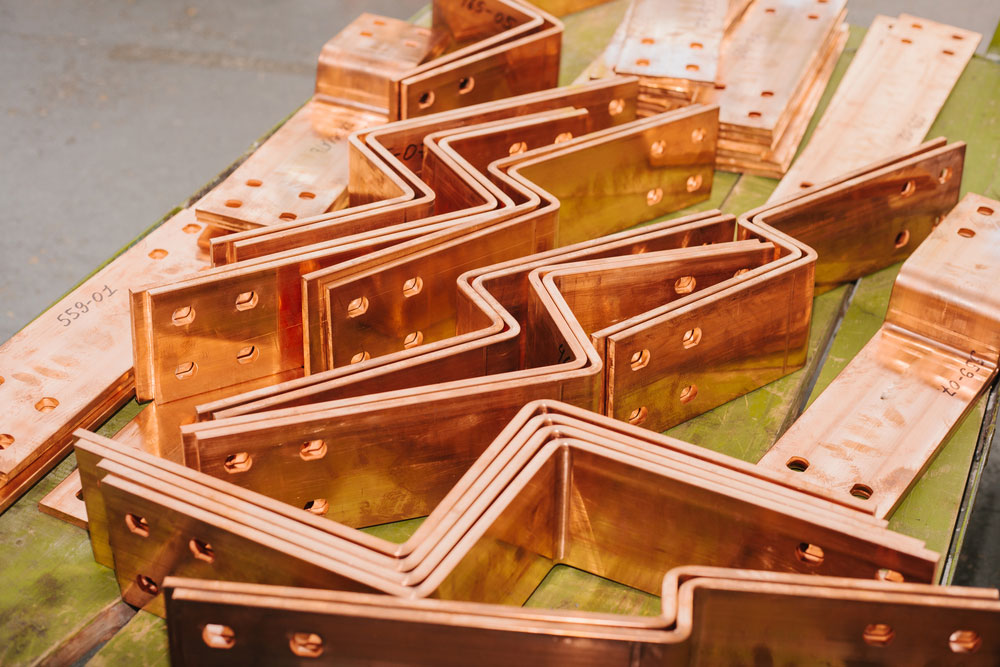
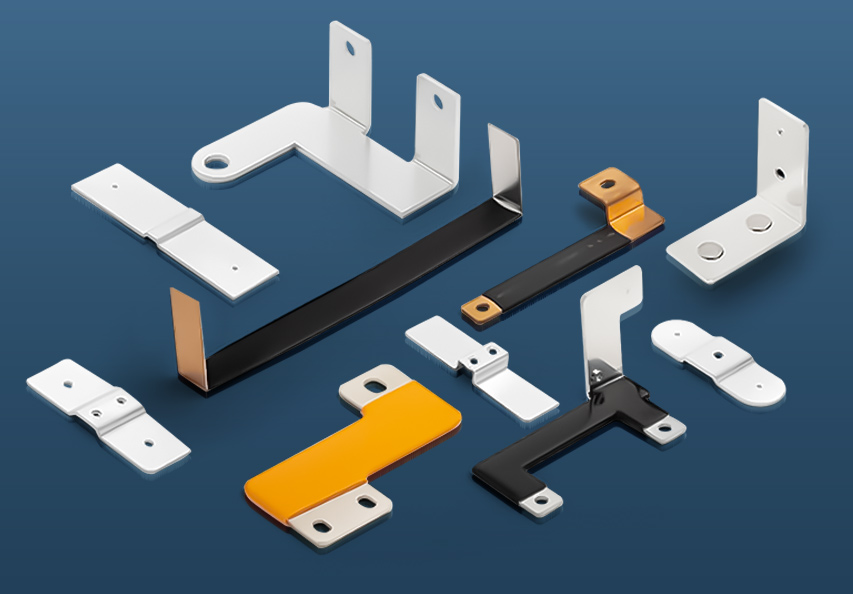
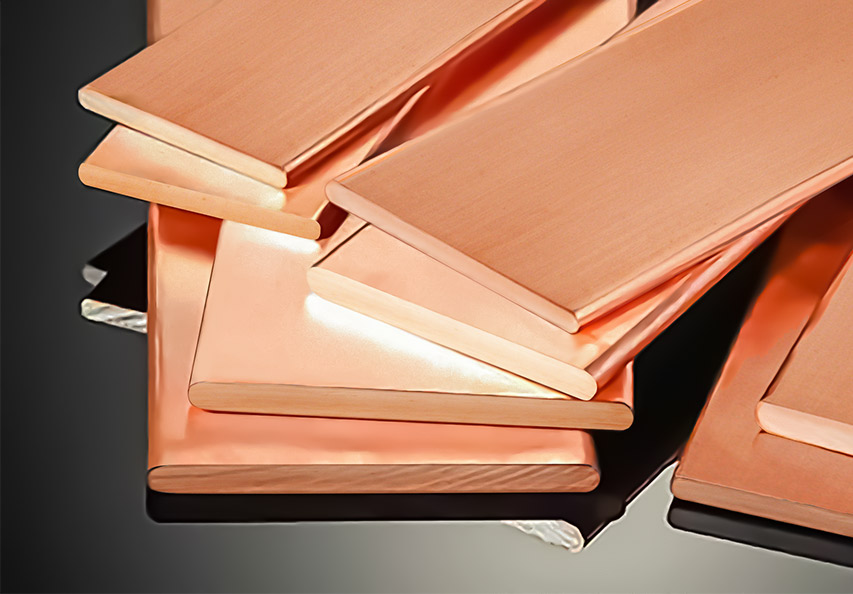
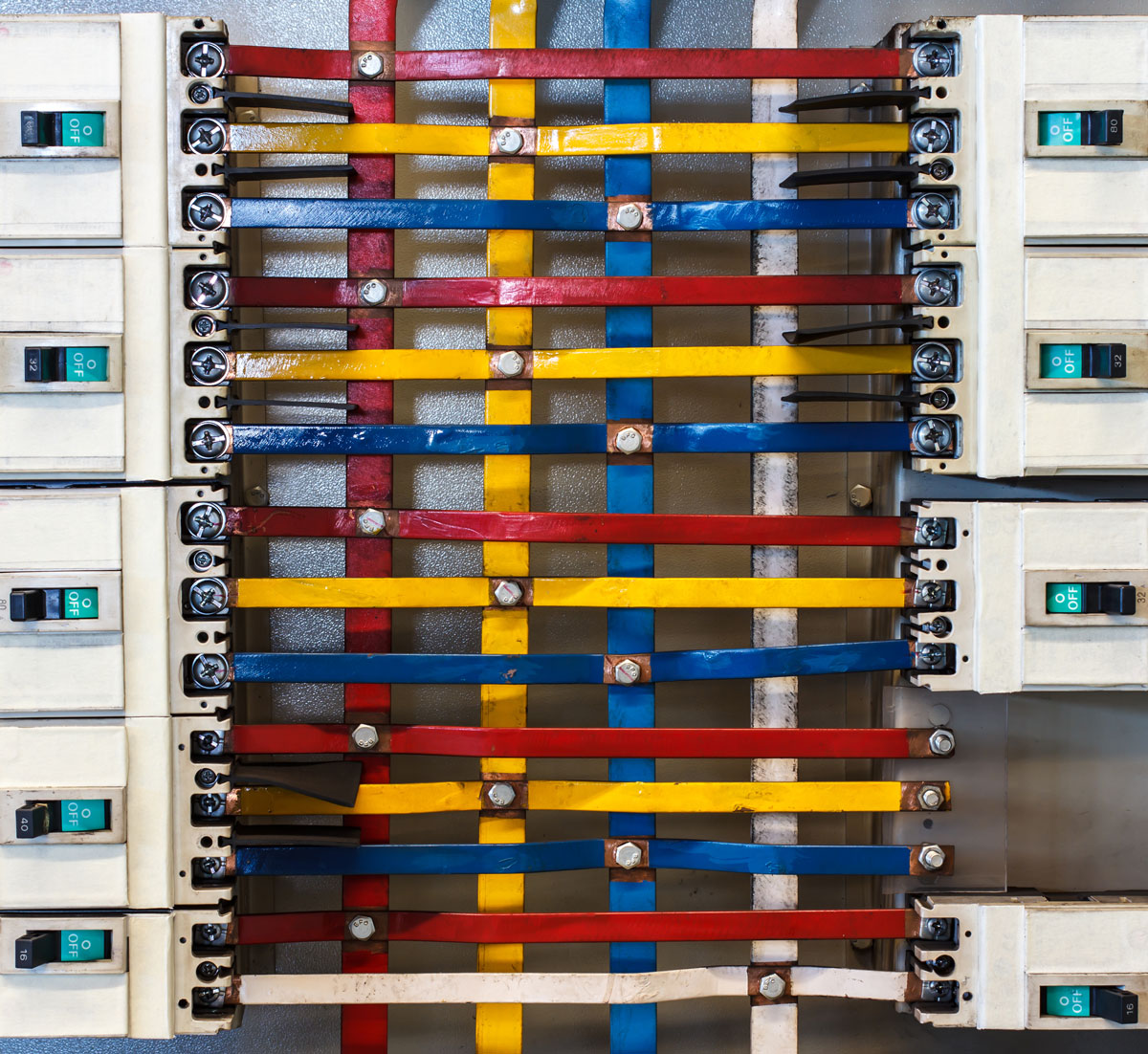
An electric bus bar is a conductive strip or bar designed to distribute electrical power efficiently across different circuits. These bars are typically made from copper or aluminum due to their excellent conductivity and durability.
Key Characteristics of an Electric Bus Bar
- High Conductivity: Allows seamless electricity flow.
- Compact and Space-Saving: Reduces the need for extensive wiring.
- Scalability: Supports expansion in power distribution systems.
- Thermal Management: Minimizes heat buildup, ensuring safety.
Electric bus bars can be found in switchgear, power panels, substations, and battery banks, among other applications. Their versatility makes them indispensable in electrical engineering.
Functions of an Electric Bus Bar
Electric bus bars serve multiple purposes in power distribution and transmission. Below are some of their key functions:
1. Power Distribution
An electric bus bar distributes electrical power from a single or multiple sources to different loads, ensuring an efficient and balanced distribution.
2. Current Carrying Capacity
Bus bars can handle large amounts of current compared to traditional wiring, reducing electrical losses and enhancing efficiency.
3. Fault Protection
By acting as a central power hub, an electric bus bar helps isolate faults in electrical systems, preventing widespread failures.
4. Space Optimization
Unlike conventional wiring, electric bus bars provide a compact solution for managing high-voltage systems while reducing clutter and cable congestion.
5. Scalability & Flexibility
Bus bars allow for easy modification and expansion of power systems, accommodating additional loads without major rewiring.
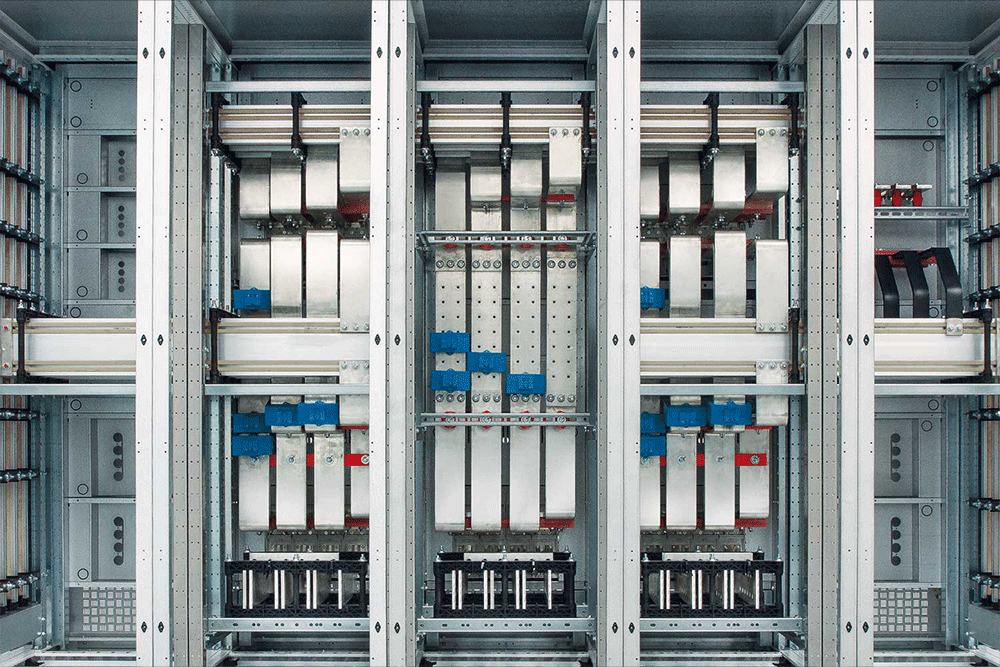
Types of Electric Bus Bars
Electric bus bars come in various designs, each suited for specific applications. Below are some of the most common types:
1. Single Bus Bar System
- Description: A simple system with a single bus bar handling all loads.
- Applications: Small-scale electrical networks, residential panels.
- Advantages: Cost-effective and easy to install.
- Disadvantages: No redundancy—failure of the bus bar affects the entire system.
2. Double Bus Bar System
- Description: Uses two parallel bus bars for redundancy and flexibility.
- Applications: High-voltage substations, industrial power plants.
- Advantages: Increased reliability, easy maintenance.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and complex to install.
3. Isolated Phase Bus Bar
- Description: Each phase is separated within an insulated enclosure to prevent short circuits.
- Applications: Power generation stations, high-voltage applications.
- Advantages: Reduces phase-to-phase faults, minimizes electrical losses.
- Disadvantages: Higher installation and maintenance costs.
4. Segregated Phase Bus Bar
- Description: Phases are physically separated within a common enclosure.
- Applications: Industrial plants, large electrical distribution networks.
- Advantages: Improved safety, better fault isolation.
- Disadvantages: More complex than a single bus bar system.
5. Non-Segregated Phase Bus Bar
- Description: Conductors of different phases are placed in a single enclosure without barriers.
- Applications: Medium-voltage applications, electrical switchgear.
- Advantages: Lower cost, simpler installation.
- Disadvantages: Less protection against faults.
Materials Used in Electric Bus Bars
Electric bus bars are primarily made of copper or aluminum, each offering distinct advantages:
|
Material |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Copper |
High conductivity, corrosion resistance, durability |
Expensive, heavier than aluminum |
|
Aluminum |
Lightweight, cost-effective, suitable for high-volume applications |
Lower conductivity than copper, prone to oxidation |
The choice between copper and aluminum depends on cost, weight considerations, and current-carrying capacity.
Applications of Electric Bus Bars
Electric bus bars are widely used in various industries due to their efficiency, scalability, and reliability. Below are some key applications:
1. Power Distribution in Industrial Facilities
Used in factories, manufacturing plants, and industrial buildings to distribute power efficiently.
Helps manage high-voltage systems with minimal energy loss.
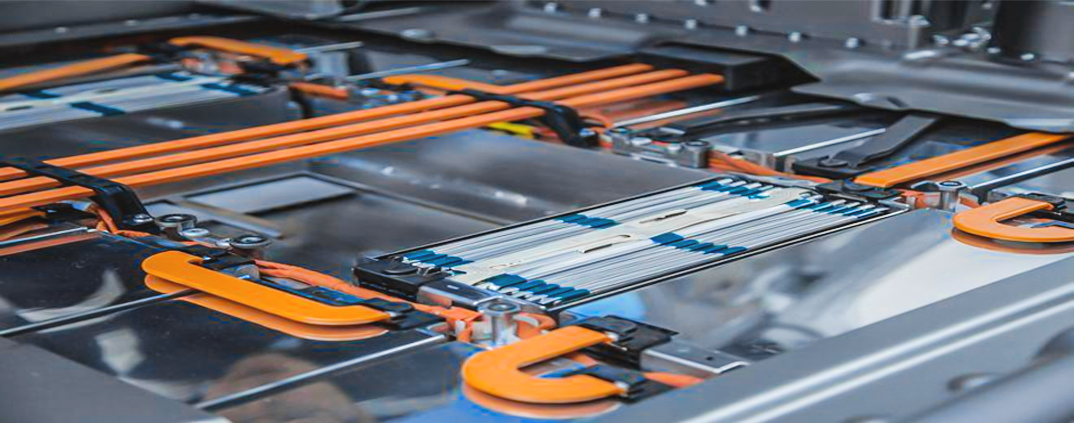
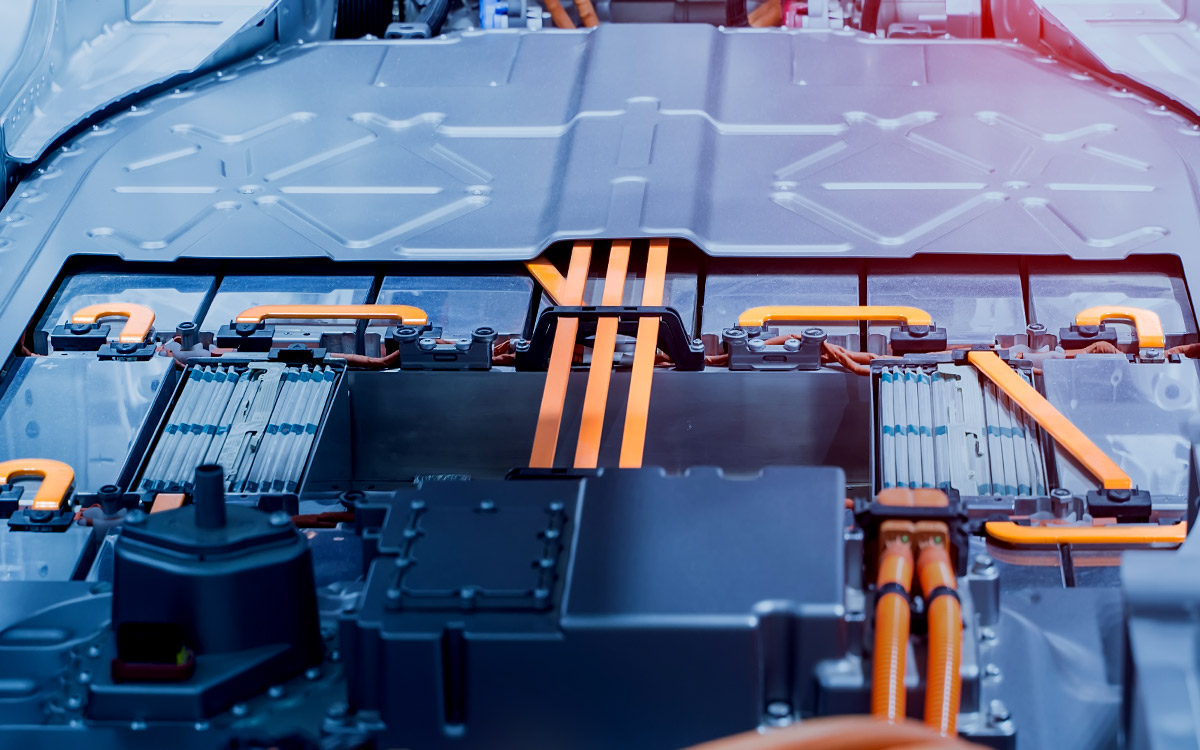
2. Renewable Energy Systems
Essential for solar and wind power stations to distribute electricity generated by renewable sources.
Enhances the efficiency of battery energy storage systems (BESS).
3. Electrical Switchgear and Substations
Found in power transmission and distribution substations for managing high-voltage networks.
Ensures fault isolation and network stability.
4. Data Centers and IT Infrastructure
Used in server rooms and data centers for distributing power efficiently to high-performance computing systems.
Reduces electrical losses and optimizes energy consumption.
5. Transportation and Railways
Found in electric trains, metros, and railway substations to supply consistent electrical power.
Ensures stable energy flow for electric transportation systems.
6. Commercial and Residential Buildings
Installed in large commercial complexes, hospitals, and high-rise buildings to streamline power distribution.
Enhances the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
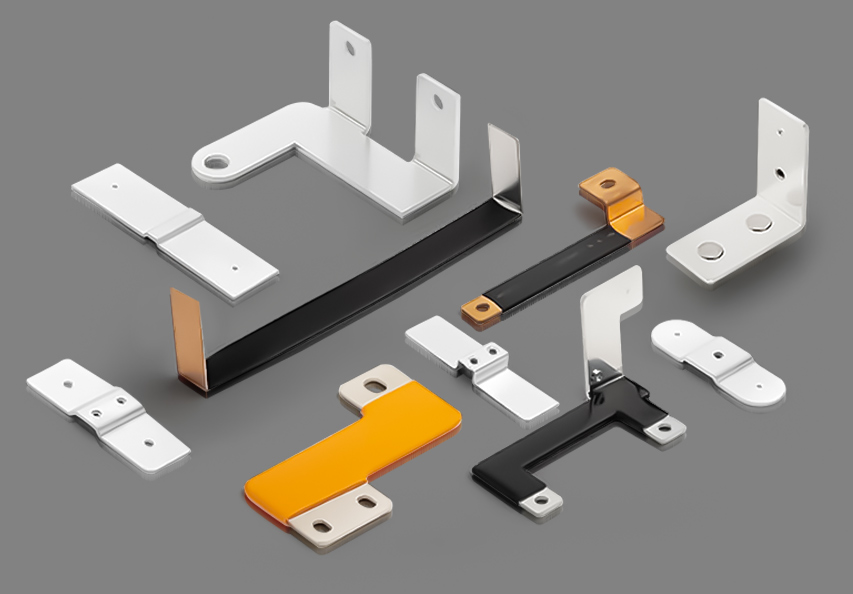

Advantages of Using an Electric Bus Bar
Using an electric bus bar offers multiple benefits compared to traditional cabling:
- Improved Electrical Efficiency – Reduces power losses and voltage drops.
Enhanced Safety – Minimizes overheating and electrical hazards.
Cost-Effective – Requires less maintenance and fewer materials.
Compact Design – Saves space in electrical panels.
Scalability – Allows for easy expansion of power systems.
Safety Considerations for Electric Bus Bars
To ensure safe operation, the following safety guidelines should be followed when installing and maintaining electric bus bars:
- Proper Insulation: Use insulated coatings or enclosures to prevent accidental contact.
- Adequate Ventilation: Avoid overheating by ensuring proper cooling mechanisms.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodic inspections help detect wear, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Correct Sizing: Select bus bars based on the current load requirements to prevent overheating.
- Short Circuit Protection: Use protective devices like circuit breakers to handle electrical faults.
Conclusion
Electric bus bars are an essential component in modern power distribution systems, providing a compact, reliable, and efficient means of transmitting electricity. With various types and materials available, selecting the right electric bus bar depends on application requirements, budget, and safety considerations.
From industrial plants and renewable energy stations to data centers and transportation networks, electric bus bars continue to play a vital role in ensuring efficient energy distribution and system reliability.