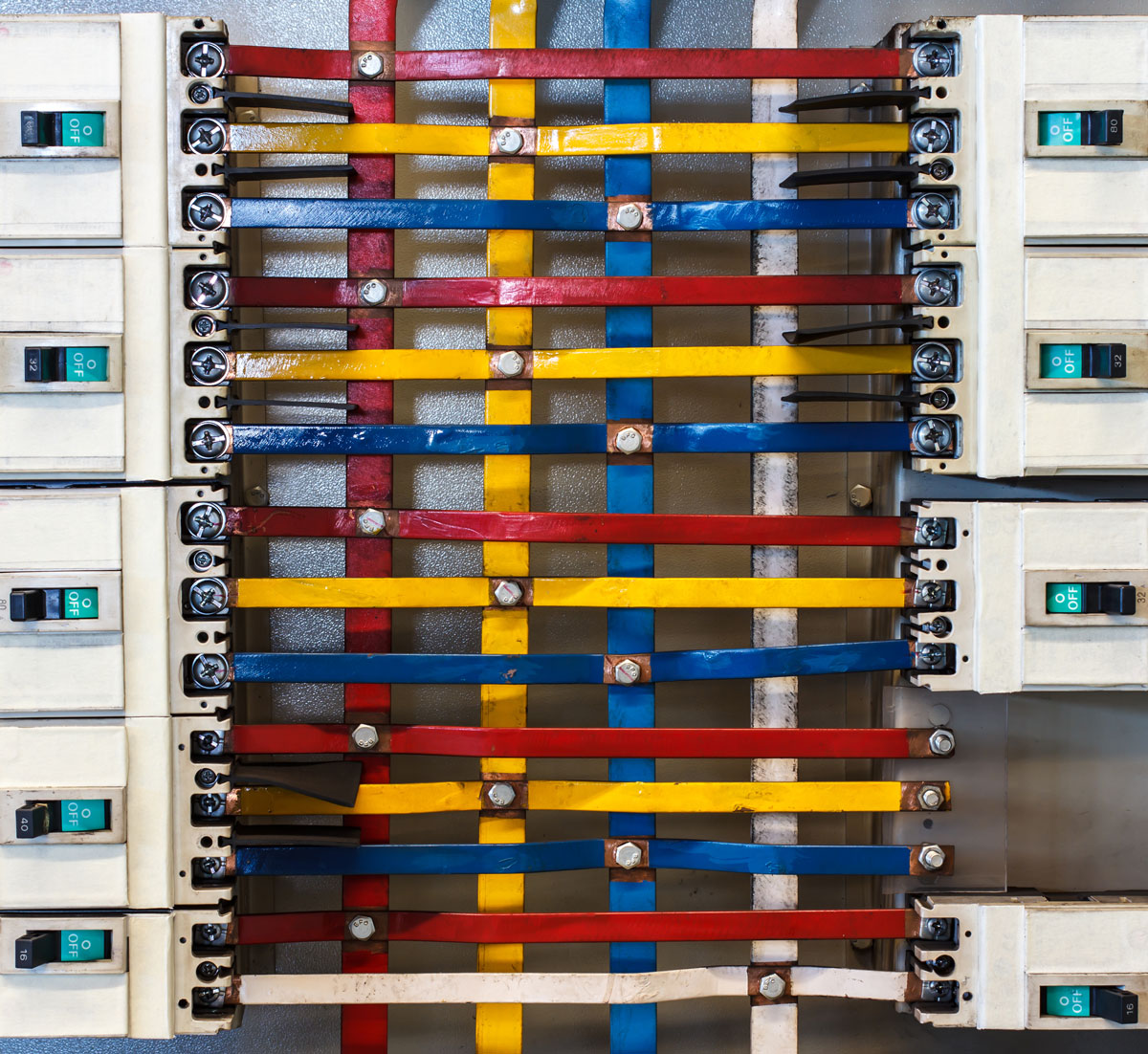
Choosing the Right Electric Panel Bus Bar
When it comes to modern electrical systems, one of the most crucial components often overlooked is the electric panel bus bar. Though it may not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think about your electrical panel, the bus bar plays a pivotal role in distributing power efficiently and safely throughout your home or commercial building. Choosing the right bus bar for your electrical panel is not a decision to be made lightly, as it impacts the reliability, safety, and performance of your entire electrical system. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about electric panel bus bars, from what they are, how they function, to the factors you should consider when selecting one for your needs.
What is an Electric Panel Bus Bar?
At its core, an electric panel bus bar is a metallic conductor found within an electrical panel that distributes electrical current to various circuit breakers or fuses. It is designed to facilitate the safe transfer of electricity from the main power supply to individual electrical circuits within the panel. Typically made from highly conductive metals such as copper or aluminum, the bus bar connects to the incoming electrical service from the utility company and acts as the main conduit through which electrical current flows to multiple circuits.
The bus bar essentially serves as a junction point, enabling the safe and efficient transfer of power to various parts of the building or facility. It’s one of the first places electrical power enters when it reaches the panel and is also the primary point for distributing power to different branch circuits.
Types of Bus Bars:
- Single Bus Bar: Typically used in smaller or residential electrical systems, where the current load is relatively moderate.
- Double Bus Bar: Often found in larger commercial or industrial systems where the electrical load is heavier and redundancy is required.
- Segmented Bus Bar: A more complex system used in high-capacity installations where different segments of the bus bar can be isolated independently.
In simpler terms, imagine your electrical panel as a power distribution center. The bus bar acts as the main highway through which electrical current flows, delivering power to every part of the system.
The Importance of the Electric Panel Bus Bar
The electric panel bus bar is not just an auxiliary part of the system but rather a critical one. If a bus bar malfunctions, the entire electrical panel will fail to operate as designed. This can lead to power outages, circuit damage, and, in the worst-case scenario, fires or electrical hazards. Here’s why choosing the right bus bar is so important:
1.Safe Distribution of Electricity
The bus bar plays a crucial role in ensuring that electricity is distributed evenly across multiple circuits. A properly installed and functioning bus bar helps prevent overloads, short circuits, and other electrical hazards. If the bus bar is improperly sized or made from low-quality material, the risk of overheating and electrical fires increases.
2.Efficiency
A high-quality electric panel bus bar ensures that the current flows smoothly, minimizing resistance and reducing the risk of power loss. In other words, it helps your electrical system operate at peak efficiency. Resistance can lead to excessive heat buildup, which compromises the system’s overall performance and safety. A low-resistance path, facilitated by the right bus bar, ensures that the electrical power is used effectively without unnecessary losses.
3.Durability
The durability of the bus bar is key to the long-term reliability of the electrical panel. Over time, electrical systems experience wear and tear due to constant power flow. A high-quality bus bar made from corrosion-resistant materials will last much longer and require fewer replacements. Moreover, a well-maintained bus bar will help ensure the safety of your home or commercial property by preventing electrical faults that could lead to damage.

Types of Electric Panel Bus Bars
While all bus bars serve the same general function—distributing electrical current—there are different types and designs depending on the specific needs of the electrical panel. Here are the most common types of electric panel bus bars:
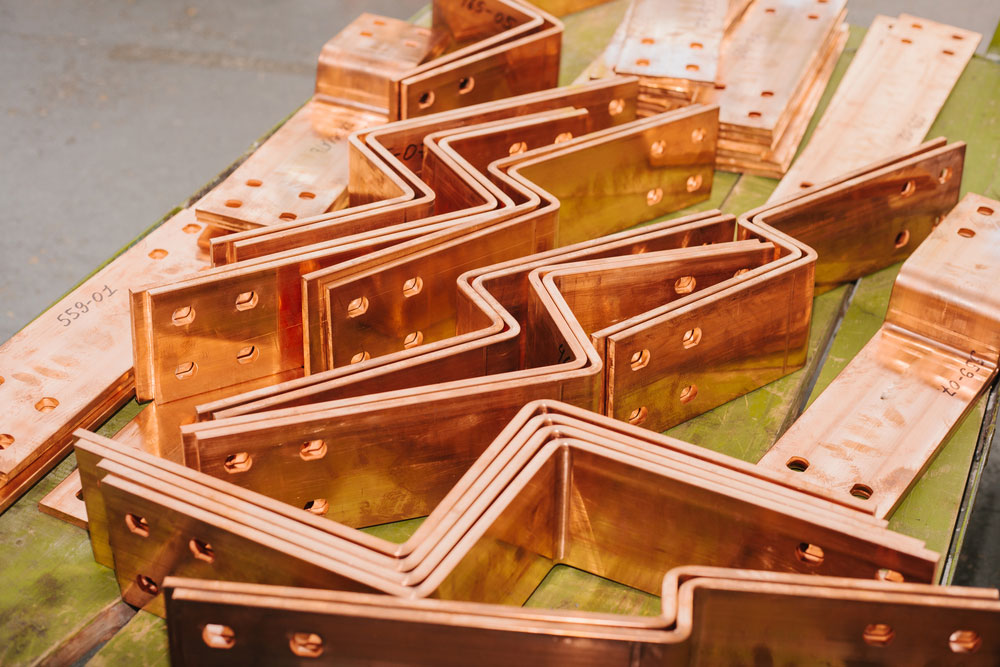
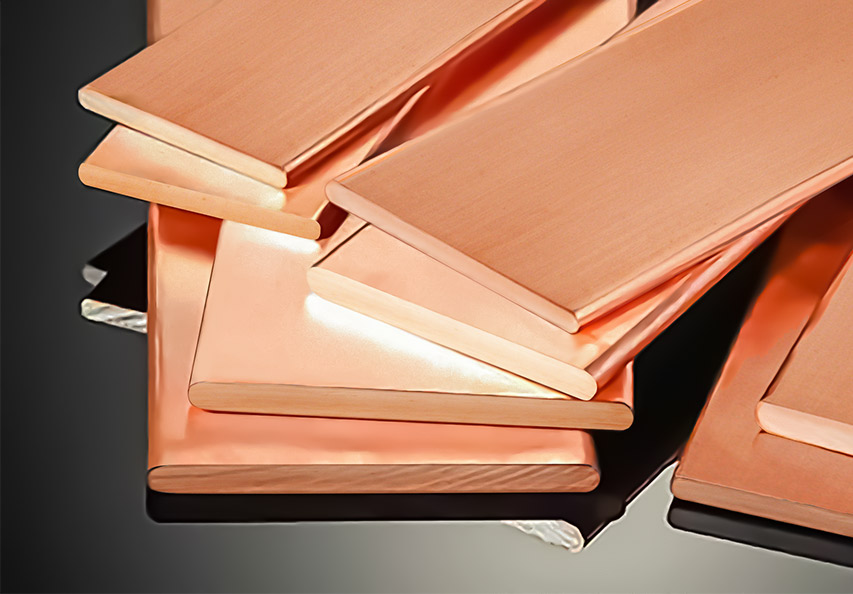
1 Copper Bus Bars
Copper is one of the most commonly used materials for electric panel bus bars due to its excellent conductivity. Copper bus bars are preferred when high electrical performance is required, especially in commercial and industrial settings. Copper is highly conductive, which means that it can carry more current without overheating or causing resistance. It’s also highly resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for environments that experience moisture or extreme temperatures.
Advantages of Copper Bus Bars:
- Superior Conductivity: Copper is known for its ability to efficiently carry electrical current. This reduces the risk of overheating and ensures smooth power flow.
- Durability and Corrosion Resistance: Copper has a natural resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
- High-Temperature Tolerance: Copper can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for areas that experience heat buildup.
Disadvantages of Copper Bus Bars:
- Cost: Copper is more expensive than aluminum, which can increase the overall cost of the electrical panel.
- Weight: Copper is heavier than aluminum, which can be a consideration in installations where space and weight are important factors.
2 Aluminum Bus Bars
Aluminum bus bars are an alternative to copper and are often used in residential electrical systems. Aluminum is lightweight and more affordable than copper, but it has a lower electrical conductivity. This means that aluminum bus bars need to be larger or thicker than copper bus bars to achieve the same level of current distribution. However, advancements in alloy compositions have made modern aluminum bus bars more effective, allowing them to be used in various applications.
Advantages of Aluminum Bus Bars:
- Cost-Effective: Aluminum is much cheaper than copper, making it a more affordable option for residential or light-duty applications.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is lighter than copper, which makes it easier to handle and install.
- Adequate Conductivity for Residential Use: For typical residential electrical systems, aluminum bus bars can perform adequately.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Bus Bars:
- Lower Conductivity: Aluminum has lower electrical conductivity than copper, meaning larger or thicker bus bars are required.
- Corrosion: Aluminum is more prone to corrosion than copper, especially when exposed to moisture or chemicals, which may reduce its lifespan unless coated or treated.
3 Tin-Plated Bus Bars
Tin-plated bus bars are typically made from copper and coated with a thin layer of tin. The tin coating provides additional protection against corrosion, making it ideal for environments with high humidity or corrosive elements, such as coastal areas or industrial settings.
Advantages of Tin-Plated Bus Bars:
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: The tin coating provides additional protection, extending the lifespan of the bus bar.
- High Conductivity: Since the core material is copper, tin-plated bus bars maintain high conductivity while benefiting from added corrosion resistance.
- Better Performance in Harsh Environments: Tin-plated bus bars are ideal for applications where environmental factors like humidity or exposure to chemicals are a concern.
Disadvantages of Tin-Plated Bus Bars:
- Higher Cost: The process of plating copper with tin adds to the cost of the bus bar.
- Tin Layer Wear: Over time, the tin coating can wear off, which may reduce the bus bar's ability to resist corrosion.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electric Panel Bus Bar
Selecting the right electric panel bus bar requires careful consideration of several factors. Below, we’ll break down the key aspects that should influence your decision:
1 Material
The material of the bus bar significantly affects its performance. Copper, aluminum, and tin-plated copper are the primary materials used, each offering different levels of conductivity, cost, and durability. Copper is the best choice for heavy-duty applications, while aluminum is a more cost-effective solution for standard residential systems. Tin-plated copper offers enhanced corrosion resistance, making it ideal for specialized environments.
2 Current Carrying Capacity
The current carrying capacity of the bus bar is one of the most important considerations. This rating indicates how much electrical current the bus bar can safely handle without overheating. It is crucial to choose a bus bar that matches the electrical load requirements of your system. Overloading a bus bar can result in excessive heat, damage to the panel, and potential safety hazards like fires.
3 Bus Bar Size
The size of the bus bar—its width, thickness, and length—directly influences its current capacity. Larger, thicker bus bars can carry more current, but they also require more space. Therefore, when choosing the size of the bus bar, you must balance current capacity with the available space in the electrical panel.
4 Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of the bus bar indicates the maximum voltage it can safely carry without risking electrical faults. Ensure that the voltage rating of the bus bar is compatible with the voltage used in your electrical system (e.g., 120V, 240V, or higher). The voltage rating should be higher than the maximum expected voltage for safety.
5 Environmental Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions where the bus bar will be used. For example, if your electrical panel is in a coastal area, high humidity could lead to corrosion. In such cases, a tin-plated bus bar or a bus bar made from materials with enhanced corrosion resistance would be ideal. Similarly, if the panel is exposed to extreme temperatures, ensure that the bus bar can withstand those conditions.
6 Bus Bar Configuration
The configuration of the bus bar refers to how the bus bar is designed to distribute current to multiple circuits. There are different types of configurations for residential and commercial systems. Residential systems typically use single-phase configurations, while larger commercial or industrial systems may require three-phase bus bars.

Conclusion
Choosing the right electric panel bus bar is essential for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical system. Factors such as material, current capacity, size, voltage rating, and environmental conditions should guide your decision. By selecting a high-quality bus bar that matches the requirements of your system, you can ensure that your electrical panel performs optimally and safely for years to come. Whether you're dealing with a residential, commercial, or industrial electrical panel, the bus bar is a critical component that should not be overlooked. Make sure to consult with an experienced electrician to ensure that your electric panel bus bar is properly chosen and installed for your specific needs.