A Comprehensive Guide to the Different Types of Electrical Bus Bars
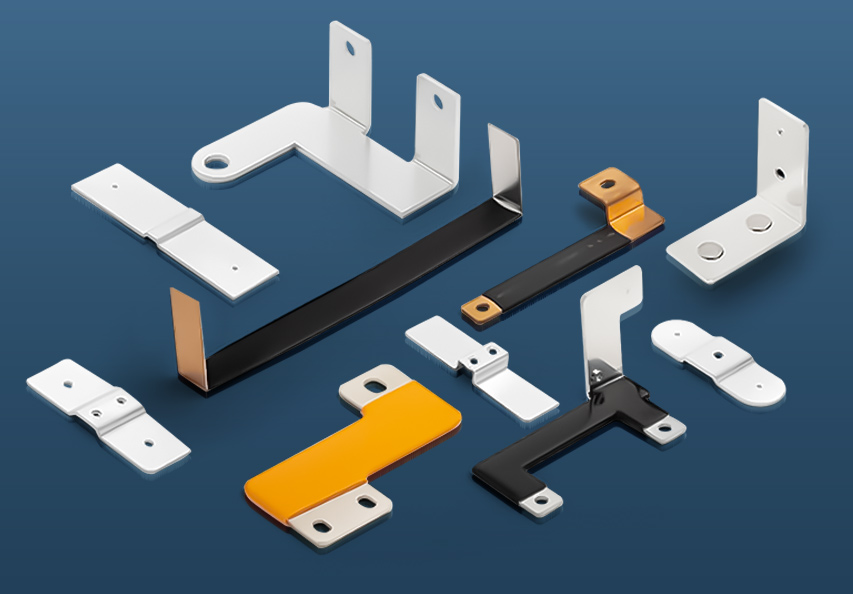
Electrical bus bars are essential components in power distribution systems, acting as the central points where electrical currents are routed and distributed across various circuits. They are widely used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications to ensure efficient and reliable electrical transmission. Whether you're designing an electrical distribution system, upgrading a facility, or simply looking to understand the underlying infrastructure, understanding the different types of electrical bus bars is crucial. This guide will explore the various types of electrical bus bars, their materials, designs, applications, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is an Electrical Bus Bar?
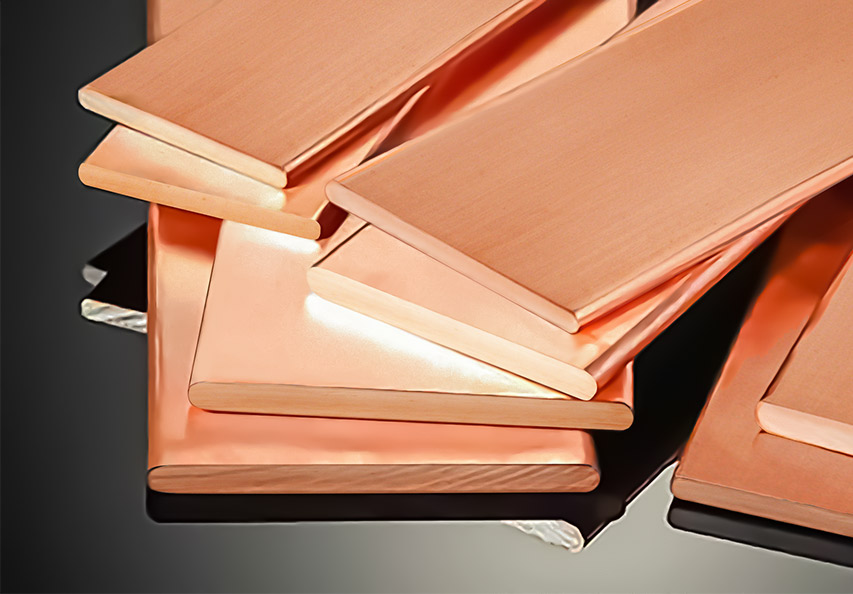
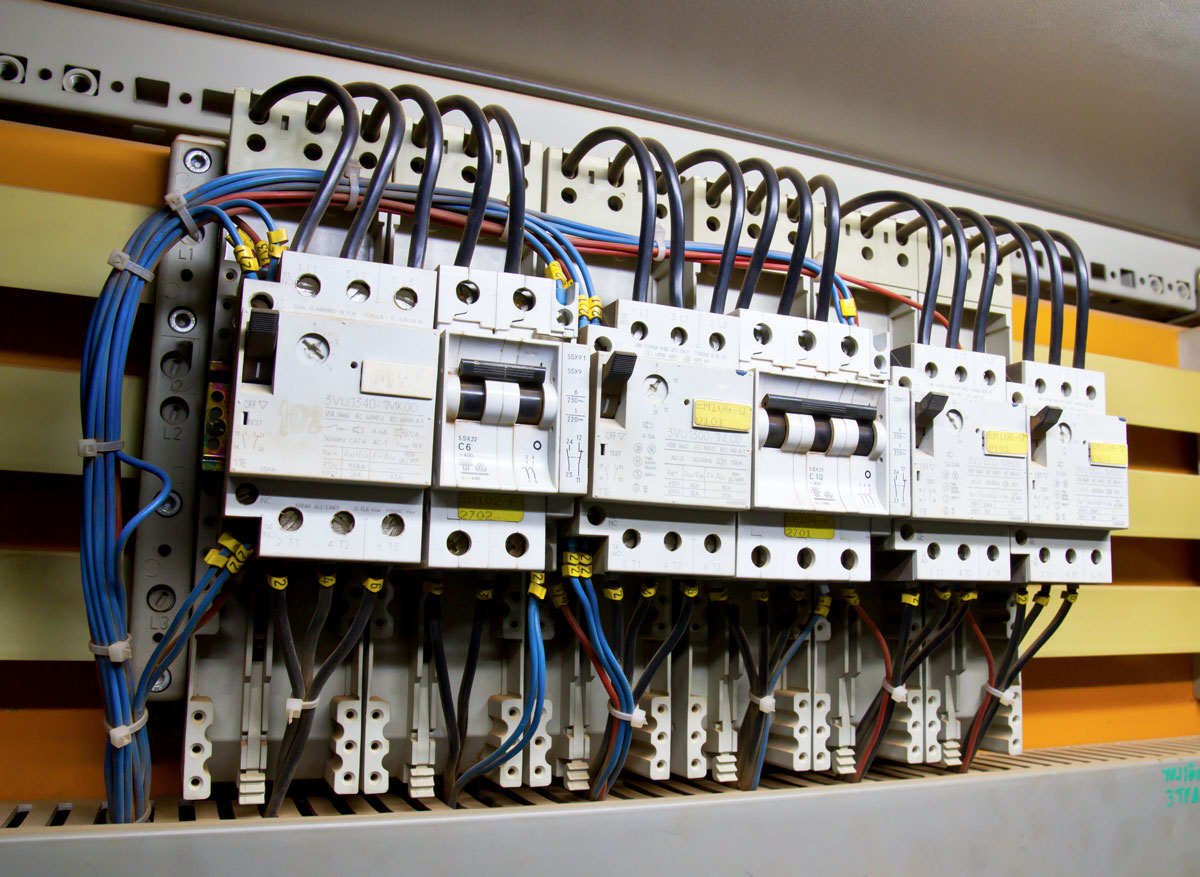
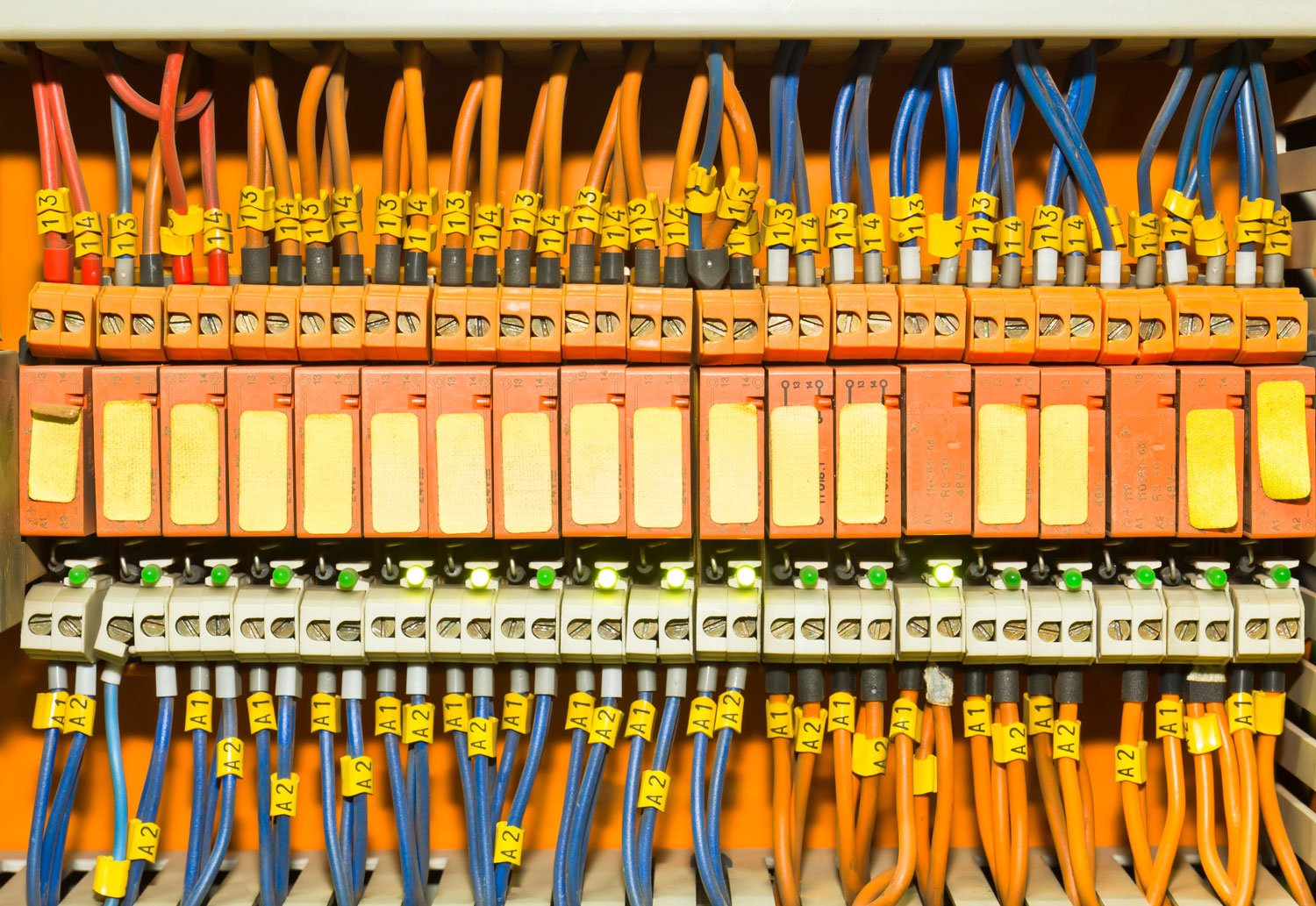
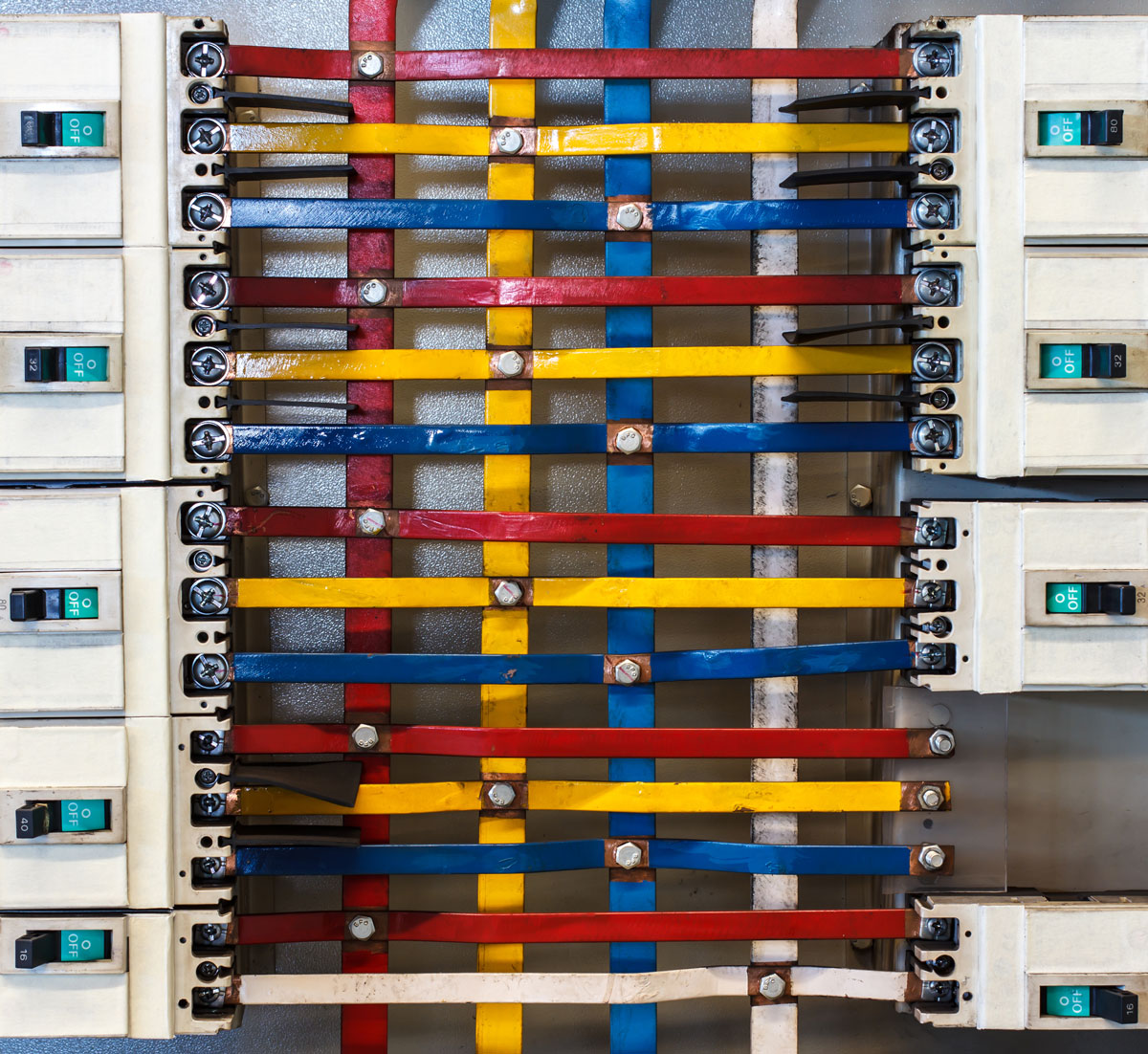
An electrical bus bar is a conductive material, typically made of copper, aluminum, or other metals, designed to carry multiple electrical currents to different circuits. In its simplest form, it is a metallic strip or bar that functions as a central point where power is distributed across various electrical components or systems. Bus bars are widely used in power plants, substations, industrial electrical panels, and even smaller appliances. They serve as the backbone of electrical systems by minimizing voltage drops, enhancing system reliability, and ensuring safety through proper current distribution.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Type of Electrical Bus Bar
Choosing the right types of electrical bus bars can significantly impact the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your electrical system. The correct bus bar will reduce energy losses, minimize heat generation, and prevent overloading. Factors like material, size, shape, current-carrying capacity, and environmental conditions should all be considered when selecting the appropriate type of bus bar.

Types of Electrical Bus Bars
There are several types of electrical bus bars, each with specific features suited for particular applications. These can be broadly categorized by their materials, design, and applications.
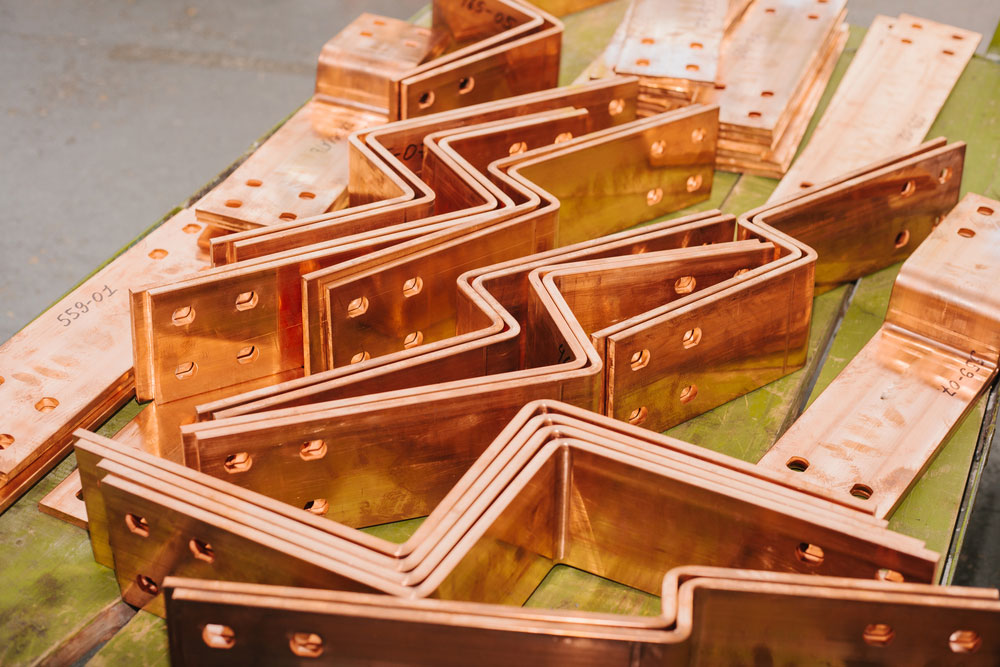
1. Copper Bus Bars
Copper is one of the most commonly used materials for electrical bus bars due to its excellent conductivity and relatively low cost compared to other metals. Copper bus bars are used in situations where high electrical conductivity is critical, such as in power distribution and high-current applications.
Features:
- High conductivity: Copper has superior electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-power applications.
- Durability: Copper bus bars have a long lifespan, even in harsh environments.
- Corrosion-resistant: Copper resists corrosion better than many other materials, particularly in dry or indoor environments.
Applications:
- Industrial power distribution systems.
- Transformers and switchgear systems.
- Electrical panels and circuit breakers.
2. Aluminum Bus Bars
Aluminum bus bars are another popular choice due to their lightweight properties and relatively lower cost compared to copper. Although aluminum has slightly lower electrical conductivity than copper, it is still an effective material for many electrical systems.
Features:
- Lightweight: Aluminum bus bars are much lighter than copper, which is an advantage in certain installations where weight is a concern.
- Cost-effective: Aluminum is more affordable than copper, which can be an important consideration for large-scale installations.
- Corrosion resistance: Aluminum is naturally resistant to corrosion due to the formation of an oxide layer.
Applications:
- Power distribution systems where weight and cost are a consideration.
- High-voltage transmission lines.
- Medium and low-voltage applications.
3. Tinned Copper Bus Bars
Tinned copper bus bars are copper bars that are coated with a thin layer of tin to enhance their corrosion resistance, particularly in moist or industrial environments.
Features:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance: The tin coating provides extra protection against corrosion, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
- Excellent conductivity: Retains the excellent electrical conductivity of copper.
- Improved durability: The tin coating helps extend the lifespan of the bus bar in harsh conditions.
Applications:
- Applications in marine environments, power stations, or chemical plants where corrosion is a significant concern.
- Power panels exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals.
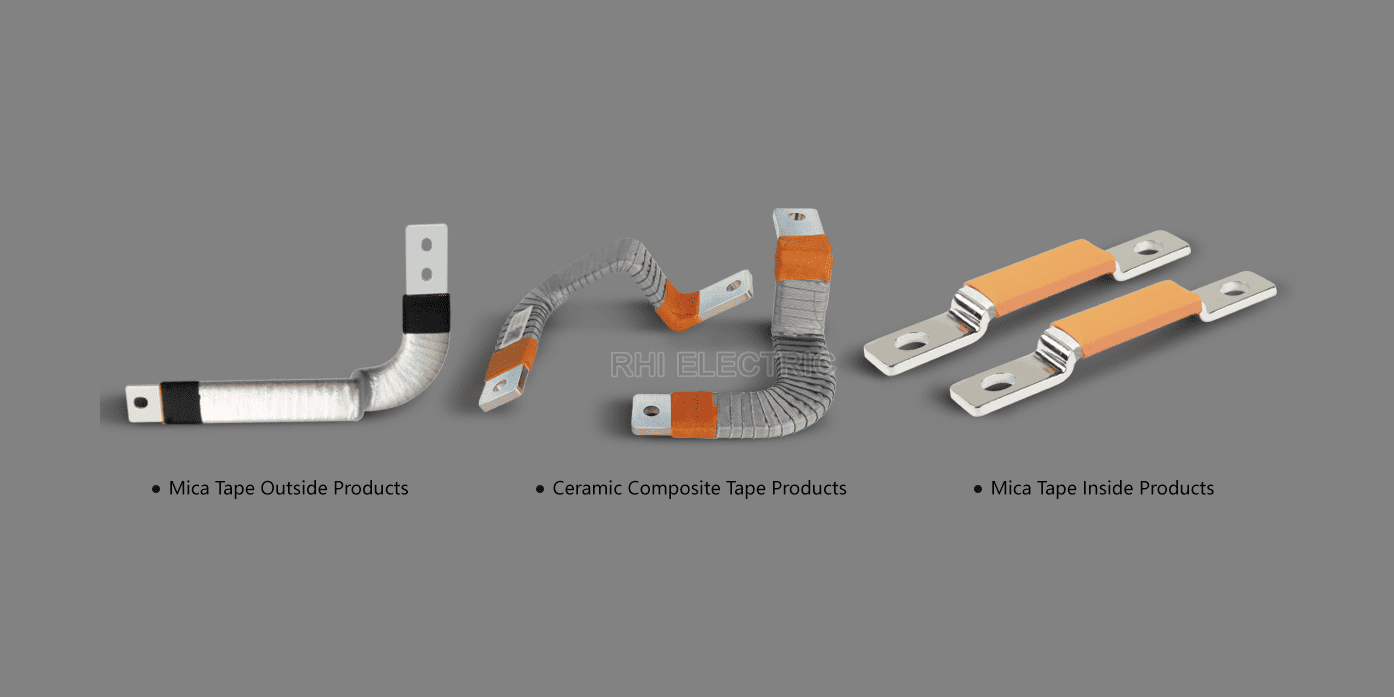
4. Insulated Bus Bars
Insulated bus bars are typically used when electrical isolation is needed between the bus bar and the surrounding environment, such as in certain industrial systems or in environments with high safety requirements.
Features:
- Insulation: The bus bar is coated with a non-conductive material, such as plastic, to prevent accidental contact with conductive surfaces or people.
- Safety: Provides additional safety by preventing short circuits and reducing electrical hazards.
- Versatility: Available in various forms such as flexible and rigid, depending on the installation requirements.
Applications:
- Electrical installations requiring safe isolation, such as in distribution boards or control panels.
- Systems where accidental contact with live parts needs to be avoided.
5. Flat Bus Bars
Flat bus bars are commonly used in compact electrical systems where space is limited, such as in small control panels, power distribution boards, and electrical equipment.
Features:
- Compact design: Flat bus bars are space-efficient and can fit into tight areas.
- Lower cost: The manufacturing process for flat bus bars is less expensive compared to other forms, making them a cost-effective solution.
- Uniform current distribution: Their flat design ensures that the current is evenly distributed across the bar.
Applications:
- Low to medium voltage distribution systems.
- Compact electrical panels and equipment.
- Control panels in machinery and automation systems.
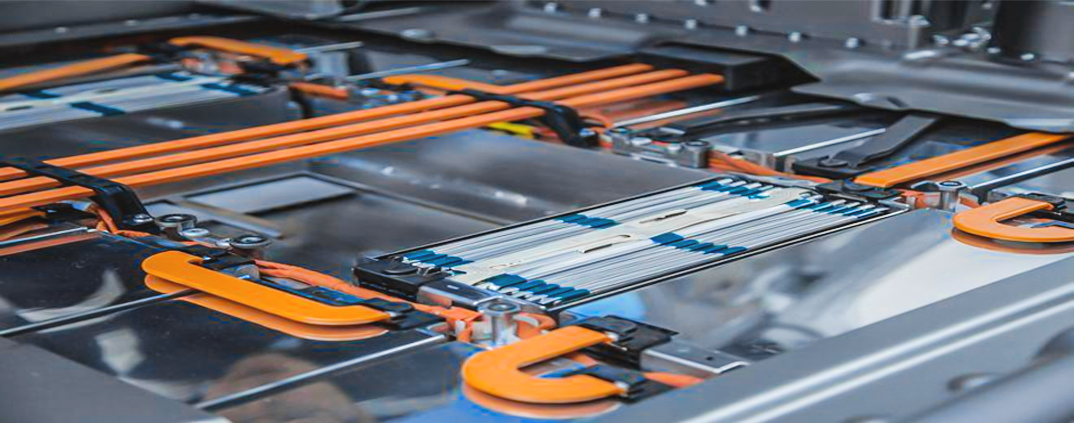
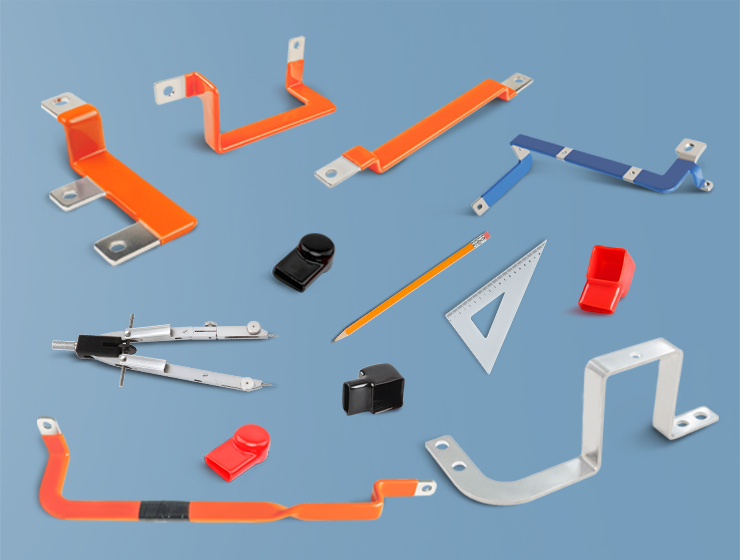
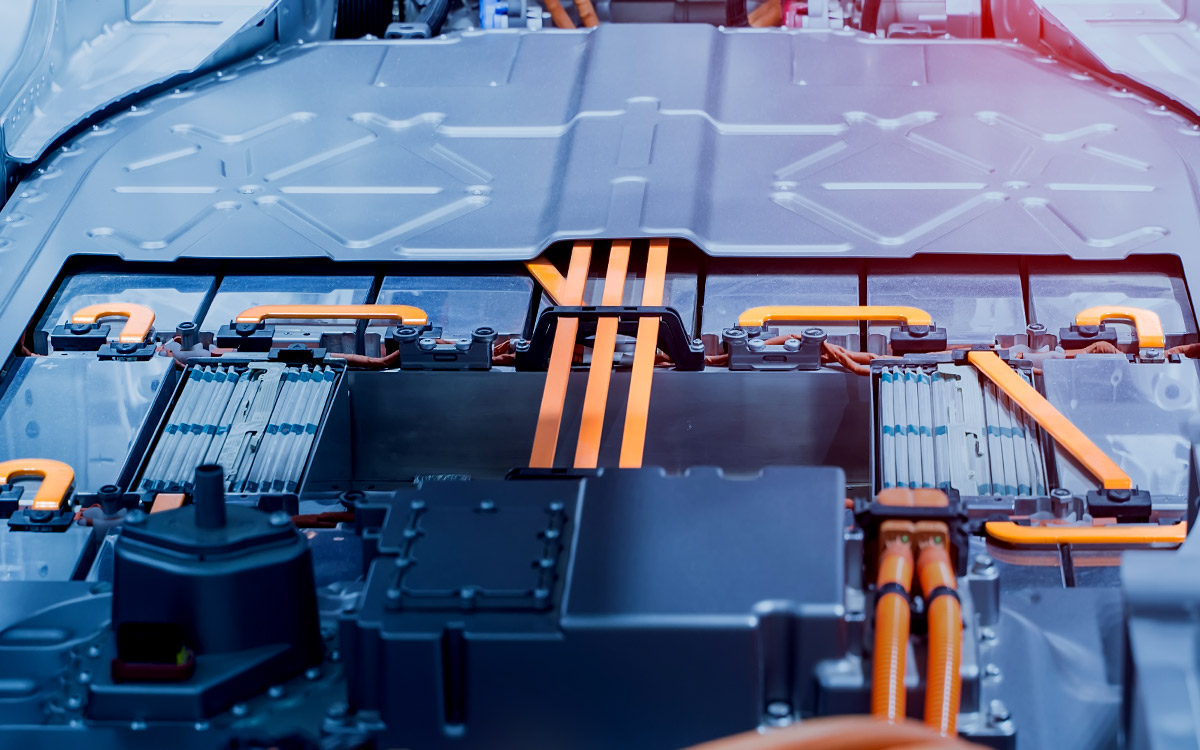
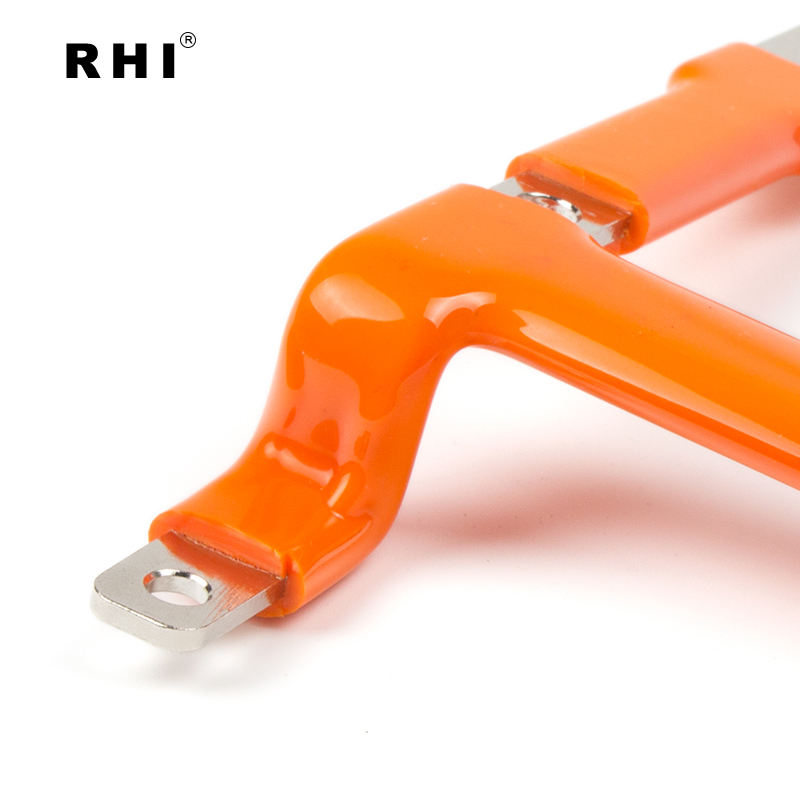
6. Flexible Bus Bars
Flexible bus bars are designed to provide electrical conductivity in applications where some movement or flexibility is required. They are typically made from a combination of copper or aluminum strands coated with a flexible insulating material.
Features:
- Flexibility: As the name suggests, flexible bus bars can bend to fit into spaces where rigid bus bars would not be able to, making them ideal for areas with limited space or complex layouts.
- Ease of installation: Their flexible nature makes them easier to install in tight or hard-to-reach spaces.
- Reduced vibration: Flexible bus bars can absorb vibrations better than rigid ones, making them ideal for applications where mechanical stress or vibrations are an issue.
Applications:
- Solar panel systems, where flexibility is needed to accommodate changes in panel positions.
- High-vibration environments, such as motors and generators.
- Complex installations where rigid bus bars cannot be used.
7. Bus Ducts (Bus Trunking)
Bus ducts, or bus trunking, are an integrated system of bus bars housed within a protective casing. This type of bus bar system is often used in large industrial installations where high-current capacities are needed.
Features:
- Enclosed system: Bus ducts provide a fully enclosed and protected system for carrying high currents, reducing the risk of short circuits or electrical fires.
- High current-carrying capacity: Bus ducts can carry a much higher current than standard bus bars.
- Modular design: The system is often modular, allowing for easy extensions or modifications.
Applications:
- Large industrial facilities such as factories and power stations.
- Power distribution systems in high-rise buildings and commercial complexes.
How to Choose the Right Type of Electrical Bus Bar
Selecting the correct type of electrical bus bar depends on several factors, including the current capacity, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Here are some key considerations when choosing the right bus bar:
- Current Rating: Determine the amount of electrical current the bus bar needs to carry. This will help you decide the material (copper or aluminum) and the bus bar’s size and design.
- Space Availability: Consider the physical space where the bus bar will be installed. For compact installations, flat or flexible bus bars may be the best choice, whereas larger systems may require more robust or insulated bus bars.
- Environment: The environmental conditions (such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures) will influence the material selection. Tinned copper bus bars or insulated bus bars are ideal for harsh environments.
- Installation Type: Consider whether the bus bar will be used in a fixed or mobile system. Flexible bus bars are ideal for mobile or vibration-prone systems, while rigid bus bars work well for stationary systems.
- Cost: Material cost can vary significantly between copper and aluminum, with aluminum often being more affordable. However, the long-term reliability and conductivity of copper may justify the higher cost in some applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of electrical bus bars is critical when designing or maintaining electrical systems. From copper and aluminum bus bars to insulated, flexible, and flat varieties, each type has specific benefits that make it suitable for certain applications. By evaluating your current rating, environmental conditions, available space, and cost considerations, you can choose the right bus bar to ensure the reliability, efficiency, and safety of your electrical distribution system.
Whether you're an engineer, technician, or simply someone interested in the workings of electrical systems, having a clear understanding of these components will help you make informed decisions when it comes to installation, maintenance, and upgrades.