Electrical Panel Bus Bars vs. Traditional Wiring: What’s the Difference?
Electrical Panel Bus Bars vs. Traditional Wiring: What’s the Difference?
In any electrical system, the efficiency, safety, and reliability of power distribution are critical. At the heart of electrical distribution are the methods used to connect and distribute power from the source to various circuits. Two common methods of power distribution within electrical panels are electrical panel bus bars and traditional wiring. While both serve the same purpose—carrying electrical current to multiple circuits—there are significant differences between these two options in terms of design, efficiency, safety, cost, and installation.
The electrical panel bus bar has grown in popularity for modern electrical systems due to its ability to provide a more efficient and compact solution compared to traditional wiring. However, traditional wiring has been the standard for decades and still remains relevant in many applications. In this blog, we will explore the differences between electrical panel bus bars and traditional wiring, highlighting their unique features, advantages, and limitations. Whether you are designing a new electrical system, upgrading an existing one, or just looking to understand the distinctions between these two methods, this guide will provide you with the essential information to make an informed decision.
What Are Electrical Panel Bus Bars?
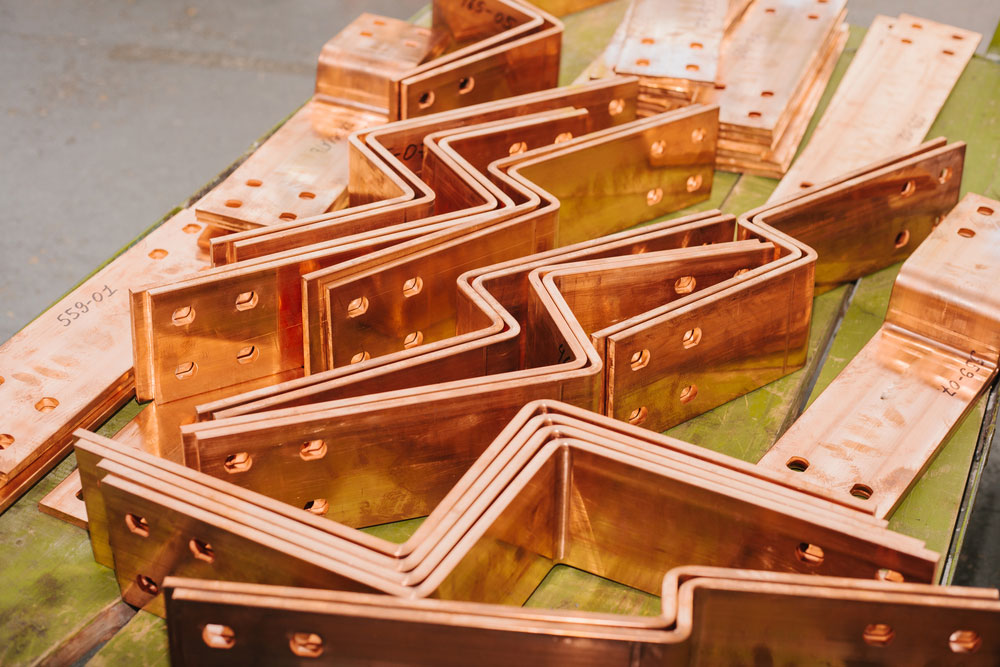
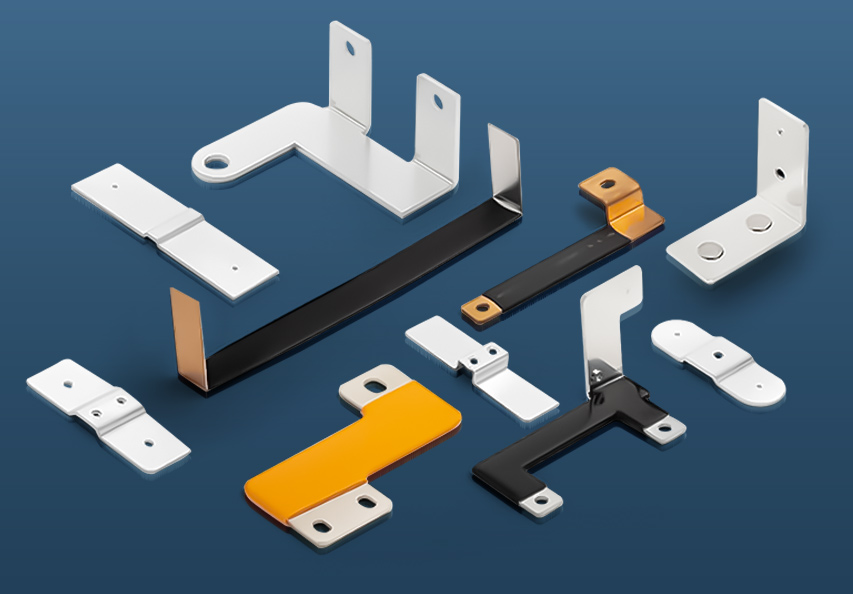
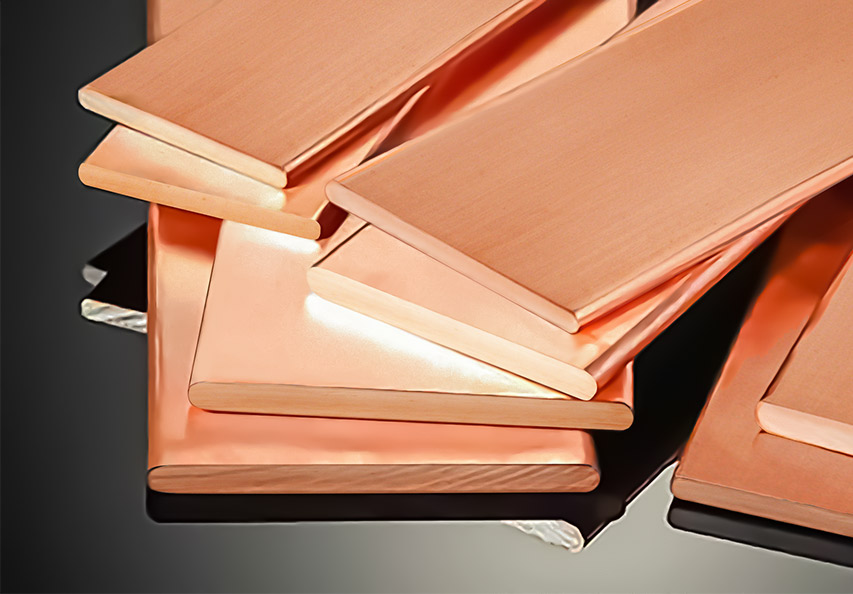
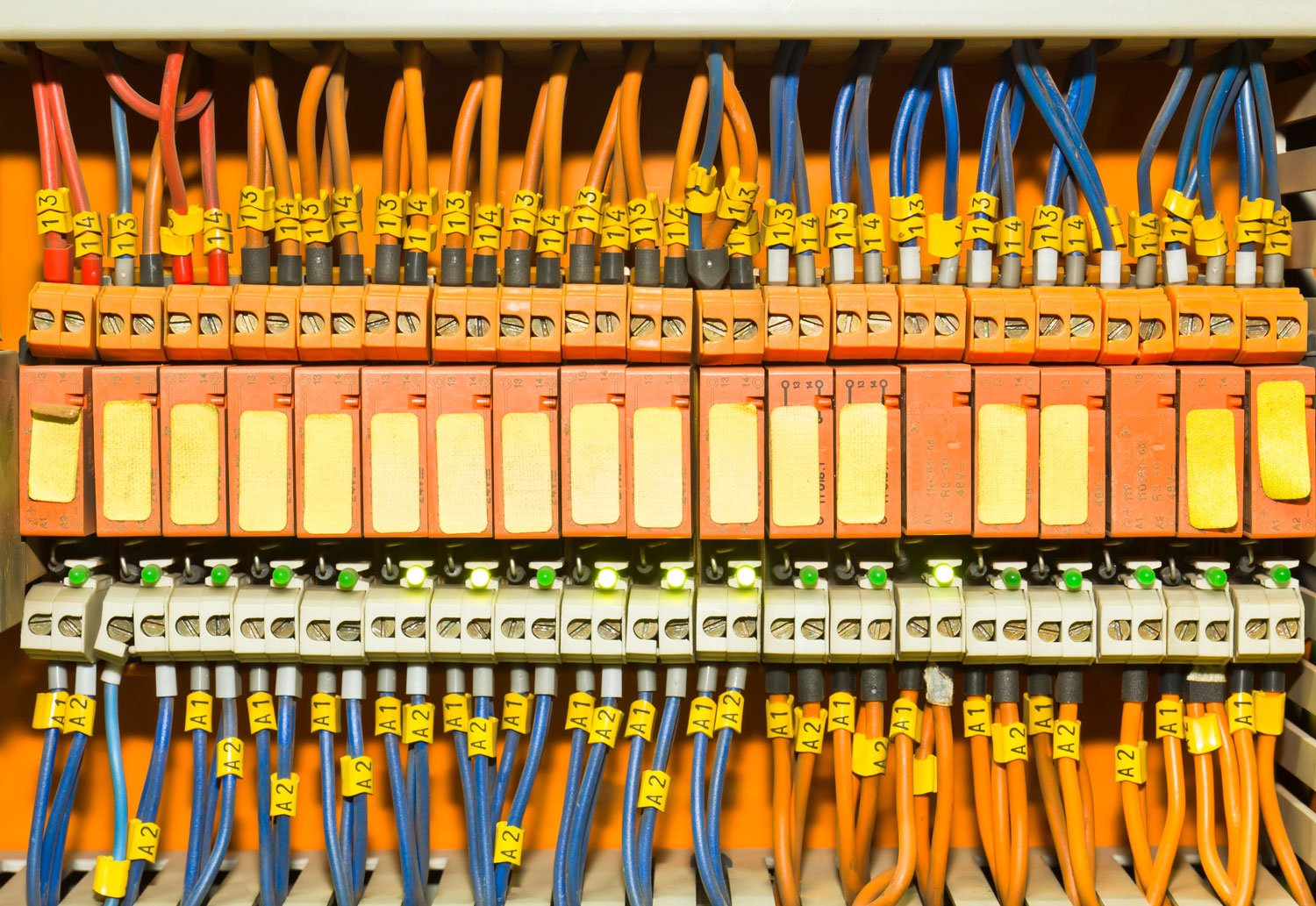
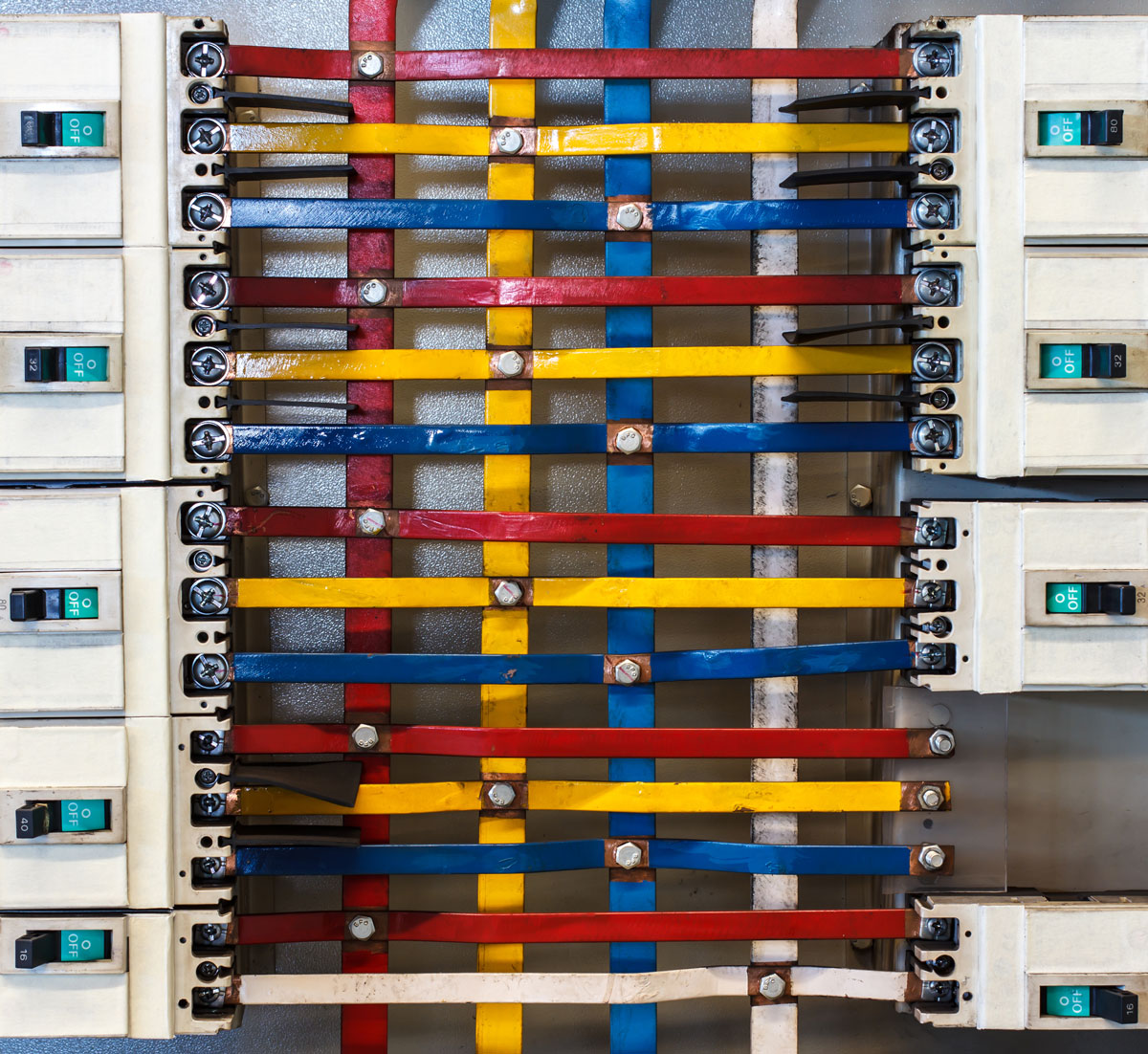
An electrical panel bus bar is a conductive metal bar that serves as a central distribution point for electrical currents in an electrical panel. Bus bars are typically made of copper, aluminum, or a combination of both, chosen for their excellent conductivity and durability. The bar itself has multiple connection points where circuit breakers or fuses are attached, allowing current to flow to multiple circuits simultaneously.
Electrical panel bus bars are commonly used in both low-voltage and high-voltage electrical systems due to their ability to handle large amounts of electrical current in a compact, organized way. In commercial and industrial settings, electrical panel bus bars are often used to distribute power more efficiently, reducing the need for multiple wires and cables that would otherwise take up more space.
The two most common types of electrical panel bus bars are:
- Single-phase bus bars: These are designed for residential and light commercial use, handling alternating current (AC) power.
- Three-phase bus bars: These are used in larger industrial and commercial systems where a higher power load is required.
One of the primary advantages of electrical panel bus bars is their ability to manage and distribute large currents without generating excessive heat, thus improving safety and efficiency.
What Is Traditional Wiring?
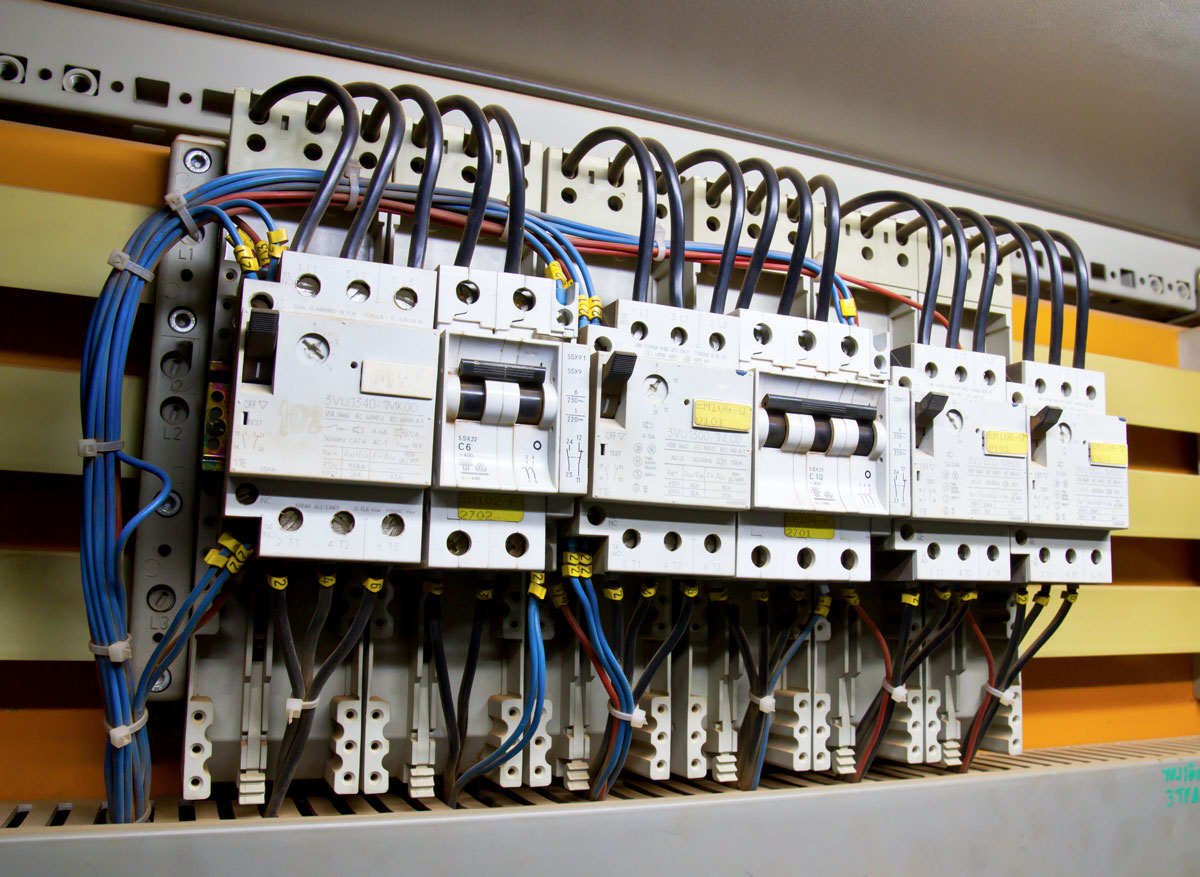
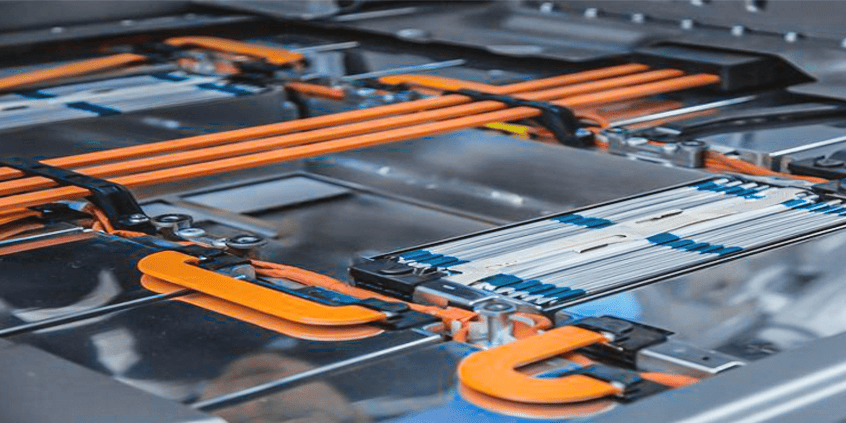
Traditional wiring refers to the use of insulated copper or aluminum wires that are connected to an electrical panel's circuit breakers or fuses to distribute power to various circuits. In traditional wiring setups, each individual circuit requires a wire to carry electrical current from the panel to the connected load.
Traditional wiring is typically made of copper or aluminum, with copper being preferred for its higher conductivity and durability. The wires are insulated with materials such as PVC, rubber, or Teflon to prevent short circuits and protect users from electric shocks. While copper is generally more efficient, aluminum wiring is often used for cost-saving reasons, especially in larger installations.
In traditional wiring systems, the wires are connected to circuit breakers or fuses, which are then connected to a bus bar inside the electrical panel. The use of individual wires can result in a cluttered panel with multiple connections, and managing this system can be more time-consuming compared to using electrical panel bus bars.
Key Differences Between Electrical Panel Bus Bars and Traditional Wiring
Efficiency:
One of the most significant advantages of electrical panel bus bars over traditional wiring is their efficiency in distributing power. Electrical panel bus bars allow for direct distribution of current to multiple circuits without the need for multiple wires. This can result in reduced electrical losses and a more streamlined system. In traditional wiring, the use of individual wires can lead to greater power loss due to resistance, especially over long distances.
Space Saving:
In comparison to traditional wiring, electrical panel bus bars take up less space within an electrical panel. This compact design allows for better organization and the ability to handle larger loads within a smaller footprint. Traditional wiring, on the other hand, often results in a cluttered panel with numerous wires and connectors taking up valuable space.
Installation:
Electrical panel bus bars simplify the installation process. Since they provide a single point of contact for multiple circuits, installers do not need to manage a large number of individual wires. This reduces both installation time and the complexity of the job. Traditional wiring requires each circuit to be connected individually to the panel, which can take longer and increase the risk of errors during installation.
Maintenance:
Maintenance is another area where electrical panel bus bars have the upper hand. With fewer individual connections and wires to manage, maintenance and troubleshooting become easier and less time-consuming. Electrical panel bus bars also tend to have a longer lifespan and require less upkeep than traditional wiring, which may need to be replaced or repaired due to wear and tear over time.
Advantages of Electrical Panel Bus Bars
Enhanced Reliability and Durability:
Electrical panel bus bars are typically more robust than traditional wiring systems, making them less prone to damage or wear. Bus bars are designed to handle large currents, making them ideal for high-load applications. They are also less susceptible to heat buildup, which can occur with traditional wiring over time.
Reduced Electrical Losses:
Since electrical panel bus bars have fewer connection points and shorter conductor paths, they reduce electrical resistance and minimize power losses. Traditional wiring, especially over long distances, can experience more significant losses due to the resistance of the wires.
Simplified Design and Installation:
The design of electrical panel bus bars is much simpler and more compact than that of traditional wiring systems, making them easier to install and more cost-effective, particularly in large-scale applications.
When to Use Electrical Panel Bus Bars vs. Traditional Wiring
While electrical panel bus bars offer a range of benefits such as improved efficiency, space-saving, and reliability, traditional wiring still has its place in many electrical systems. Choosing between the two depends on several factors, including the scale of the electrical system, the load requirements, space considerations, and the long-term goals of the installation. Here’s a more detailed look at when each method is best suited:
- Electrical Panel Bus Bars: Best for commercial, industrial, and high-load residential applications where efficiency, space-saving, and reliability are key factors.
- Traditional Wiring: Suitable for small-scale residential applications where the electrical load is relatively low, and space is not a significant concern.
Safety Considerations
Both electrical panel bus bars and traditional wiring are safe when installed correctly, but electrical panel bus bars generally offer additional safety advantages. One of the main benefits is the robust insulation typically built into bus bars, which significantly reduces the risk of electrical fires. Bus bars are enclosed in protective housings, making them less susceptible to accidental damage or exposure to environmental factors like moisture or dust, which could cause short circuits. Additionally, the design of bus bars allows for better heat dissipation, preventing overheating, which is a common risk factor in electrical systems.
In contrast, traditional wiring can be more vulnerable to issues like overheating, especially if the wires are not properly sized for the electrical load or if they are installed incorrectly. Over time, the insulation on traditional wires can degrade, increasing the likelihood of short circuits or electrical faults. Proper installation and regular inspections are essential to maintaining the safety of traditional wiring, but the inherent risk is generally higher compared to bus bar systems, especially in high-load applications.
.png)
Cost Comparison
Electrical panel bus bars may come with a higher upfront cost than traditional wiring, but they often provide long-term savings. Their efficiency in power distribution leads to reduced energy losses, which can lower overall electricity costs over time. Moreover, bus bars typically require less maintenance due to their durable design, which can result in fewer repairs and replacements, reducing long-term operational costs.
On the other hand, traditional wiring is typically less expensive to install initially, making it a cost-effective choice for smaller residential applications. However, traditional wiring may incur higher energy costs over time due to power losses, and it may require more frequent maintenance and repairs, especially if the system is subjected to heavy use or improper installation. Therefore, while the initial cost of traditional wiring is lower, the overall long-term cost of ownership may be higher compared to electrical panel bus bars due to energy inefficiencies and maintenance needs.
Conclusion
In the debate between electrical panel bus bars and traditional wiring, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. For larger systems requiring high efficiency, space optimization, and reliability, electrical panel bus bars are the superior choice. However, traditional wiring still holds its place in smaller, low-cost applications.
Choosing the right system for your electrical needs depends on your specific requirements, including load capacity, space constraints, budget, and long-term maintenance considerations. Ultimately, whether you choose electrical panel bus bars or traditional wiring, understanding the differences will help you make an informed decision that best suits your electrical distribution needs.