Understanding Aircraft Electrical Bus Bars: Functions and Applications
Aircraft are complex machines that require a highly reliable and efficient electrical system to operate. Central to this system are aircraft electrical bus bars, which play a critical role in distributing power to various components of the aircraft. Whether it’s for avionics, lighting, or other essential systems, understanding the function and application of aircraft electrical bus bars is key to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the aircraft.
In this blog, we will dive into the role of aircraft electrical bus bars, how they work, the types available, and their applications in modern aviation. We will also explore best practices for maintaining these critical components, as well as the latest advancements in bus bar technology.
.png)
What is an Aircraft Electrical Bus Bar?
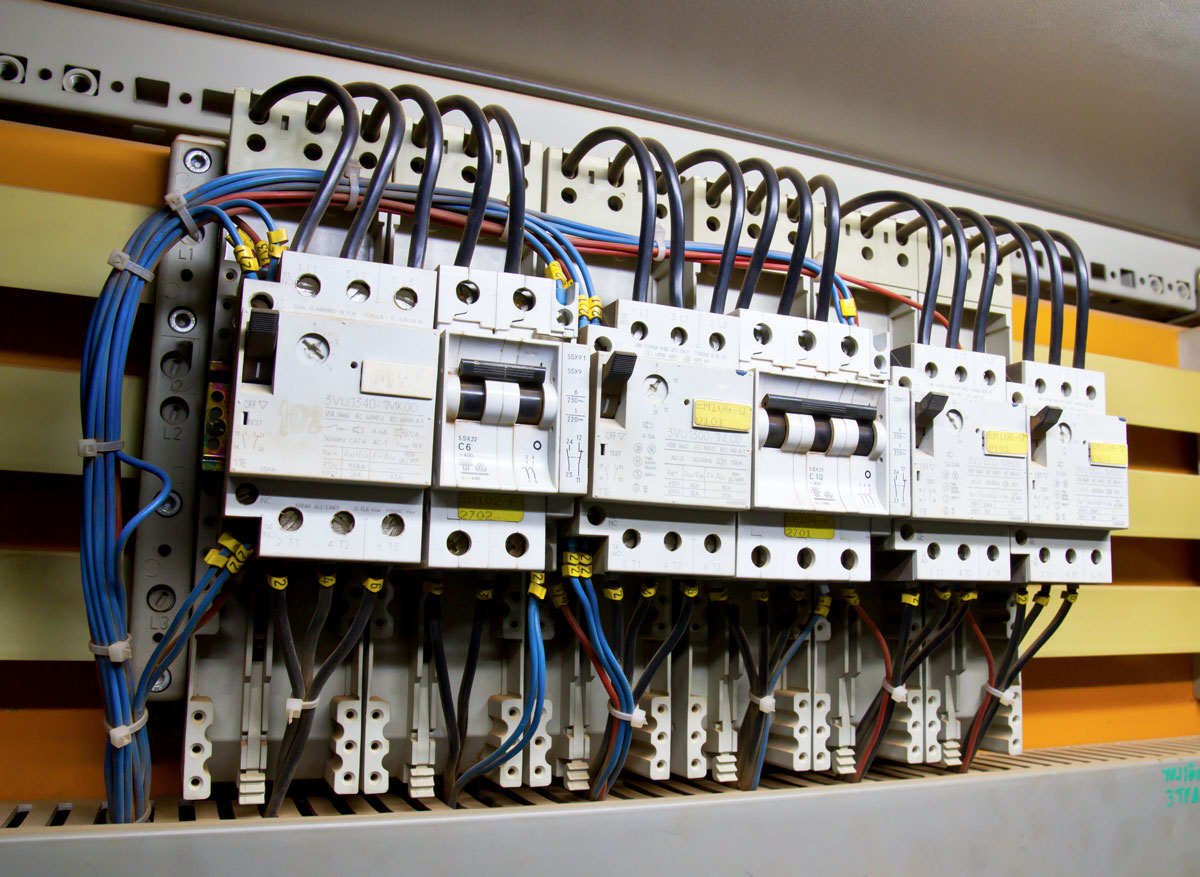
An aircraft electrical bus bar is a central electrical component used to distribute power from a single source to multiple destinations within an aircraft. Essentially, it serves as a conduit or connection point for distributing electrical power across the various systems and components on board.
Bus bars are typically made from high-conductivity metals, such as copper or aluminum, and they are designed to handle high current loads. They are used to connect power sources (like generators or batteries) to different electrical circuits, ensuring that each part of the aircraft receives the necessary power for operation.
The Functions of Aircraft Electrical Bus Bars
Aircraft electrical systems are often divided into different buses, each serving a specific function. The primary role of the aircraft electrical bus bar is to ensure that electrical power is efficiently and reliably distributed to these various systems.
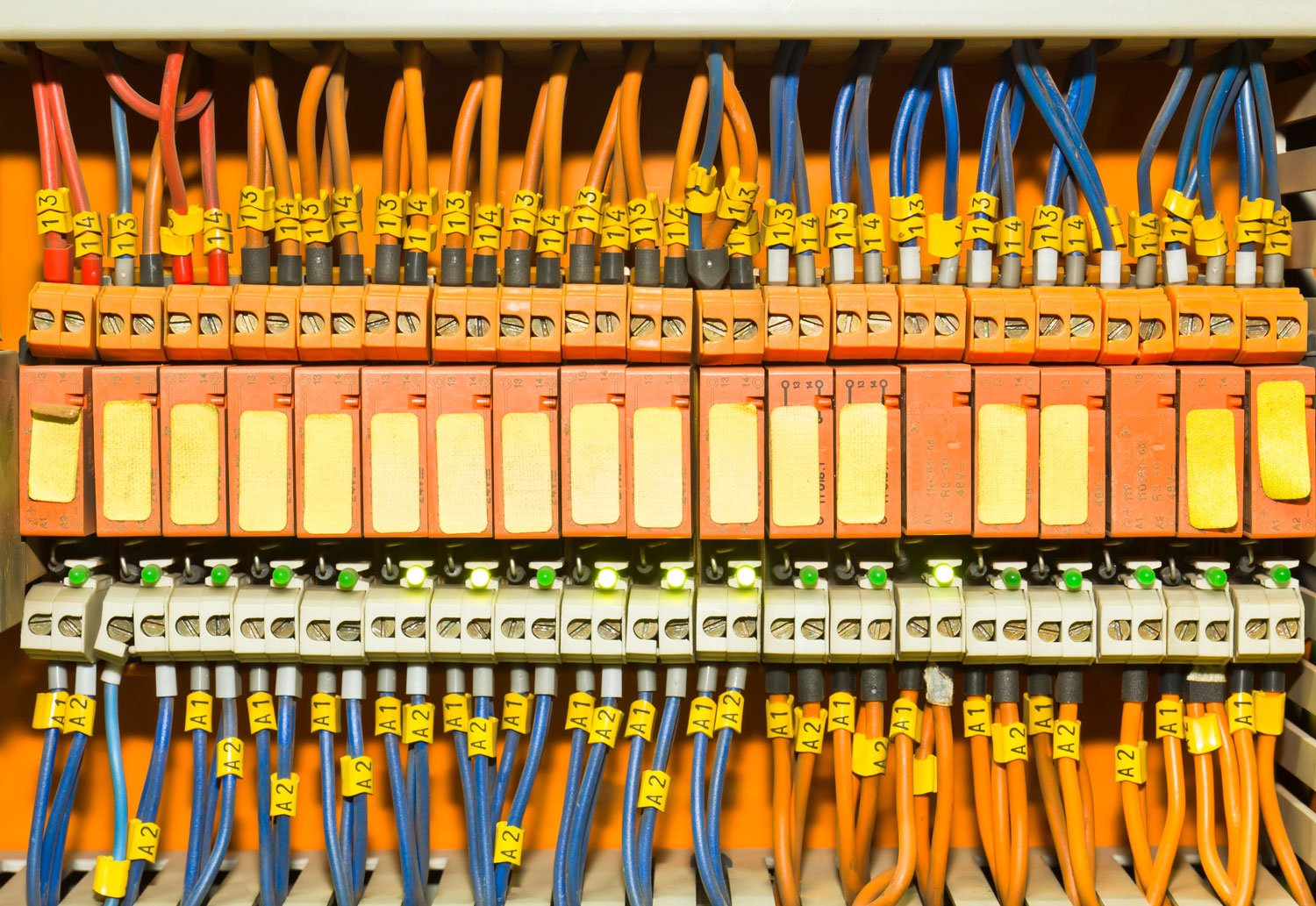
- Power Distribution: The most fundamental function of an aircraft electrical bus bar is to distribute power. This means routing electricity from power sources to the electrical components that need it, including lights, avionics, motors, and other critical systems.
- Centralized Connection: By providing a centralized point for power distribution, the bus bar simplifies the design of electrical systems in aircraft. Instead of wiring each individual component to a power source, the bus bar allows all circuits to be connected to a single point, improving the system's overall organization and reliability.
- Load Balancing: Aircraft electrical bus bars help balance the load of power across the aircraft's electrical system. With multiple bus bars, the power load can be distributed across several paths, preventing any single circuit from becoming overloaded and ensuring that the aircraft’s electrical systems continue to function smoothly.
- Short Circuit Protection: Aircraft electrical bus bars are often equipped with circuit breakers or fuses to protect against electrical faults, such as short circuits. In the event of a fault, these protective devices can isolate the affected circuit, ensuring that the rest of the system remains operational.
- Redundancy: Modern aircraft are designed with redundancy in mind to ensure reliability in the event of system failures. Bus bars are an essential part of this redundancy, as they can be configured in parallel or have backup circuits to ensure that electrical power continues to be supplied, even if one source fails.
Types of Aircraft Electrical Bus Bars
There are different types of aircraft electrical bus bars, each designed to suit specific requirements. These include:
- Primary Bus Bars: These are the main bus bars in an aircraft’s electrical system. They connect to the primary power sources, such as generators or batteries, and distribute power to essential systems like avionics, flight controls, and lighting.
- Secondary Bus Bars: These bus bars are used to distribute power to less critical systems, such as cabin lighting, entertainment, and other non-essential components. Secondary bus bars are often connected to primary bus bars but may have their own circuit protection devices for safety.
- Tie Bus Bars: Tie bus bars are used to link multiple power sources together. For example, if an aircraft has more than one generator, a tie bus bar can connect them, allowing the power from both generators to be shared across the aircraft’s electrical systems.
- Emergency Bus Bars: These are dedicated bus bars designed to provide power to essential systems in the event of an emergency. Emergency bus bars are often connected to backup power sources like emergency batteries, ensuring that critical systems, such as navigation and communication, remain operational even during power outages.
- Bus Bar Taps: Bus bar taps are used to connect individual circuits to the main bus bar. These taps allow different components to receive power from the bus bar without disrupting the main power flow.
Applications of Aircraft Electrical Bus Bars
The aircraft electrical bus bar is a versatile and crucial component that finds applications across a wide range of aircraft systems. Here are some key applications:
1. Avionics Systems
Avionics are some of the most critical systems on any aircraft. They include navigation systems, communication systems, flight management systems, and radar. The aircraft electrical bus bar ensures that all avionics components receive a steady and reliable supply of power. Without the proper power distribution, avionics systems could fail, leading to a loss of communication or navigation capabilities, which could compromise flight safety.
2. Lighting Systems
Aircraft lighting systems, including cockpit lights, cabin lights, and external lights, all depend on a reliable power source. The aircraft electrical bus bar plays a key role in ensuring that power is delivered to these systems. In modern aircraft, the lighting systems are often divided into different circuits, and the bus bar ensures that each of these circuits is powered appropriately.
3. Flight Control Systems
Flight control systems, such as autopilot, trim, and rudder systems, require continuous electrical power to operate. A failure in these systems can result in a loss of control over the aircraft, so ensuring that they have a constant power supply is critical. The aircraft electrical bus bar ensures that power is distributed efficiently to these systems, helping to maintain flight stability.
4. Power Generation and Distribution
In addition to distributing power to various systems, the aircraft electrical bus bar is involved in the management of the aircraft’s power generation. Aircraft typically have multiple generators that work together to supply the necessary power. The bus bar ensures that power from these generators is shared efficiently, and it can also distribute power to backup systems if a primary power source fails.
5. Auxiliary Power Systems
Many aircraft are equipped with auxiliary power units (APUs) that provide electrical power when the main engines are not running. The aircraft electrical bus bar helps manage the distribution of power from the APU to systems such as air conditioning, lighting, and other essential functions when the aircraft is on the ground.
6. Aircraft Cabin and Comfort Systems
Comfort systems in the aircraft, such as climate control, entertainment, and food services, also rely on power distribution from the aircraft electrical bus bar. These systems are crucial for ensuring passenger comfort during long flights, and the bus bar ensures that power is supplied to these systems consistently.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Given the critical role of aircraft electrical bus bars in ensuring the safe operation of an aircraft, regular maintenance and inspections are necessary. Here are some best practices for maintaining these components:
- Regular Inspections: Periodic inspections of the bus bars, their connections, and associated components are necessary to detect any wear or corrosion that could impact their functionality.
- Cleanliness: Dust, dirt, and corrosion can cause electrical resistance, leading to overheating and potential failures. Keeping bus bars clean and free of contaminants is essential for their longevity.
- Circuit Protection: Ensuring that all circuits connected to the bus bar are properly protected by fuses or circuit breakers is vital. These protection devices should be regularly checked to ensure they function correctly in case of a fault.
- Avoid Overloading: Bus bars should not be overloaded with too many circuits or excessive power demands. Overloading can lead to overheating and potentially cause a failure of the bus bar or associated systems.
- Upgrades and Modernization: As aircraft systems evolve, it is important to consider upgrading bus bars and related components to accommodate new technologies or higher power demands.
Conclusion
Aircraft electrical bus bars are fundamental components that ensure the safe, reliable, and efficient distribution of electrical power throughout an aircraft. From powering avionics to lighting systems, and from flight controls to cabin comfort systems, these bus bars play a pivotal role in ensuring that all electrical components operate seamlessly.
Understanding the functions and applications of the aircraft electrical bus bar is essential for aviation engineers, technicians, and anyone involved in the design, maintenance, and operation of aircraft electrical systems. Regular maintenance and a focus on safety can ensure that these critical components continue to function as intended, supporting the safety and performance of the aircraft.